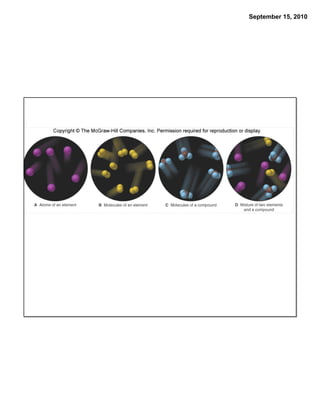
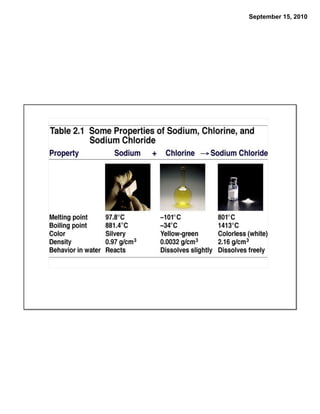
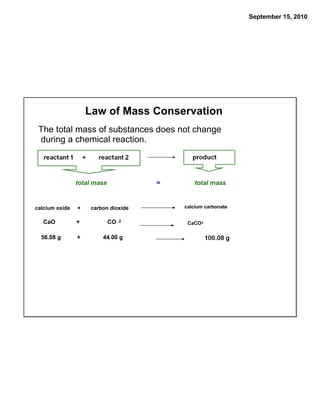
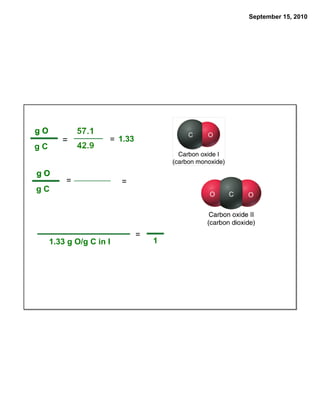
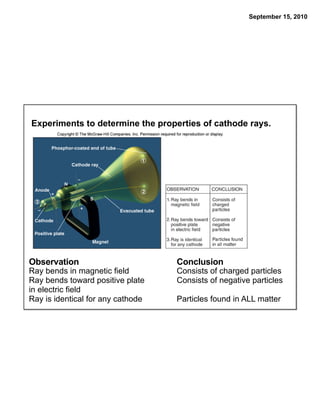
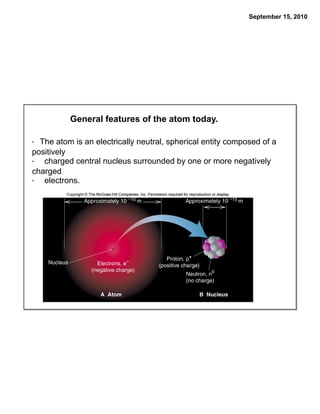
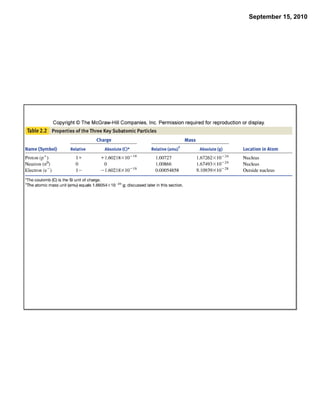
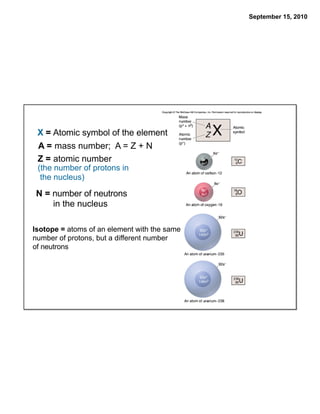
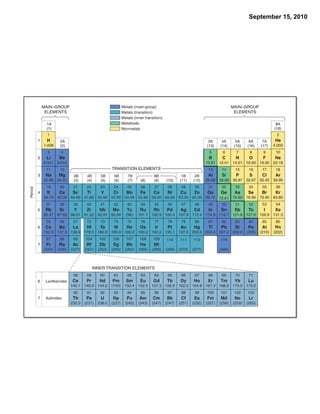
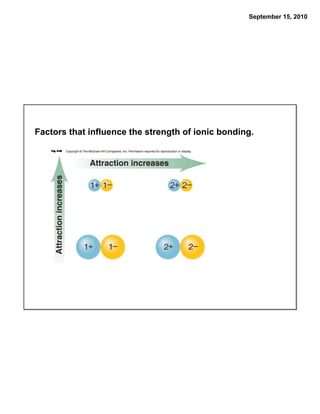
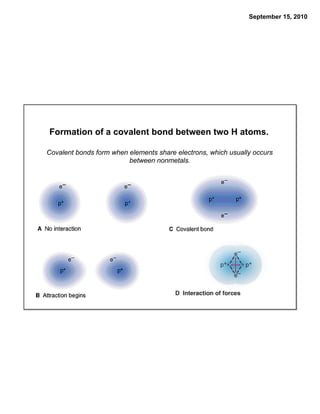
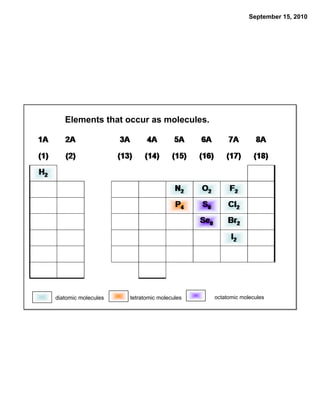
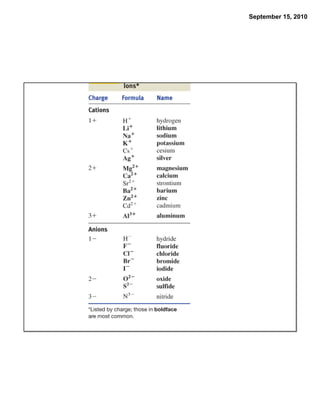
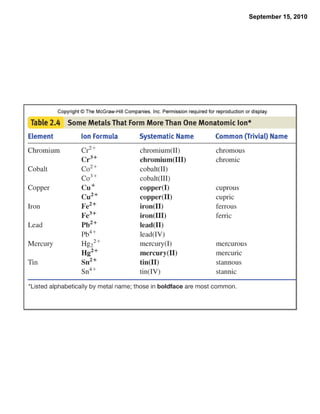
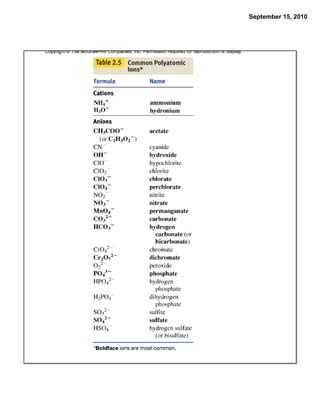
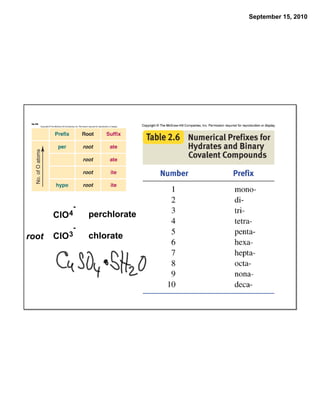
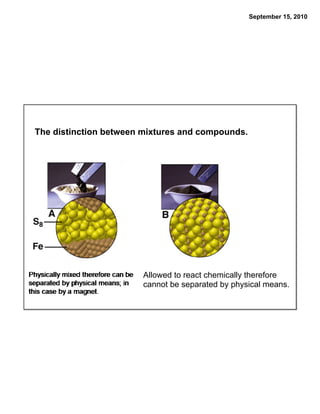
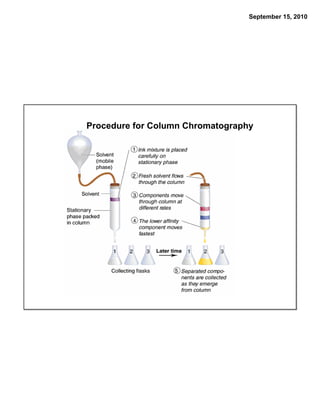
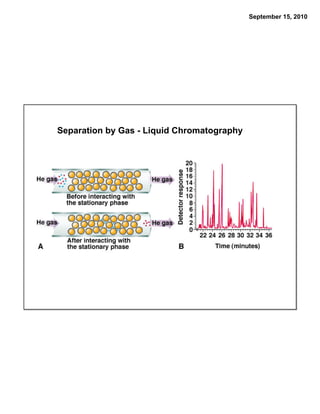
This chapter discusses the components of matter including elements, compounds, and mixtures. It introduces key concepts such as Dalton's atomic theory which states that all matter is made of atoms that combine in whole number ratios. The chapter also discusses how experiments led to discoveries such as the nuclear atom model, including evidence for a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. It defines modern atomic structure and symbols.