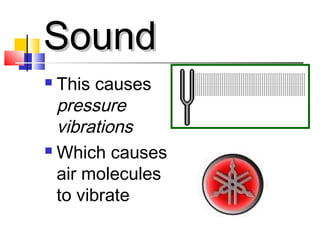
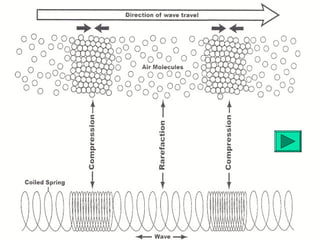
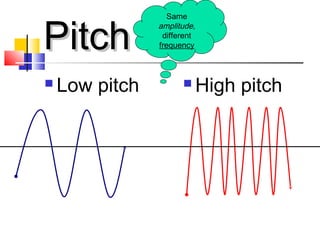
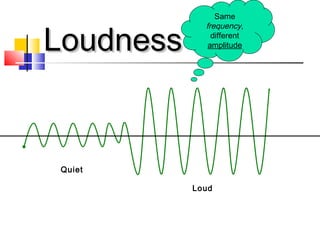
The document discusses different types of waves including mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves, transverse waves, and longitudinal waves. It provides examples that electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, require a medium, and particles in transverse waves vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave travel. The document also reviews characteristics of different types of waves.