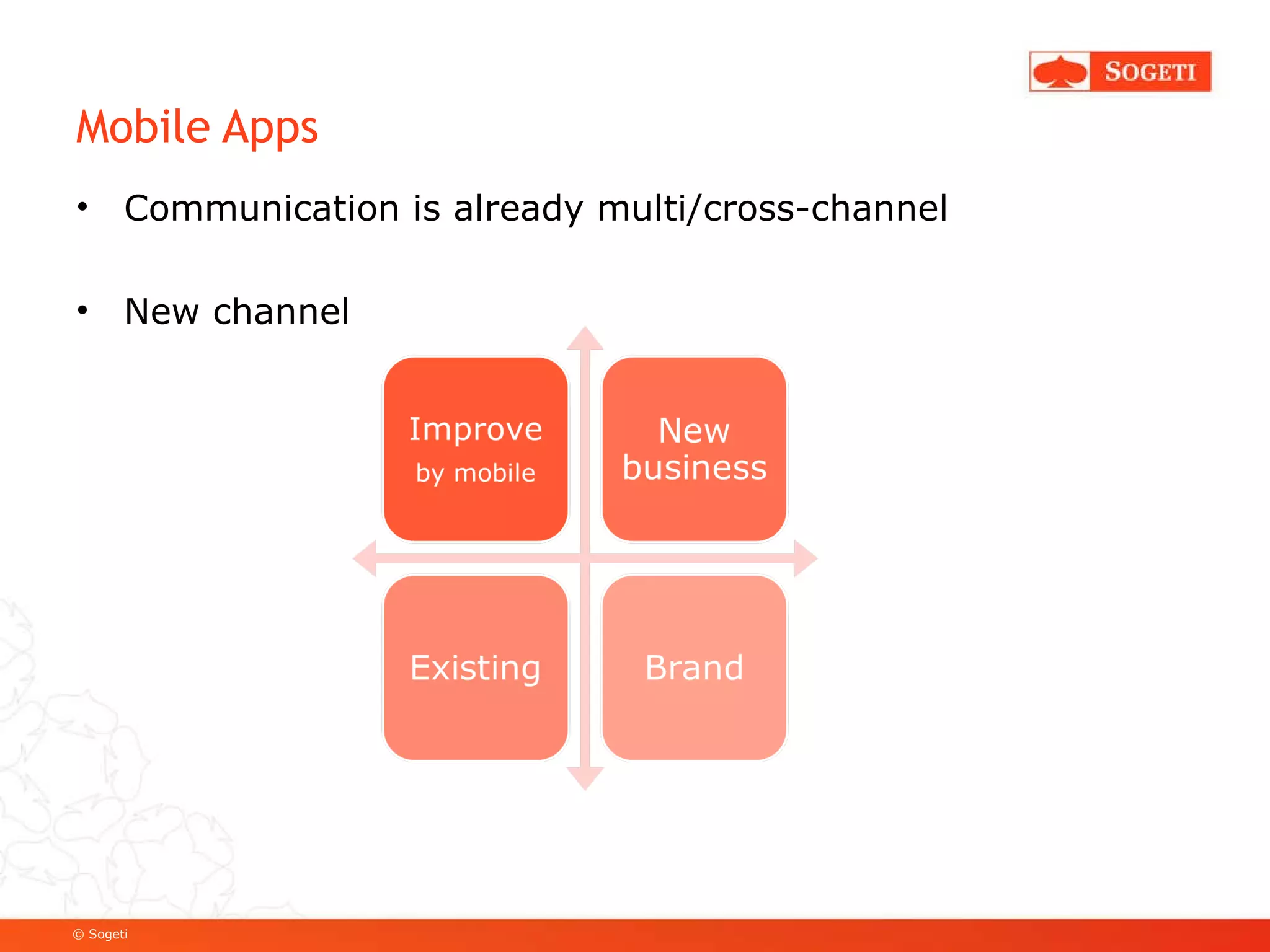
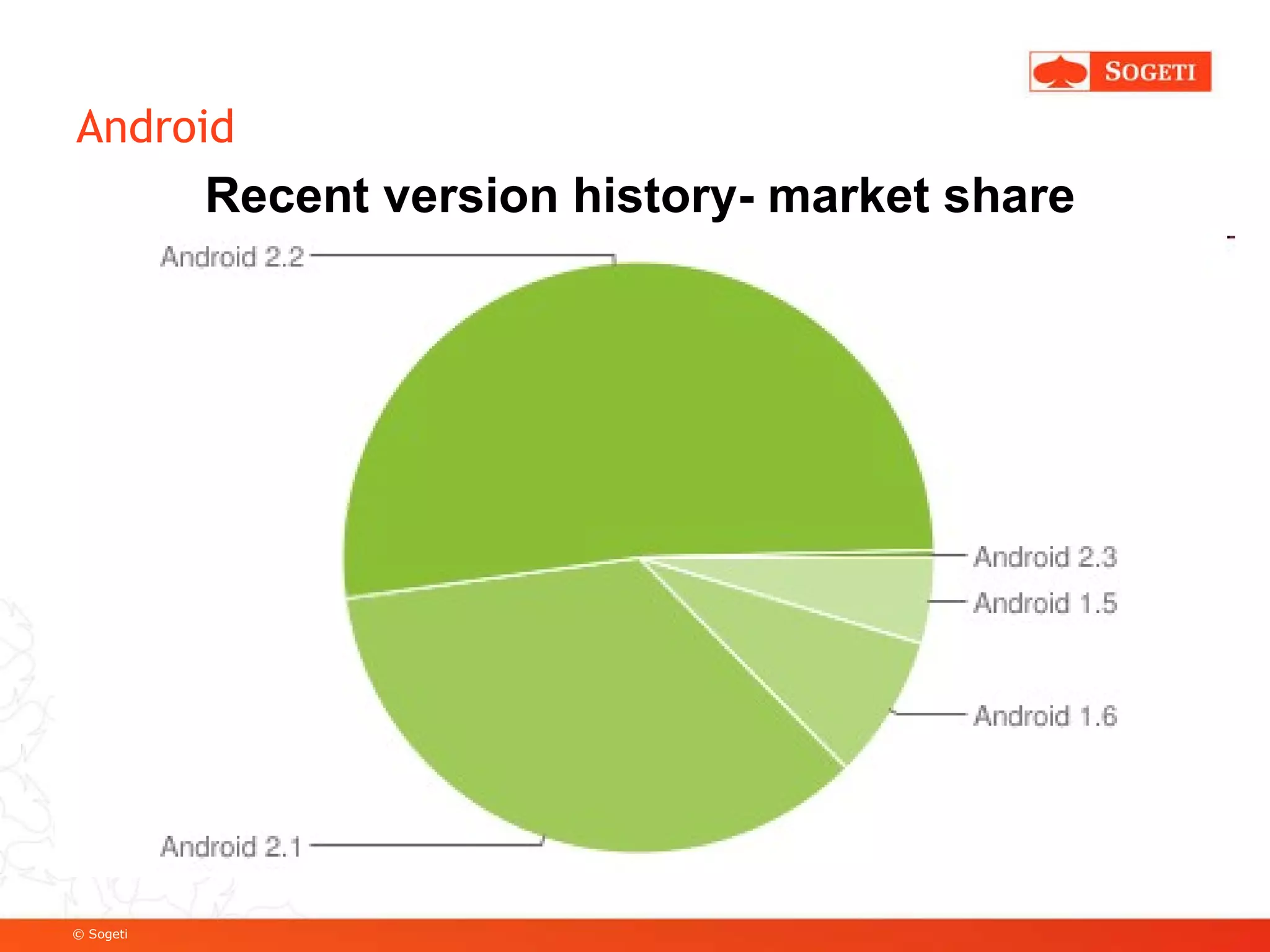
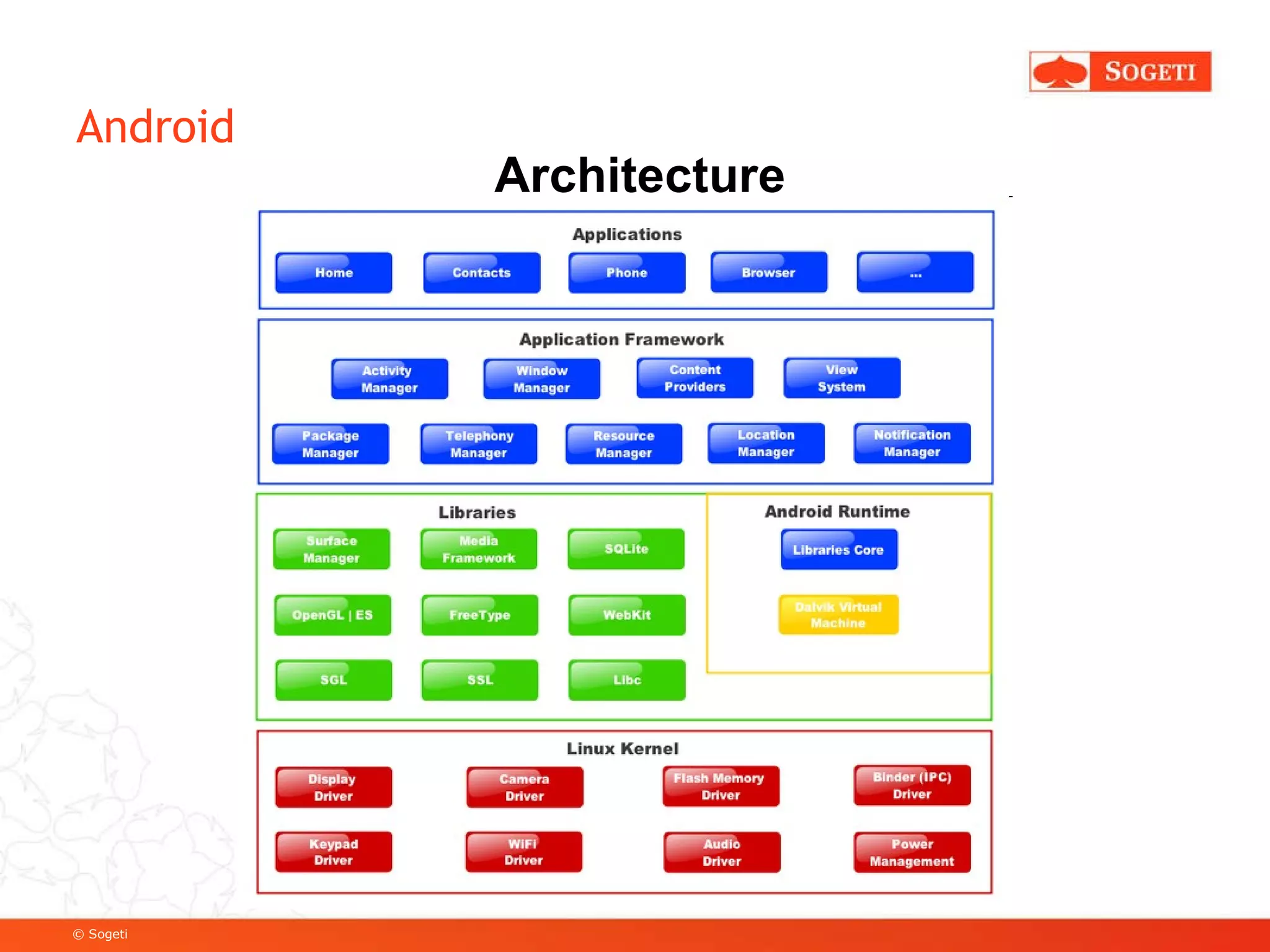
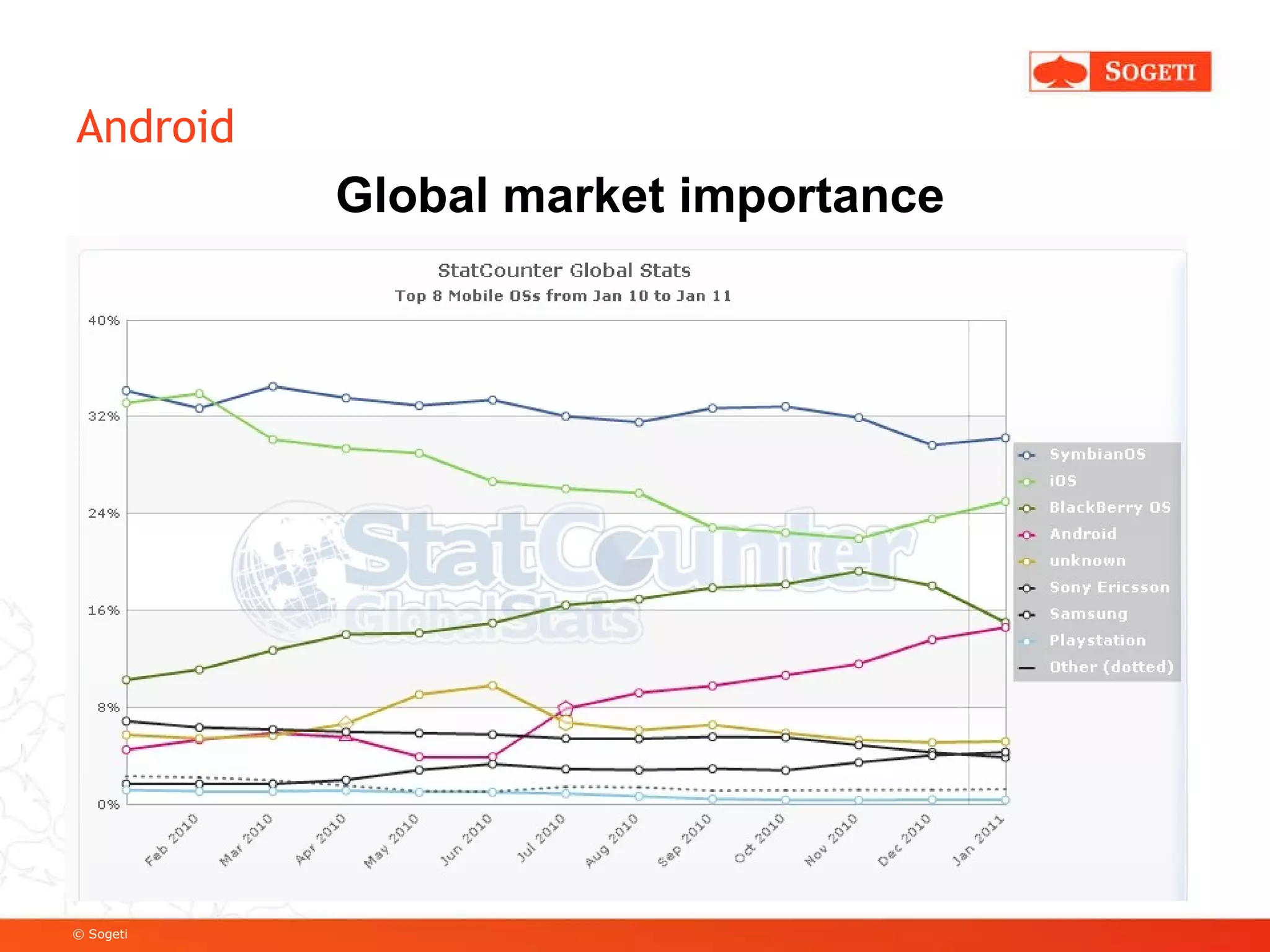
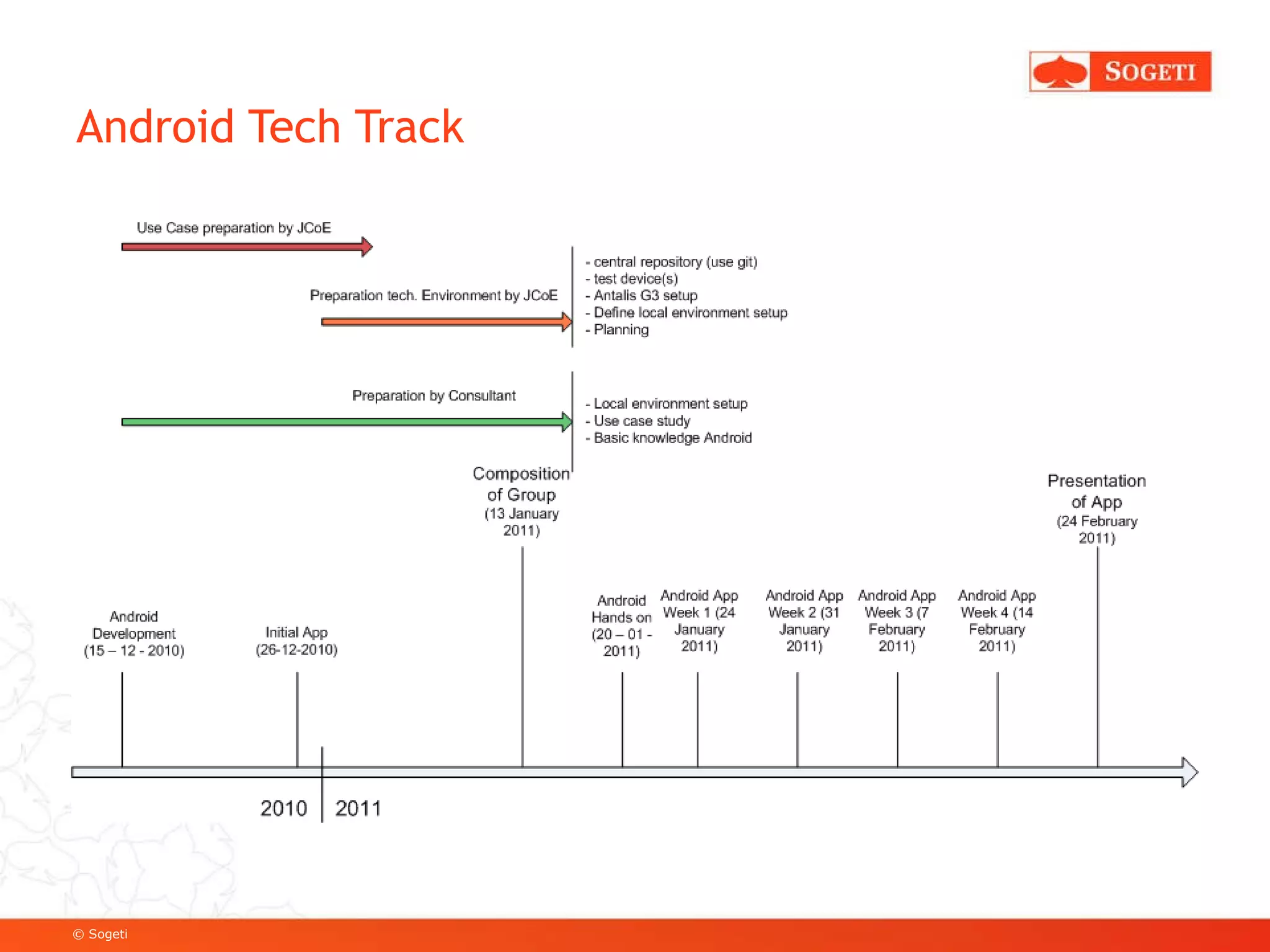
The document discusses mobile app development, focusing on Android as a prevalent platform. It examines the benefits of mobile apps over mobile websites, the evolution of Android through its versions, and various development tools and techniques, including SDK usage and service implementation. Additionally, it highlights the significance of consistent user experience and the integration of advanced features in mobile applications.