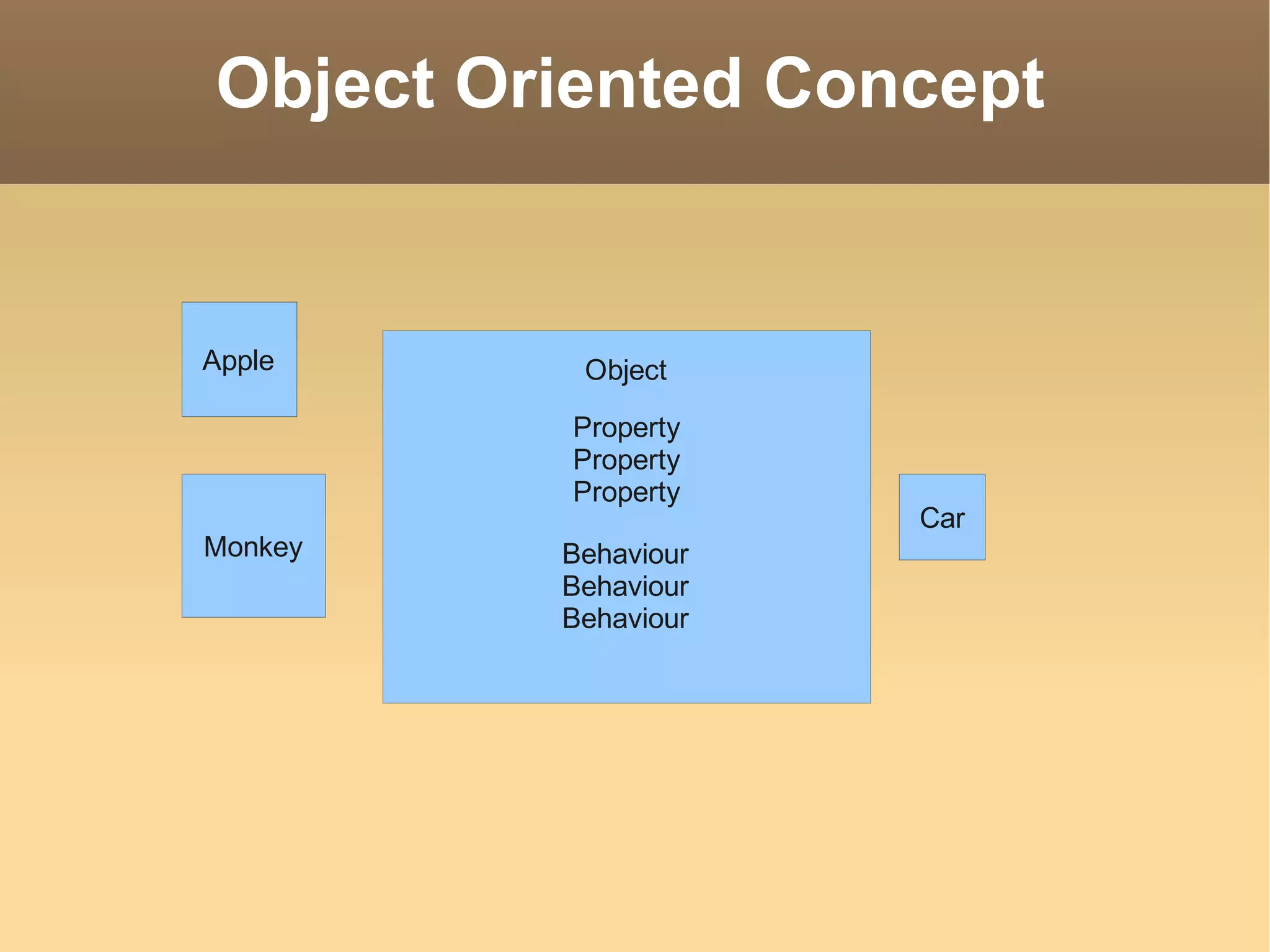
The document discusses the principles of object-oriented design (OOD) and object-oriented programming (OOP), highlighting essential concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It outlines key principles such as the Single Responsibility Principle, Open/Closed Principle, Liskov Substitution Principle, Dependency Inversion Principle, and Interface Segregation Principle, emphasizing their importance in software design. The document also mentions the transition from procedural to object-oriented programming and the challenges associated with grasping OOP concepts.