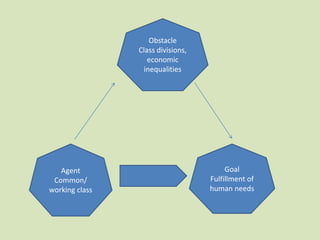
This document discusses the key concepts and history of socialism. It outlines that socialism originated in the 19th century as a response to liberalism, with socialists objecting to the competition and individual liberty of capitalism. Socialists believe that human beings are by nature social and cooperative, not competitive, and that the goal of a socialist society is to ensure liberty, justice and prosperity for all through public ownership of major means of production and a more equal distribution of wealth and power. The document traces the spread and evolution of socialist ideas and parties in the 20th century, noting divisions between communist and social democratic forms of socialism as well as challenges to socialism in recent decades.