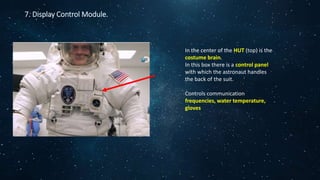
Spacesuits have several key components to protect astronauts in the harsh environment of space. The suits include a cooling garment with tubes to circulate water and regulate body temperature. A hard upper torso connects the suit systems to the life support backpack. The lower torso has shaped trousers, boots, and waist closure. Gloves protect the hands while allowing dexterous movement. The helmet provides oxygen and ventilation while the visor protects the eyes from the sun. The life support backpack houses oxygen supplies, carbon dioxide removal, power, water circulation, and communication systems to allow astronauts to survive during spacewalks.