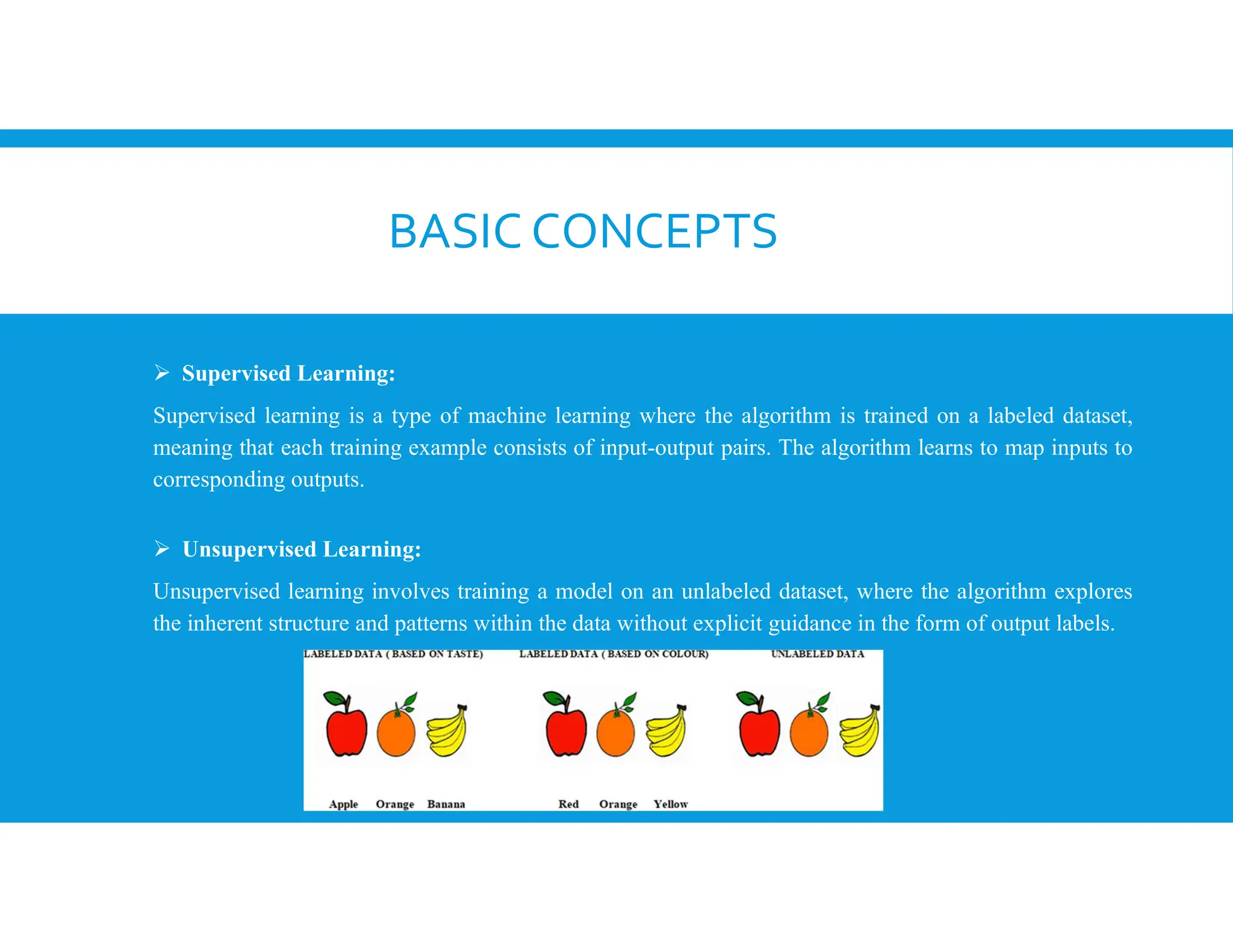
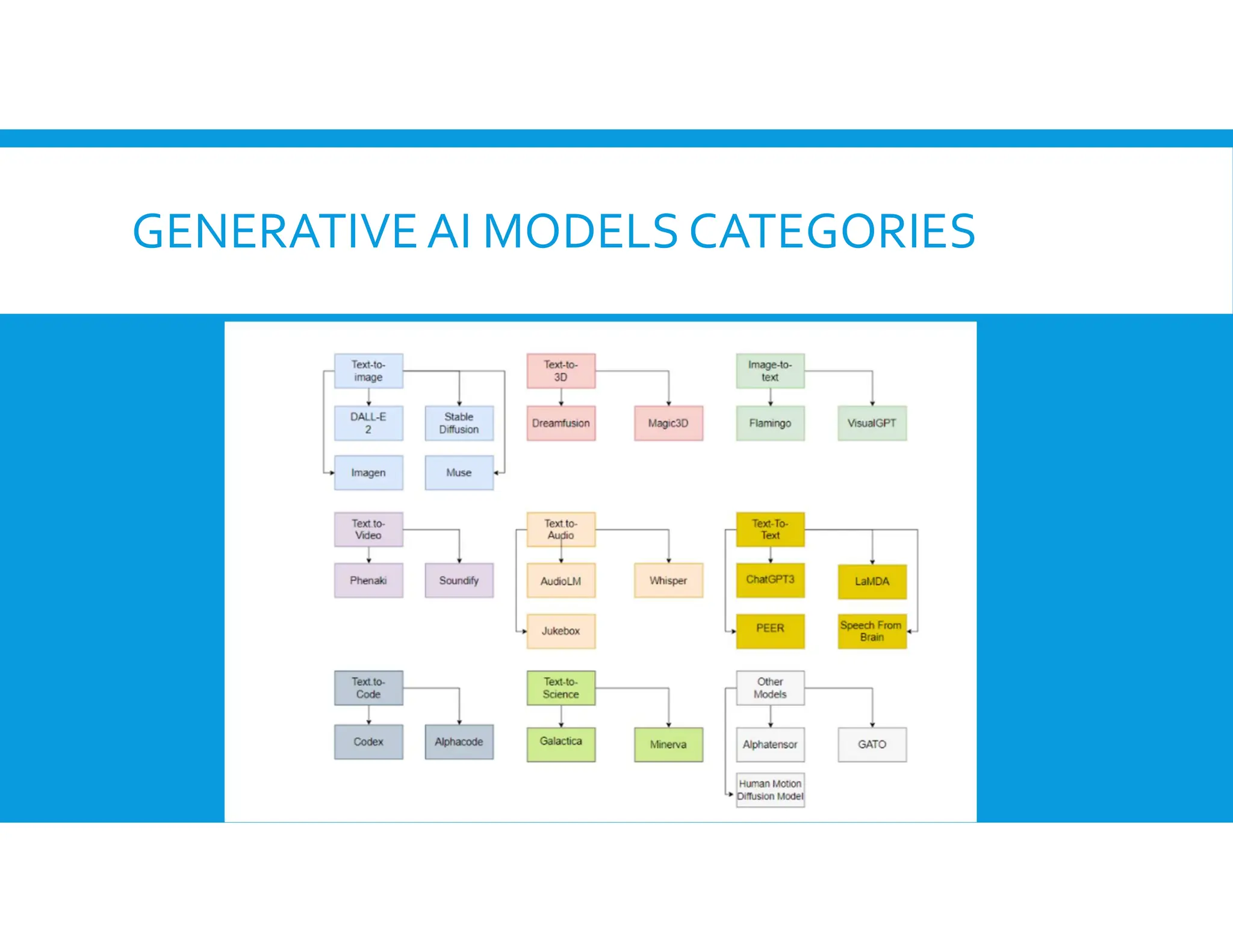
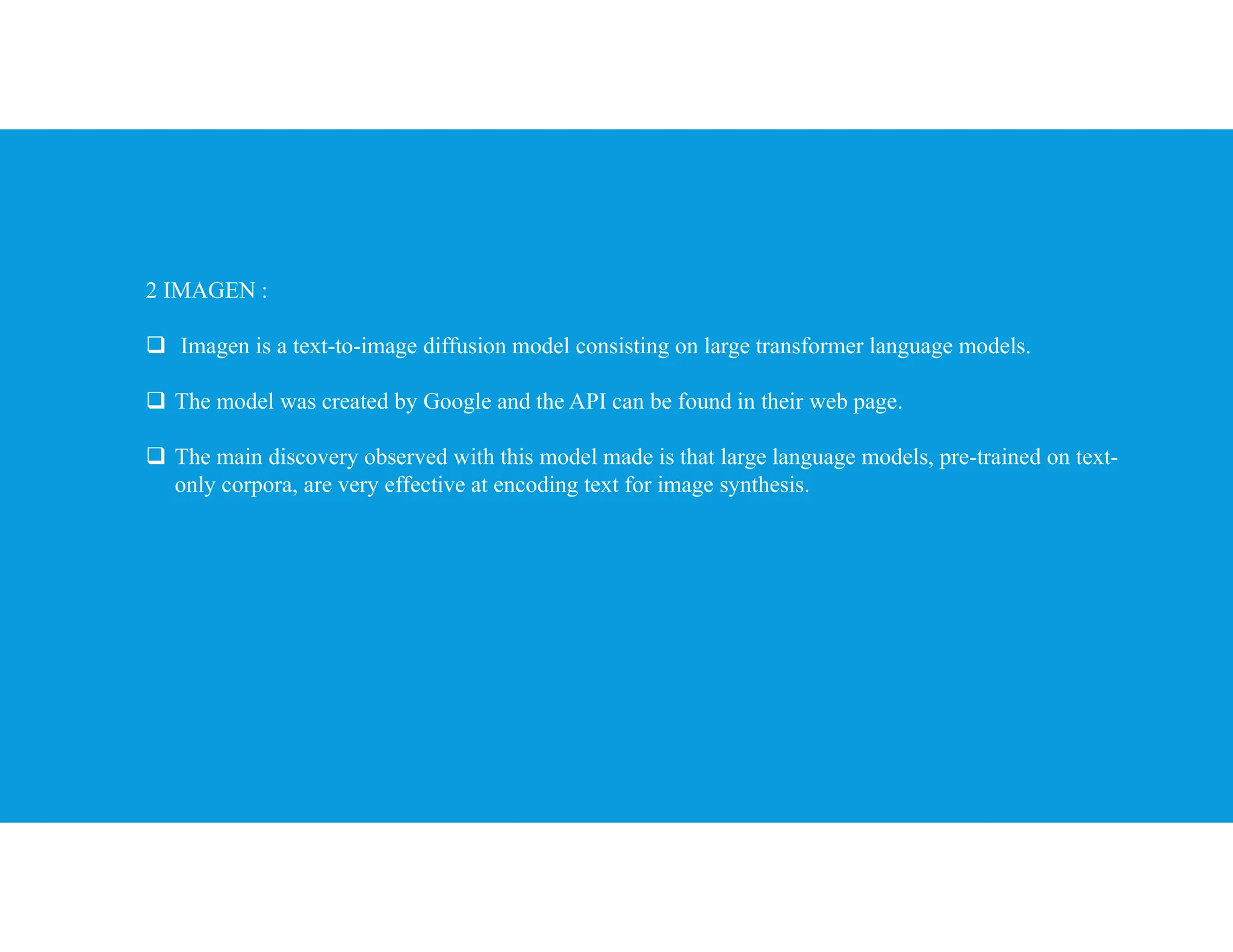
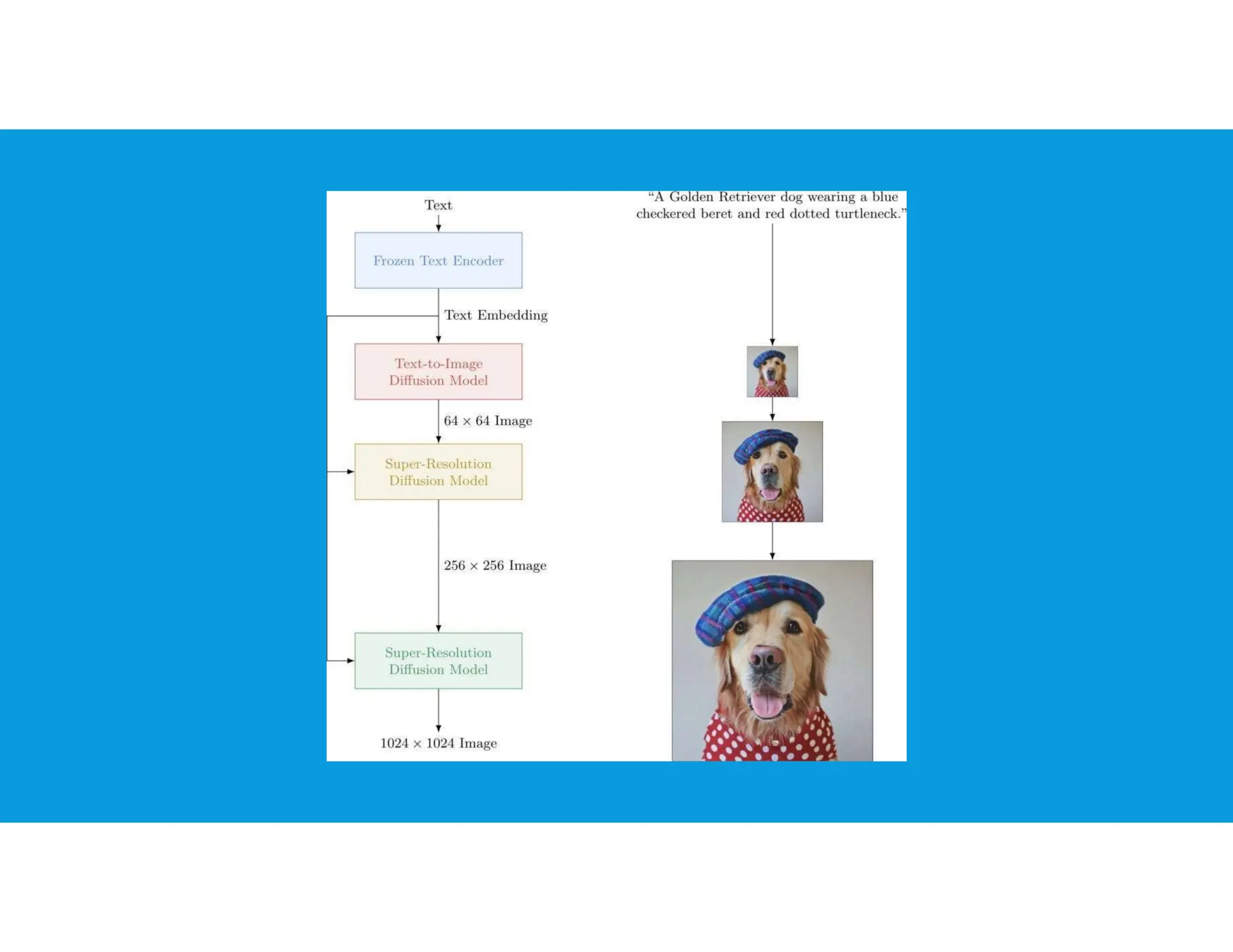
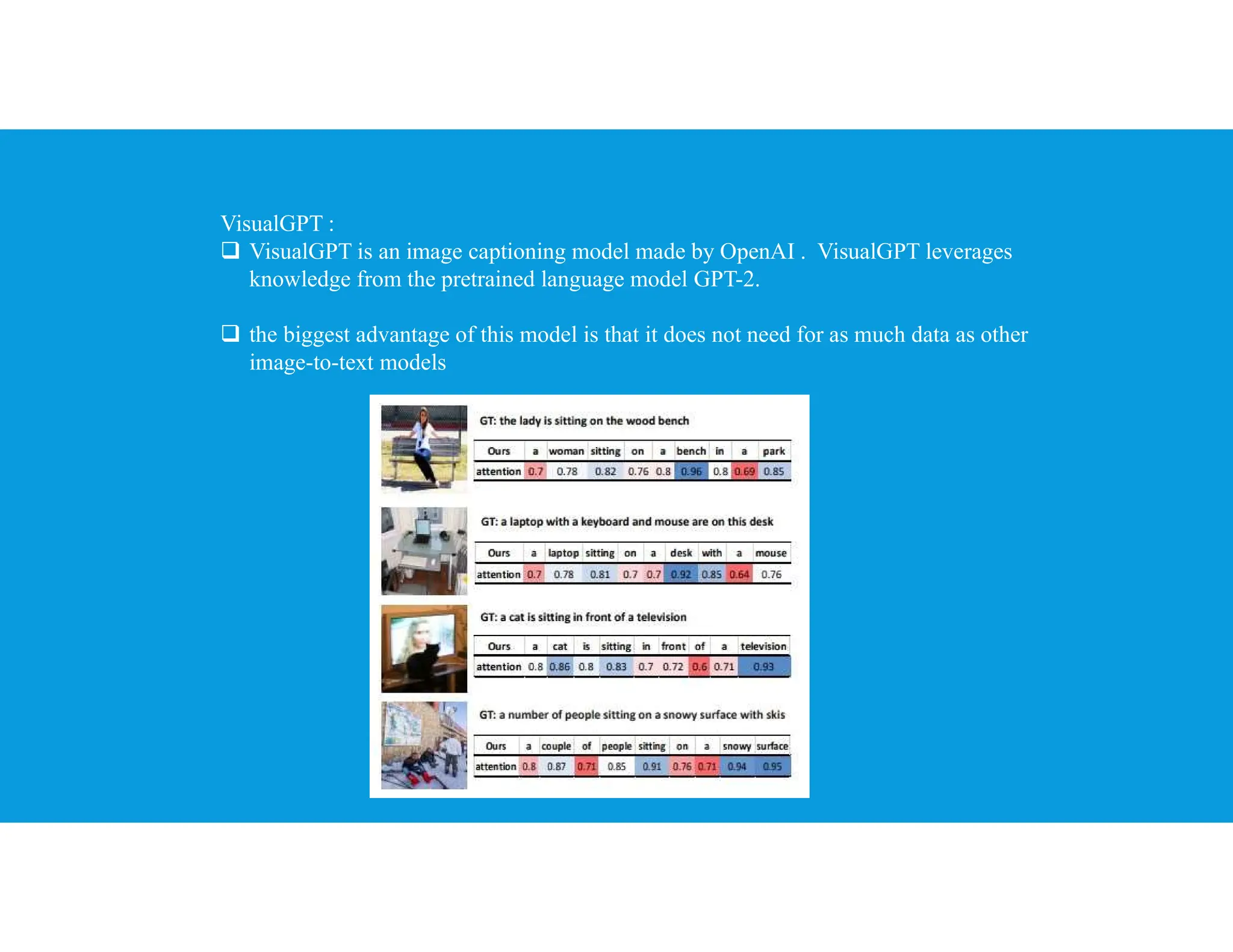
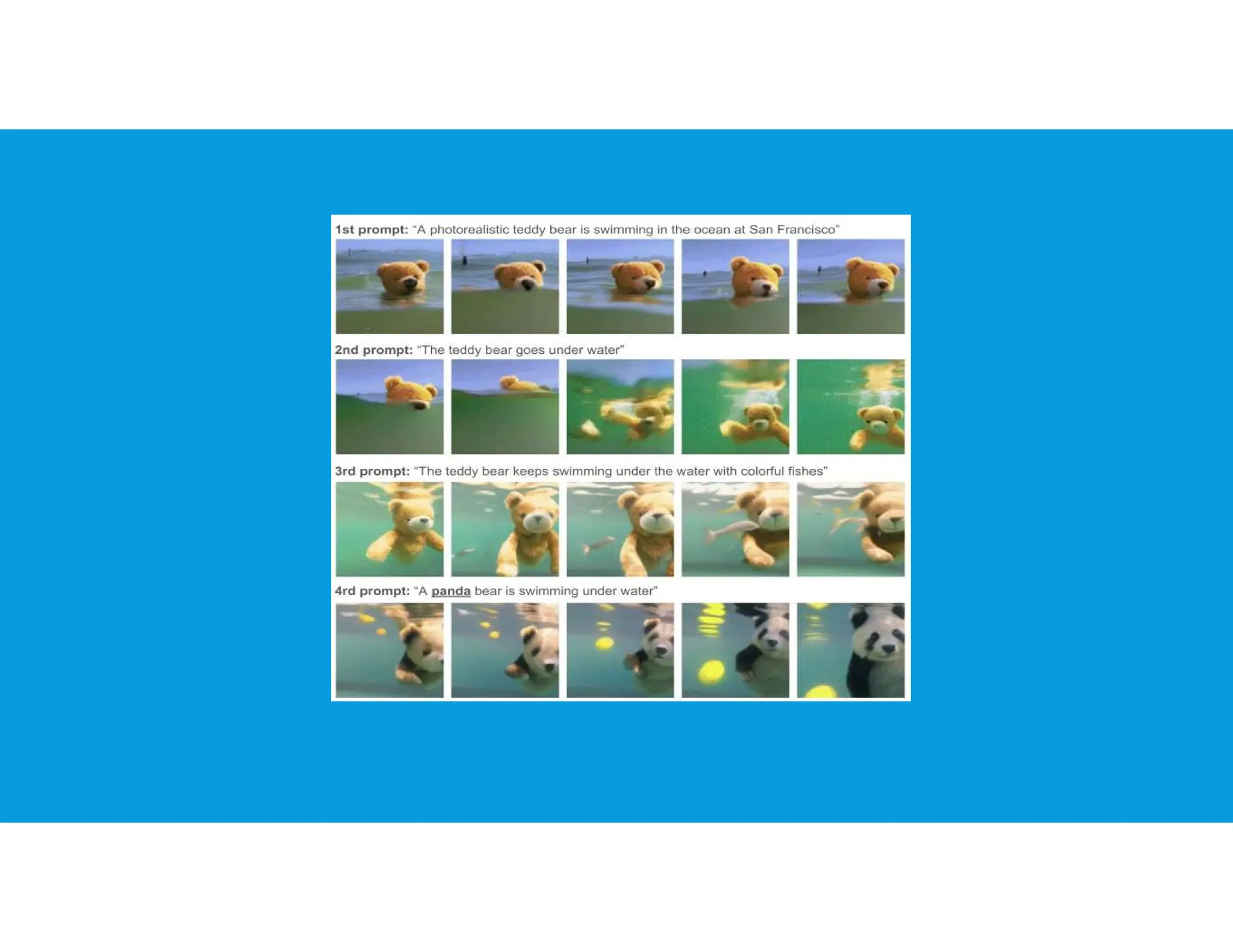
The document provides an overview of generative artificial intelligence, focusing on its ability to create new content like text, images, and audio by learning from existing data patterns. It categorizes generative AI models, including text-to-image, text-to-3D, image-to-text, and text-to-video models, and discusses prominent examples such as DALL-E 2, DreamFusion, and Phenaki. Additionally, it outlines basic concepts of supervised and unsupervised learning, differences between generative and discriminative models, and the neural network architectures commonly employed, such as autoencoders and GANs.