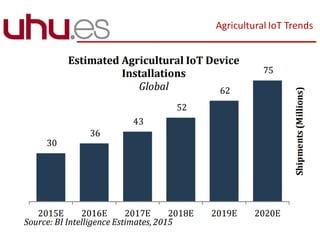
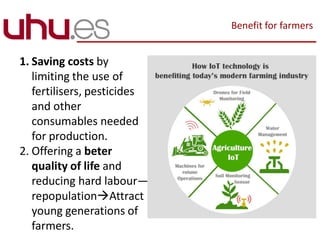
This document discusses the potential of smart agriculture and internet of things technologies to address challenges facing the world's food supply as the population grows. It notes that population is projected to reach 9.8 billion by 2050, increasing pressure on the food system. Smart agriculture uses sensing, data collection, and analysis to help farmers increase production while saving costs, resources, and labor. example applications and benefits are described such as precision irrigation, crop management, and traceability. Challenges for farmers include costs, remote locations, and climate impacts. The internet of things has potential to help overcome barriers if protocols and connectivity solutions can meet farmer needs.