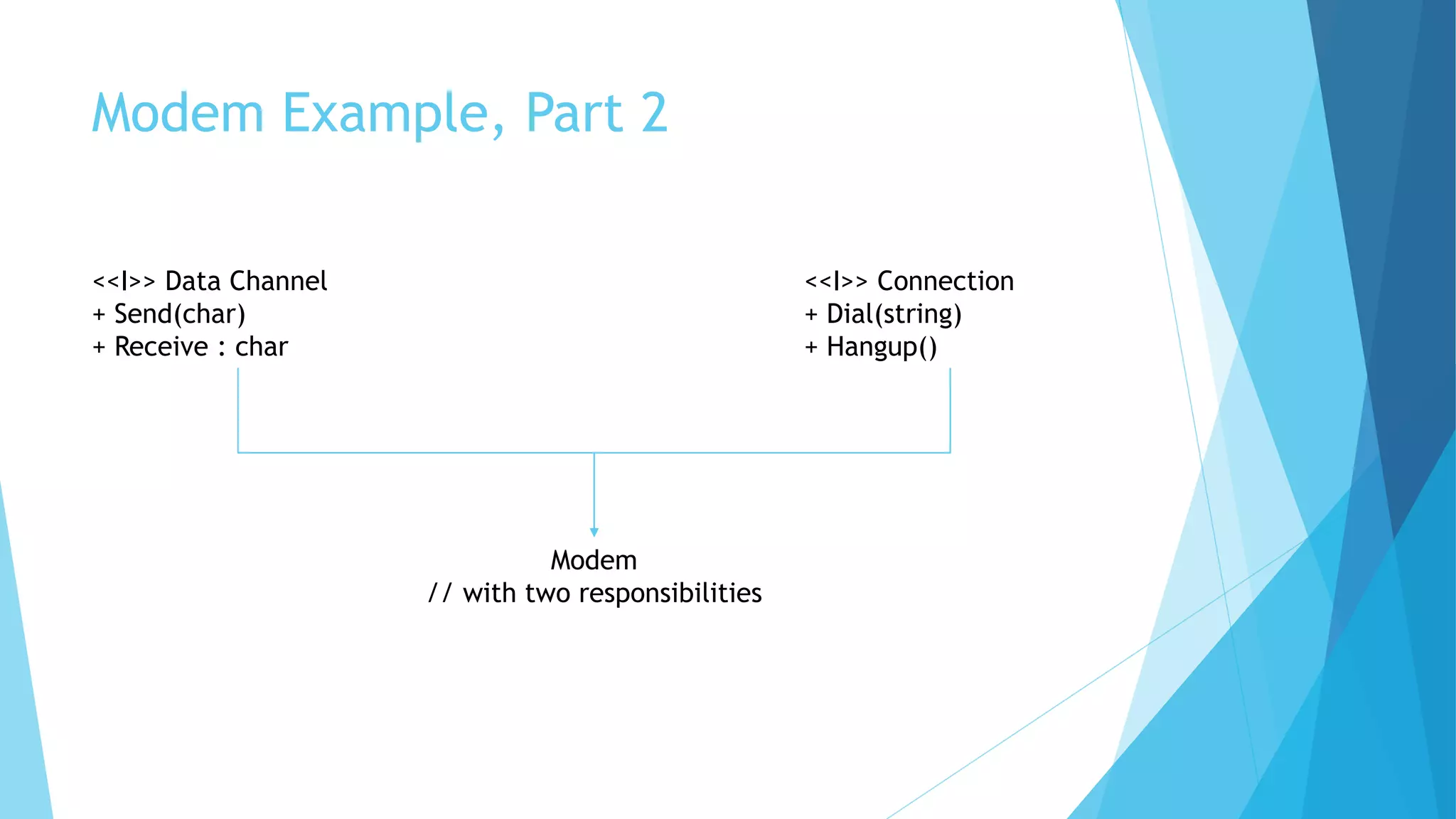
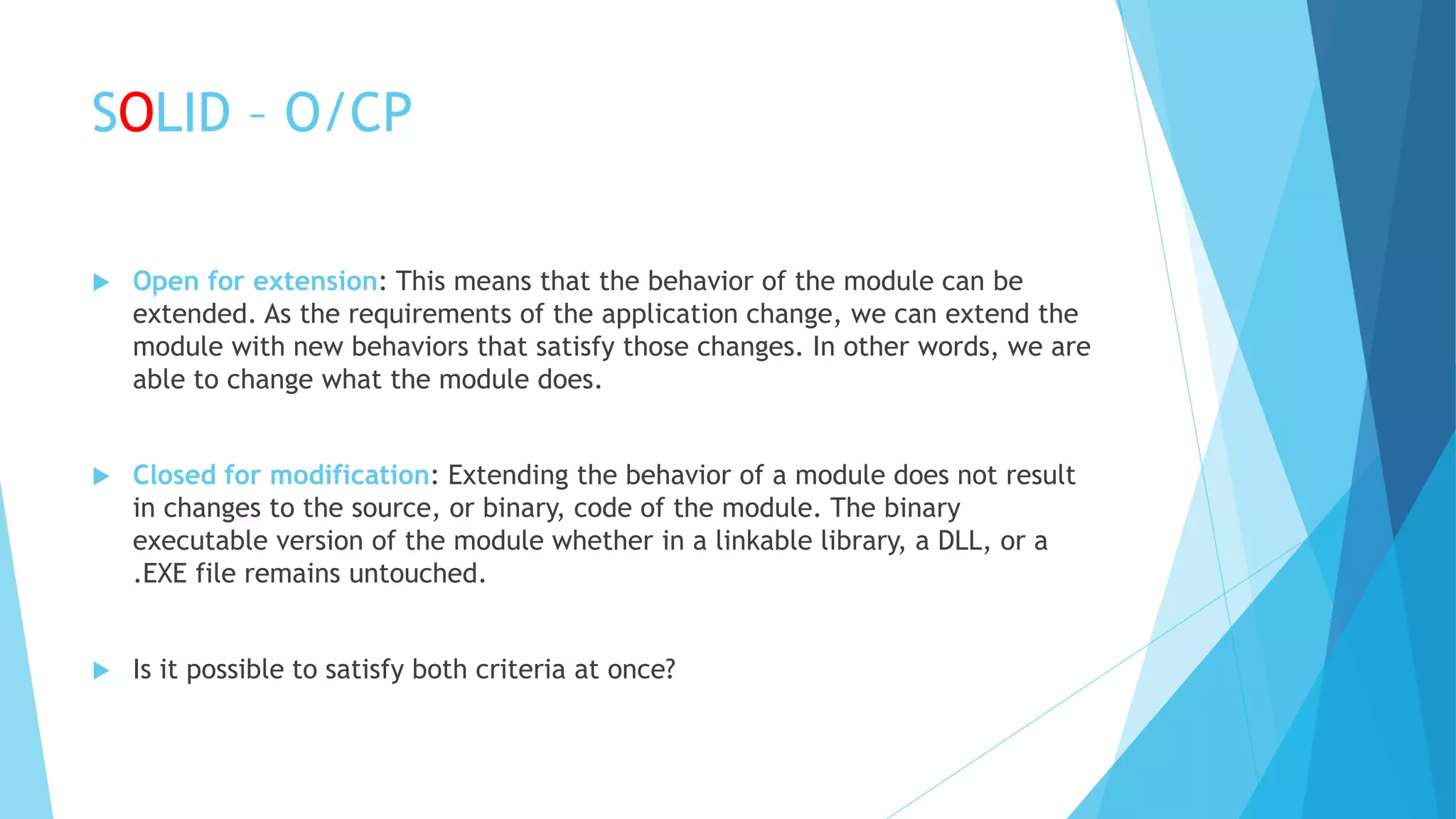
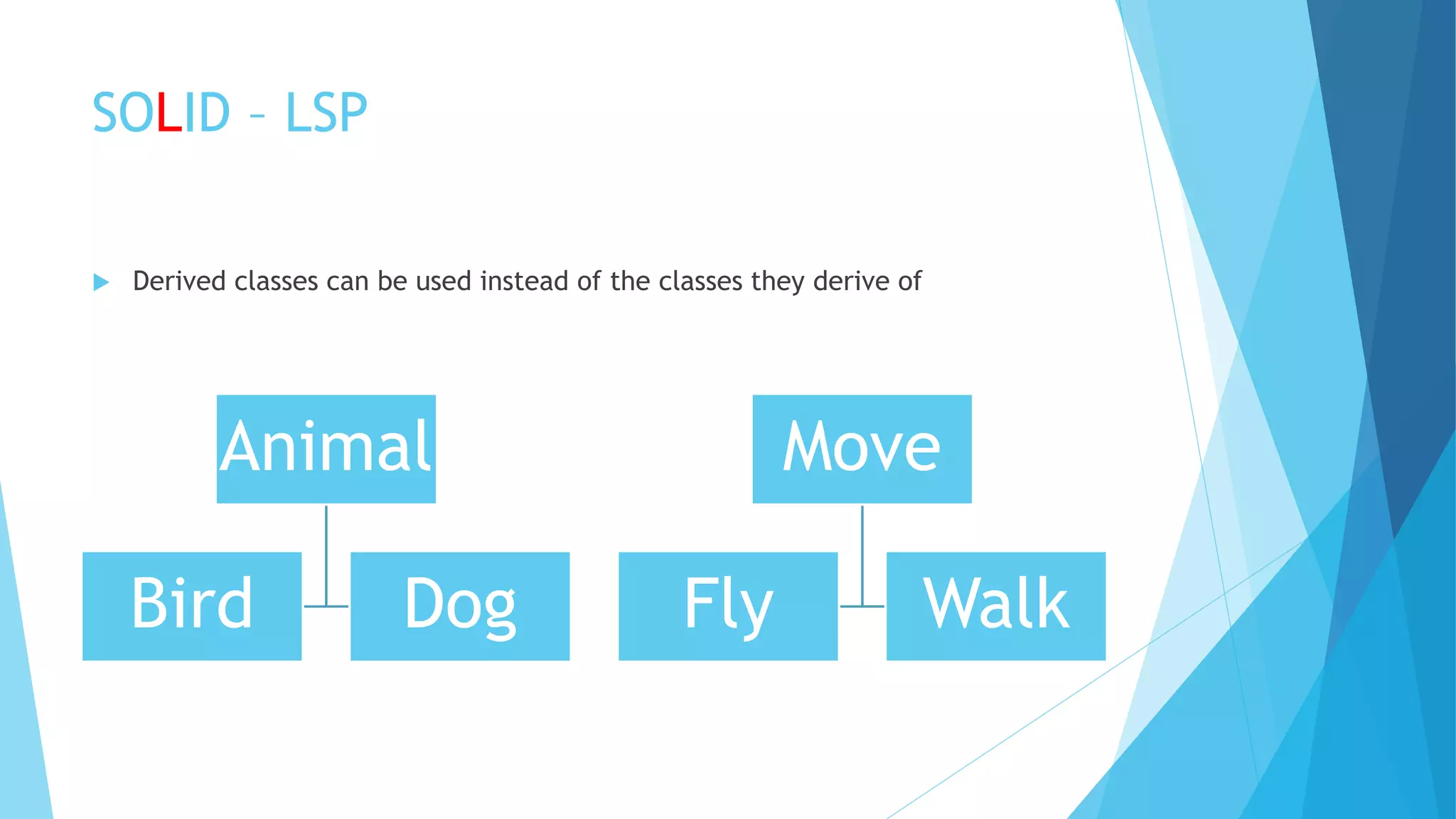
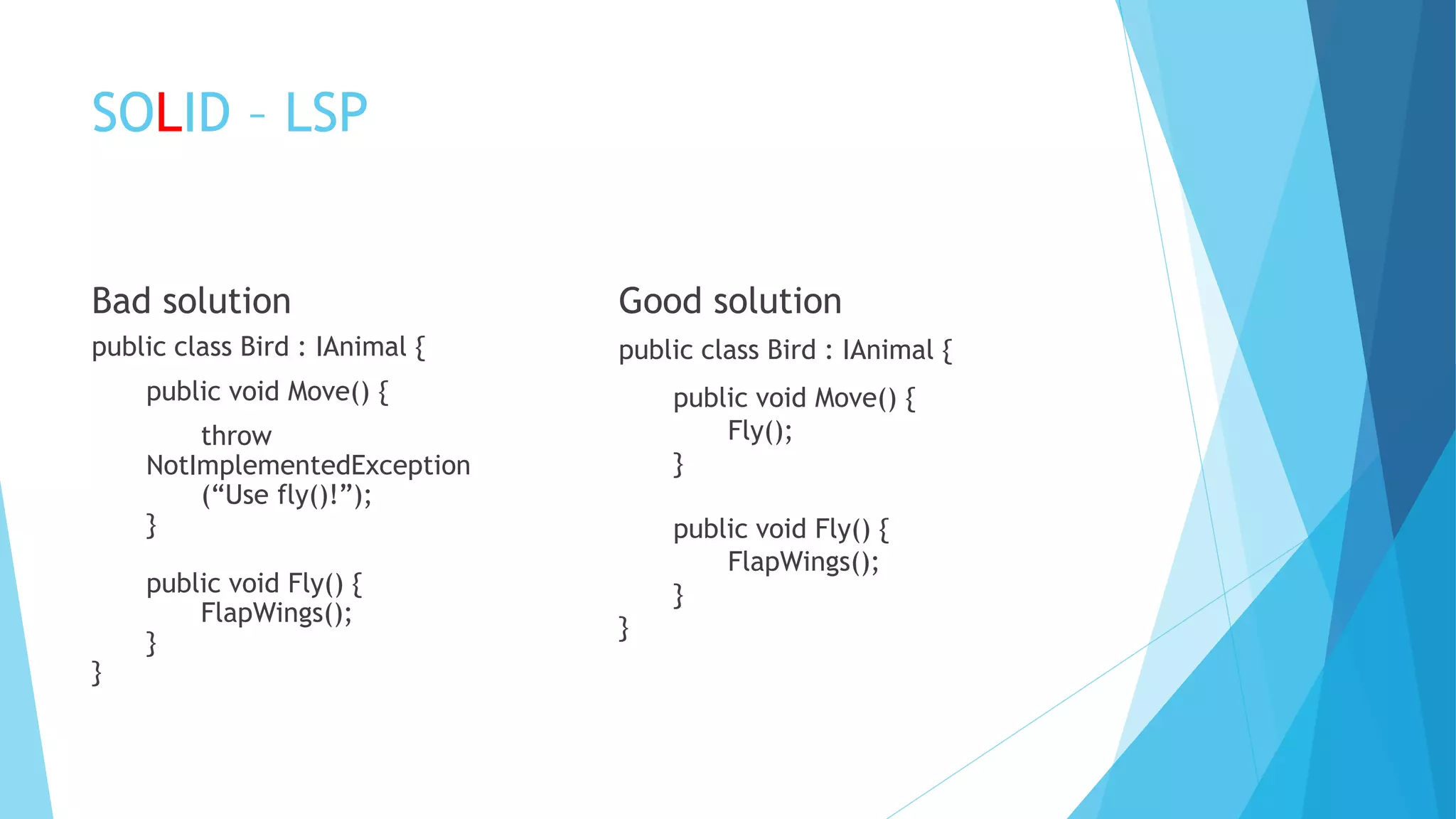
The document discusses the SOLID principles of object-oriented programming, emphasizing the importance of each principle such as single responsibility, open/closed, Liskov substitution, interface segregation, and dependency inversion. It provides explanations, examples, and bad practices to illustrate proper implementation and the significance of high cohesion and low coupling in software design. The author highlights the necessity of relying on abstractions and interfaces to maintain flexible and maintainable code.