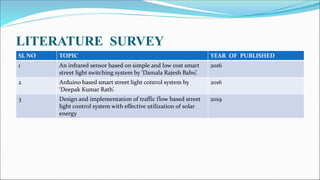
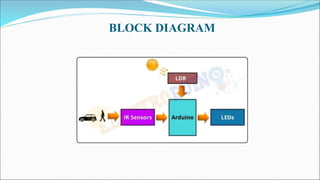
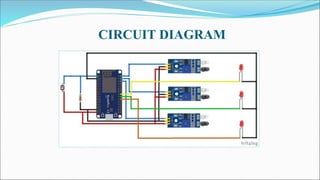
This document describes a student project to develop a street light energy saving control system. The system uses an Arduino nano, infrared sensors, LEDs and an LDR to dim streetlights when no vehicle movement is detected, in order to reduce energy consumption. When an IR sensor detects a vehicle, the LED streetlights in that area will glow at full intensity, and then the next block of lights will turn on as the vehicle moves forward. The system aims to save electrical power by only keeping streetlights dimmed at 40% intensity when roads are inactive. The document outlines the methodology, hardware components, software, results and applications of the smart streetlight control system.