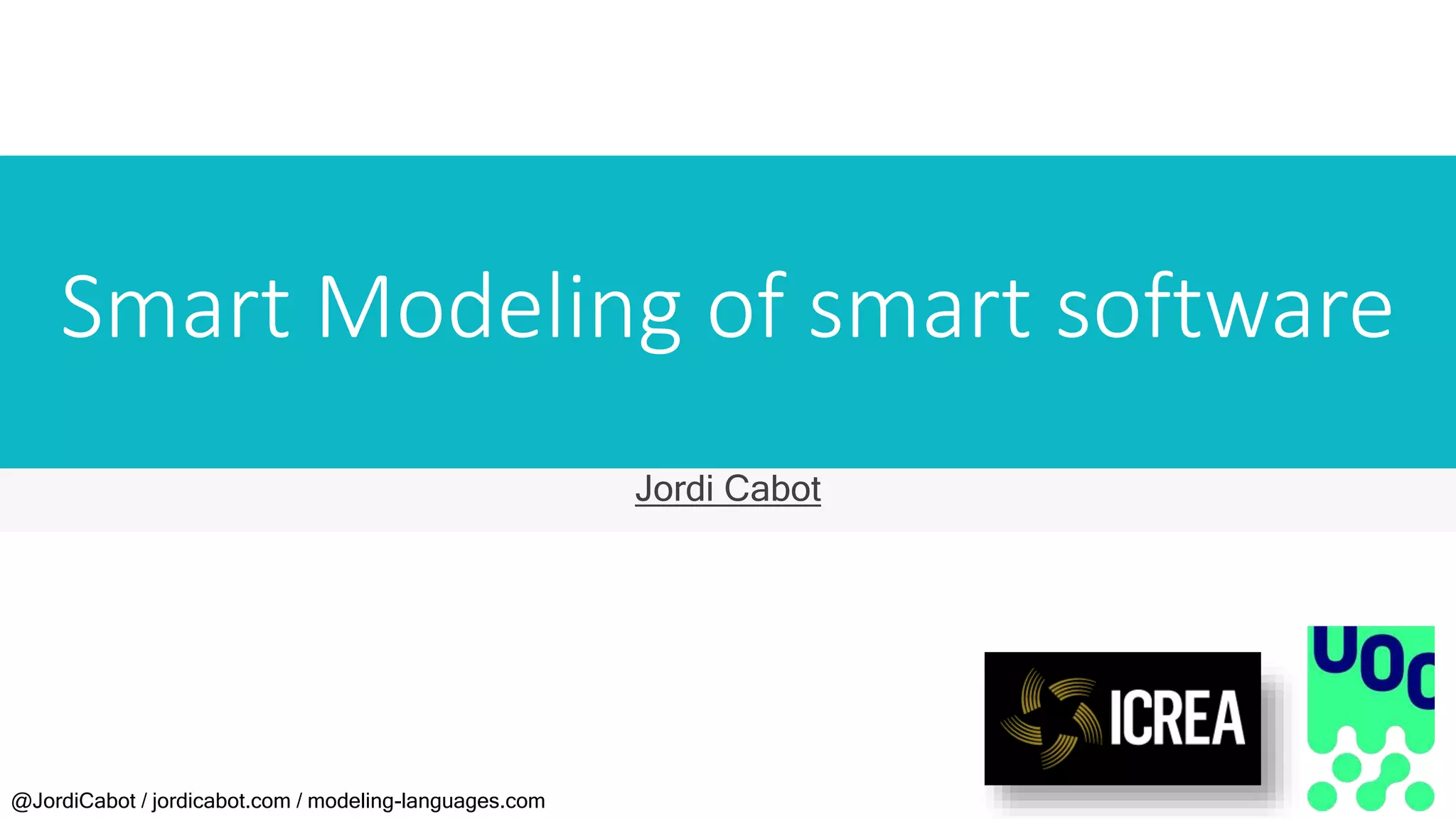
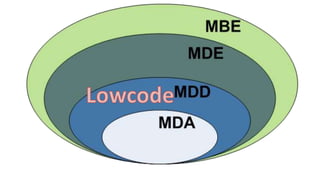
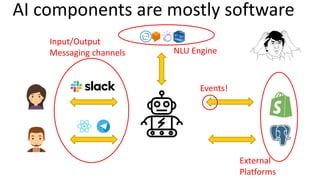
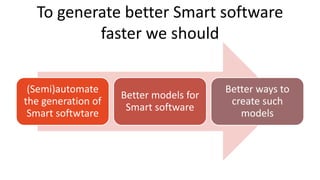
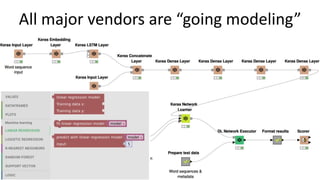
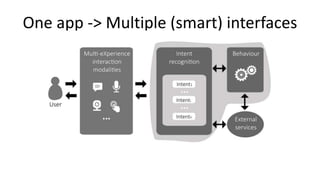
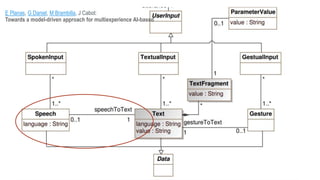
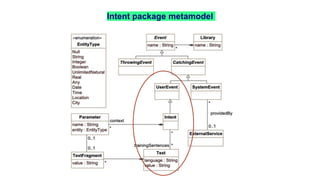
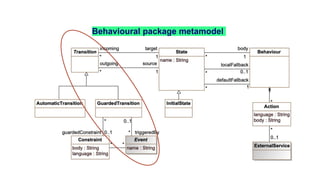
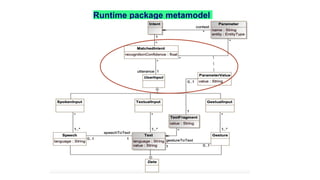
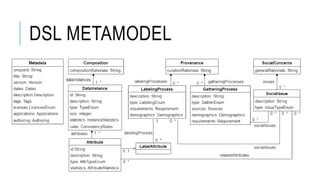
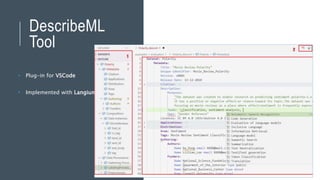
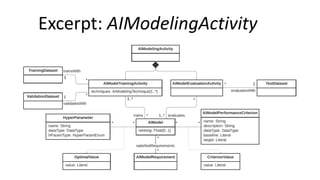
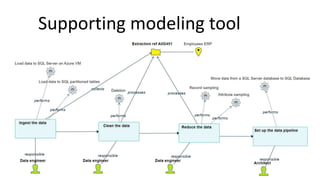
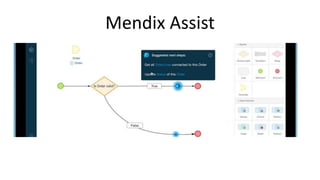
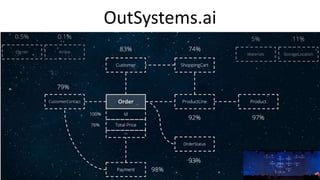
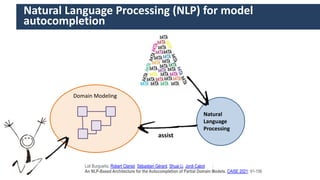
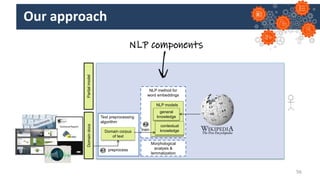
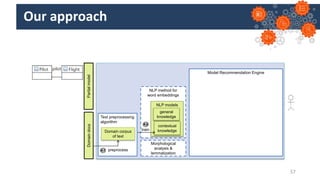
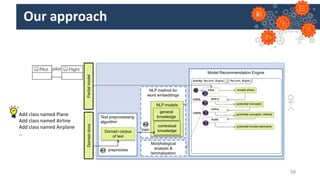
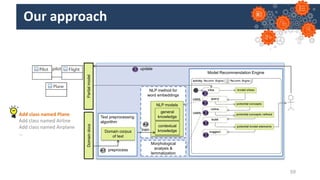
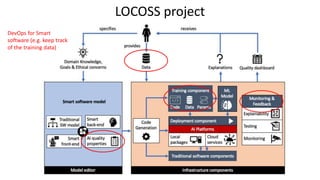
Jordi Cabot discusses modeling approaches for smart software development. He argues that modeling can help generate smart software faster by automating parts of the process and using better models. His research focuses on domain-specific languages for modeling different aspects of smart systems, like interfaces, datasets, development processes, and more. The goal is to provide guidance and structure to help multidisciplinary teams successfully develop complex AI-based applications.