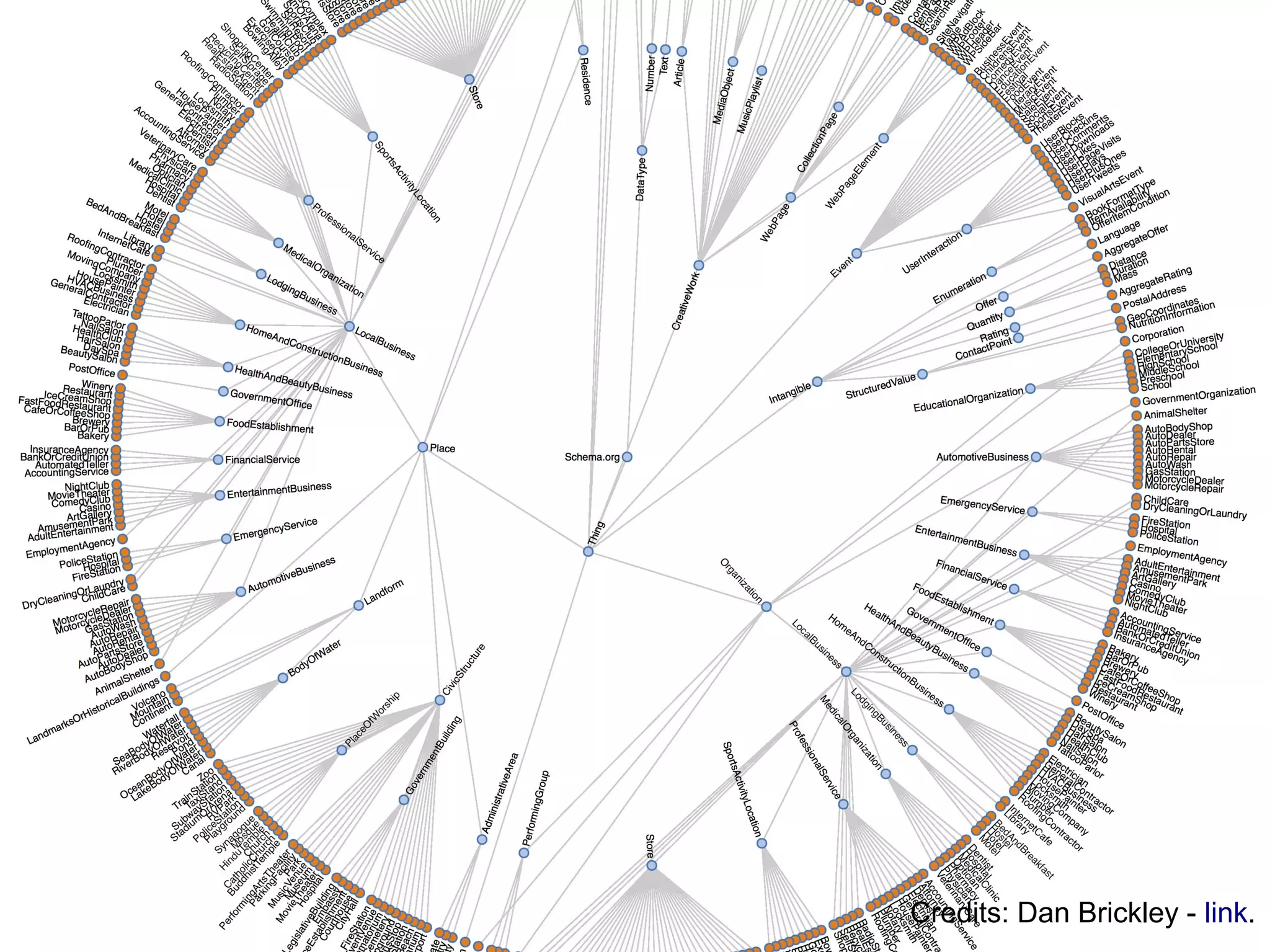
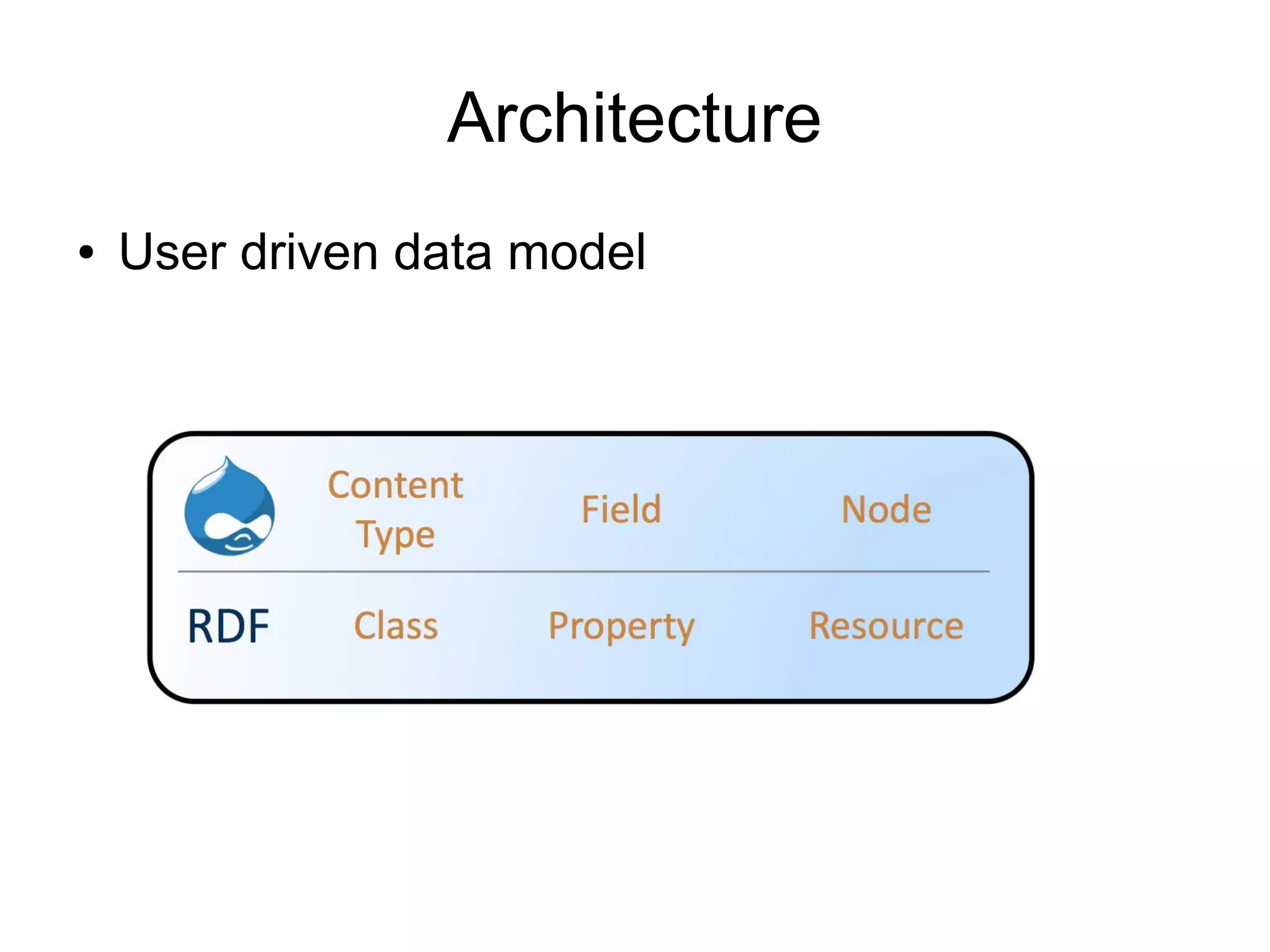
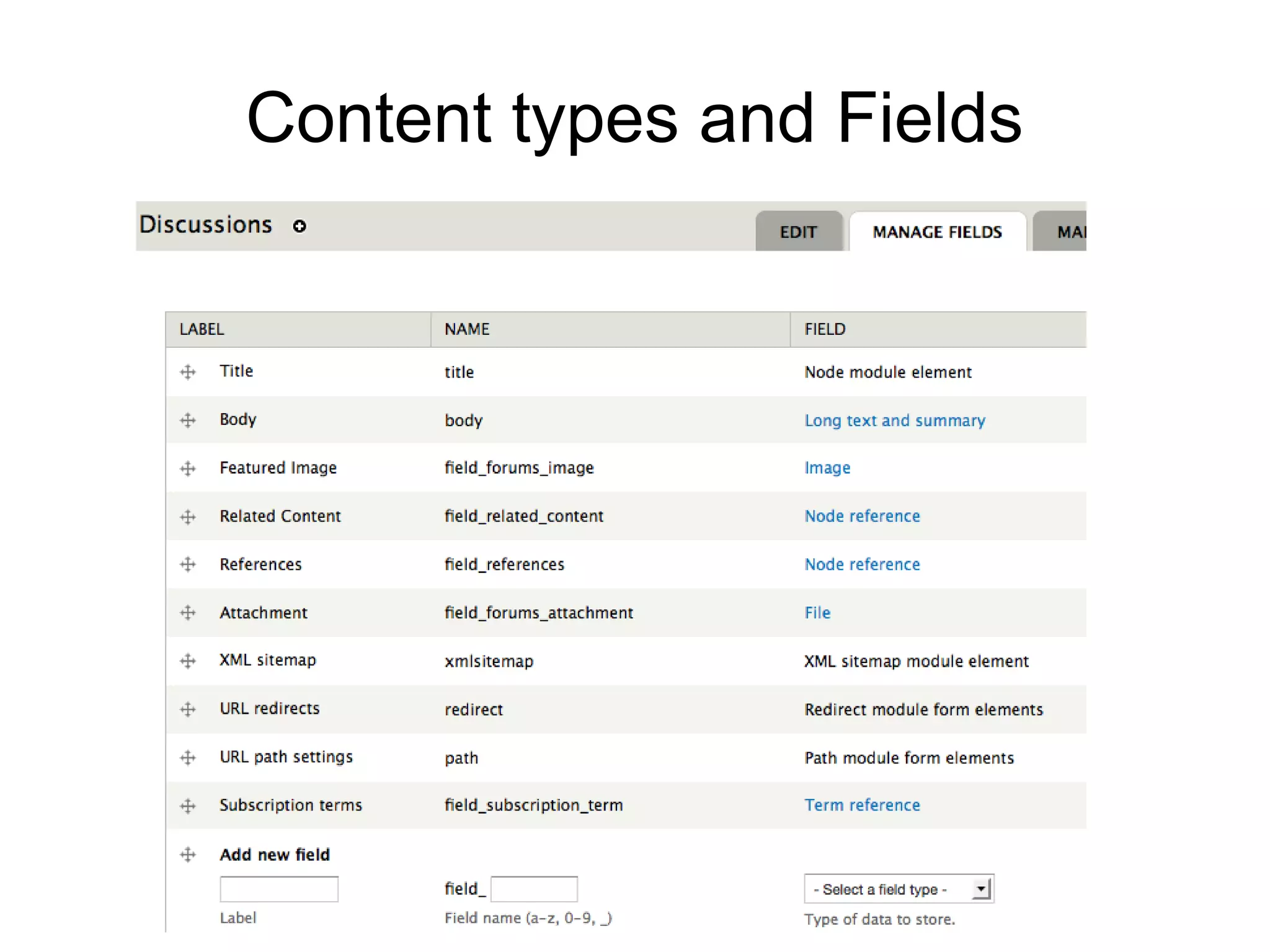
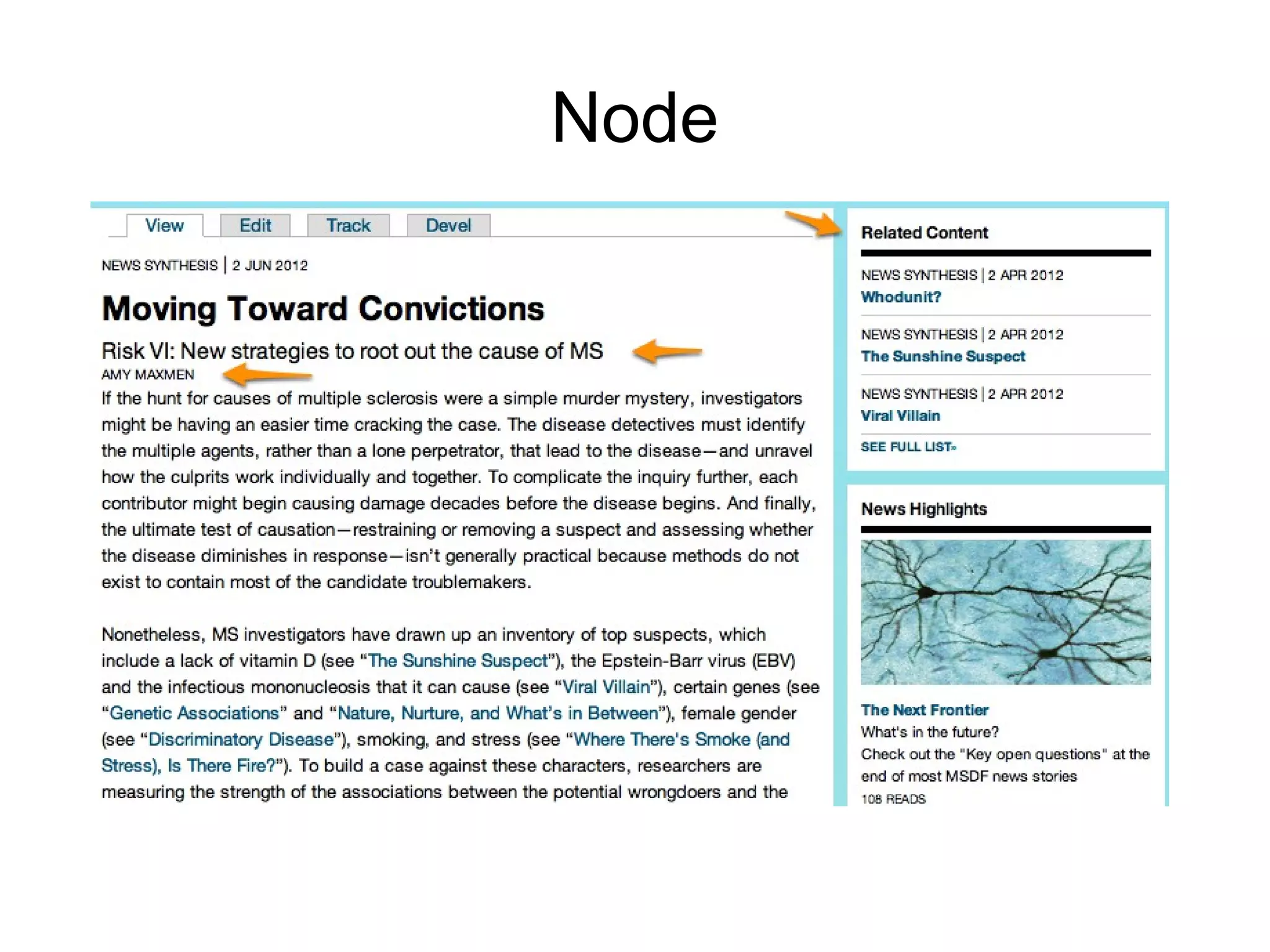
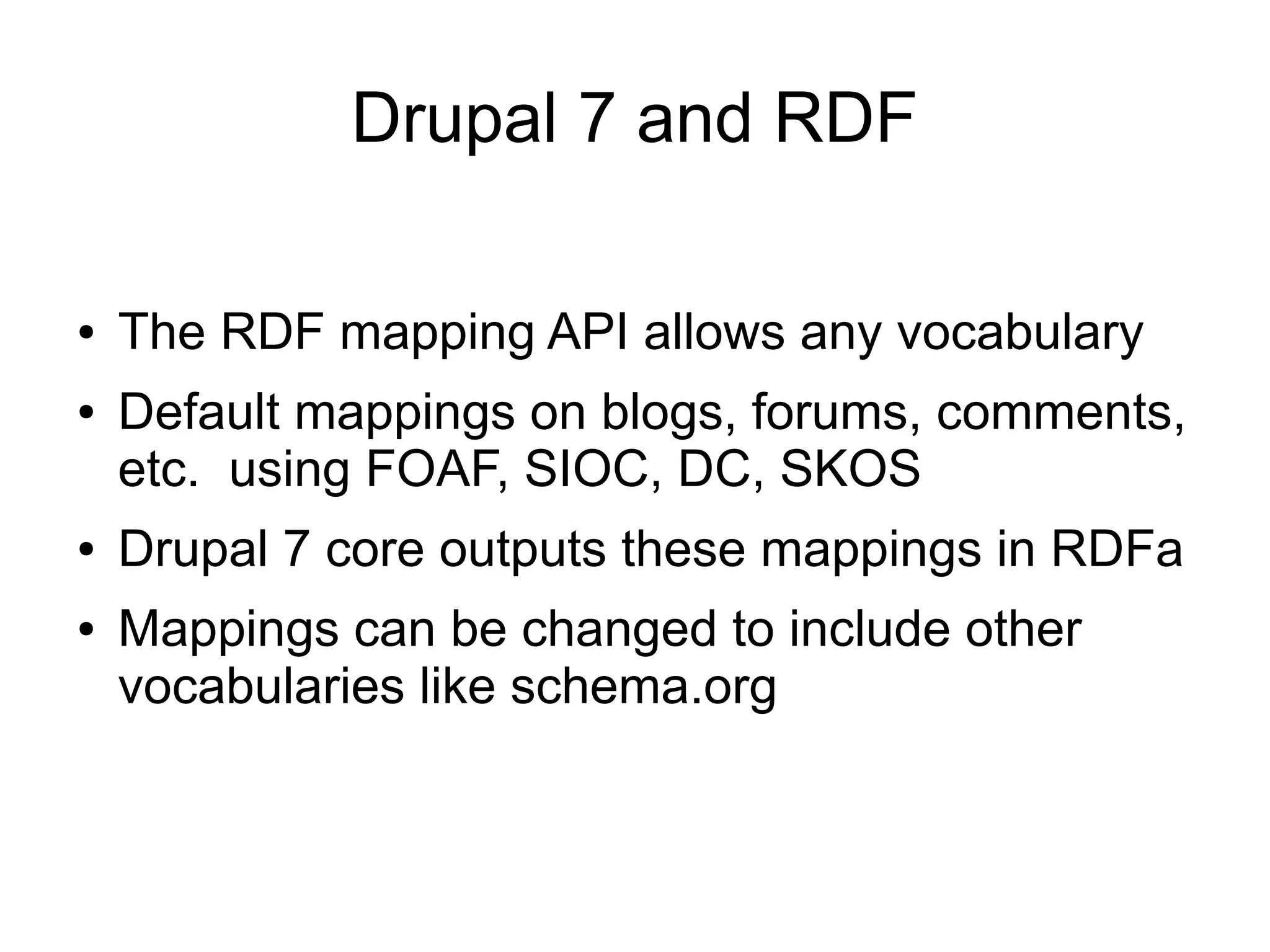
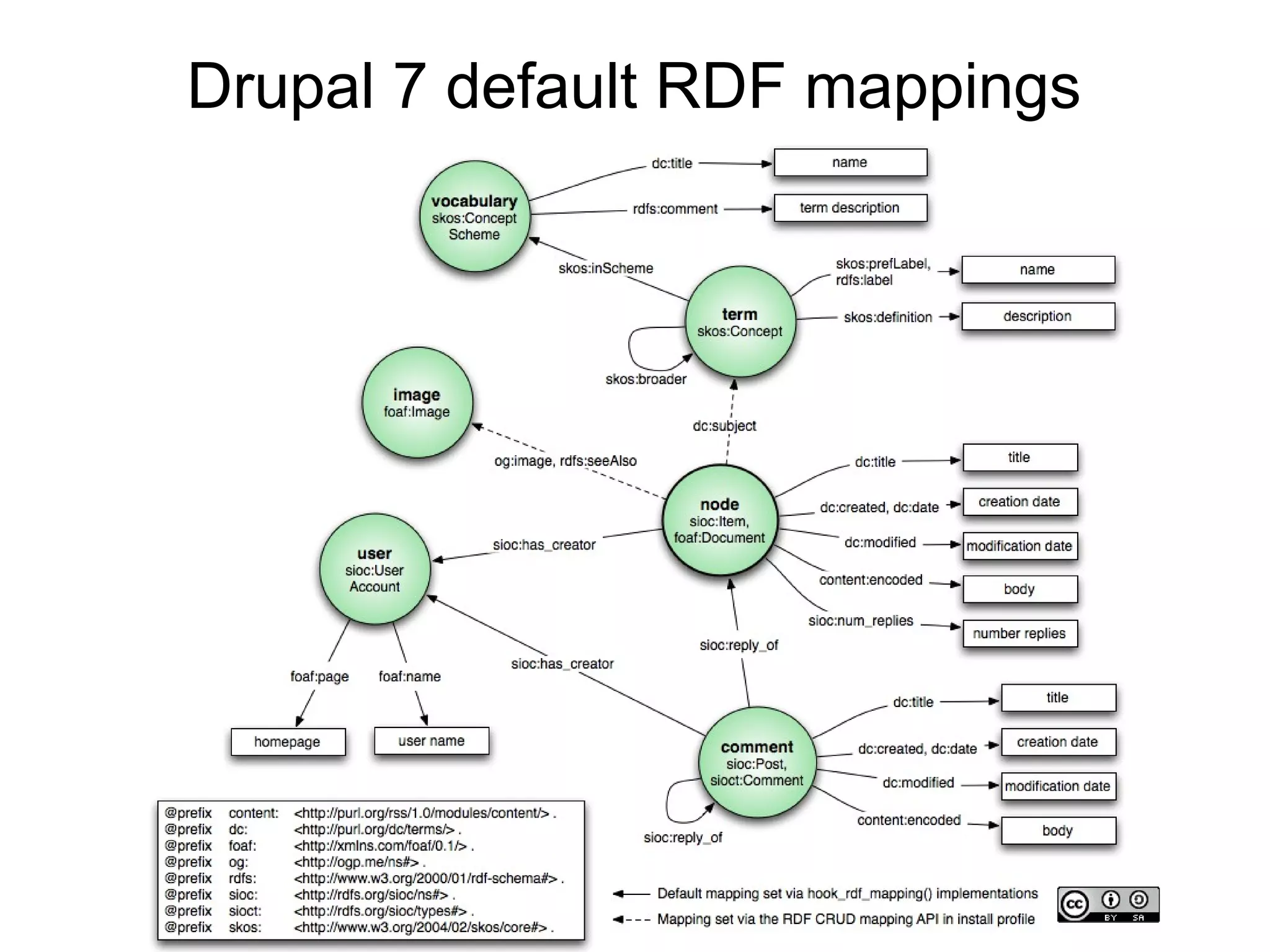
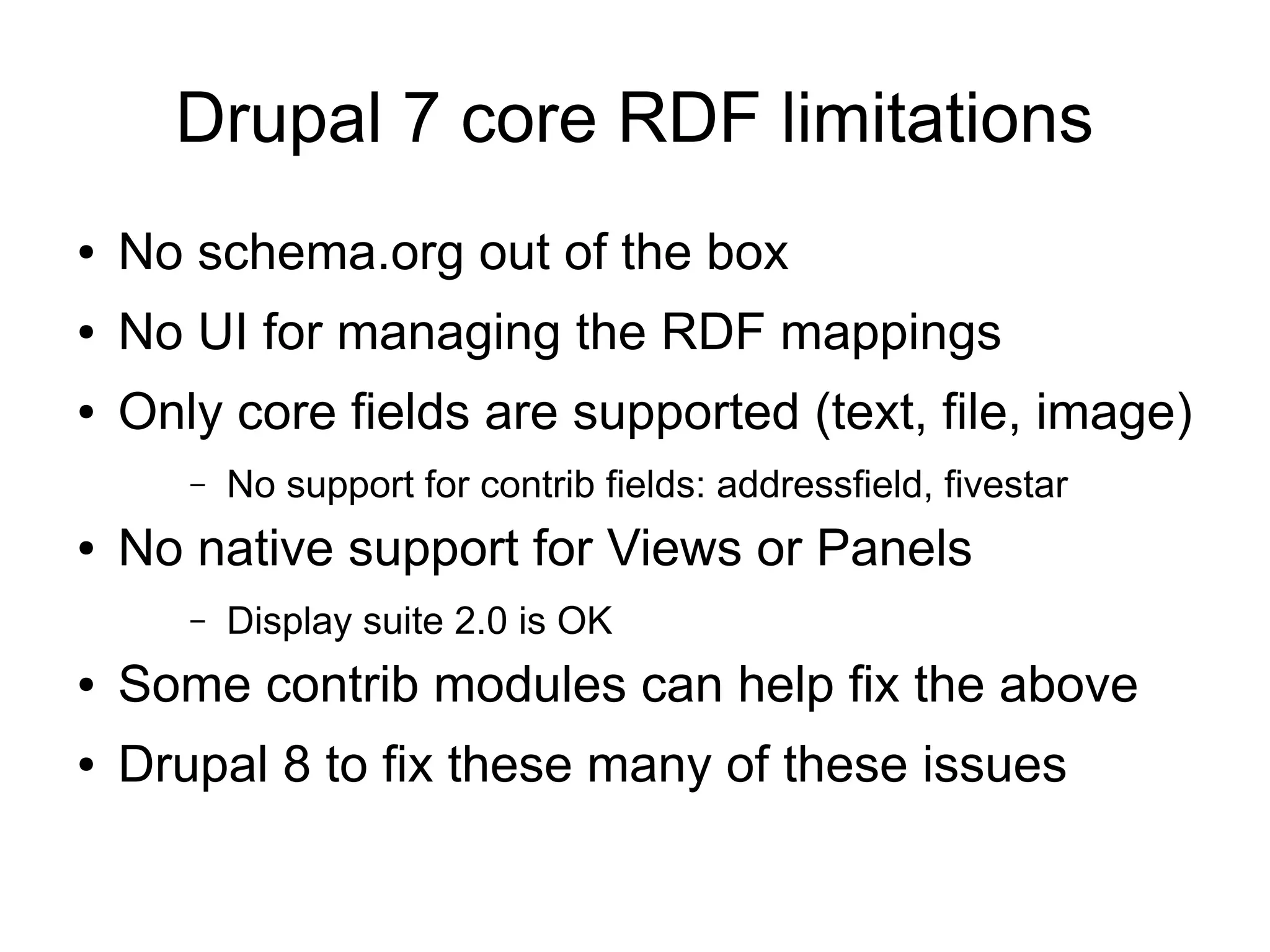
This document summarizes a presentation about using semantic web technologies like the Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Linked Data with Drupal 7. It discusses how Drupal 7 maps content types and fields to RDF vocabularies by default and how additional modules can add features like mapping to Schema.org and exposing SPARQL and JSON-LD endpoints. The presentation also covers how Drupal integrates with the larger Semantic Web through technologies like Linked Open Data.




















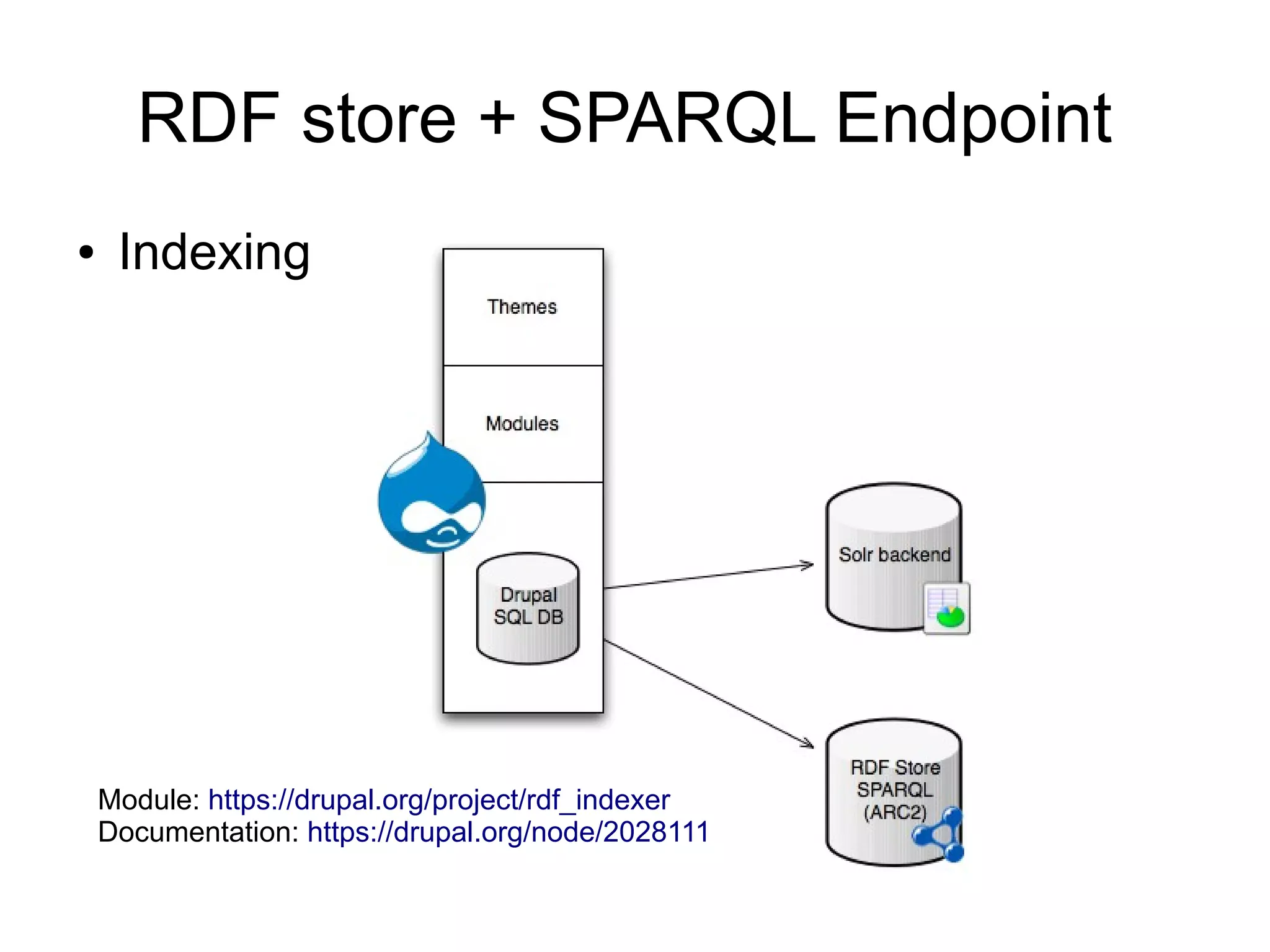


![RDF store + SPARQL Endpoint
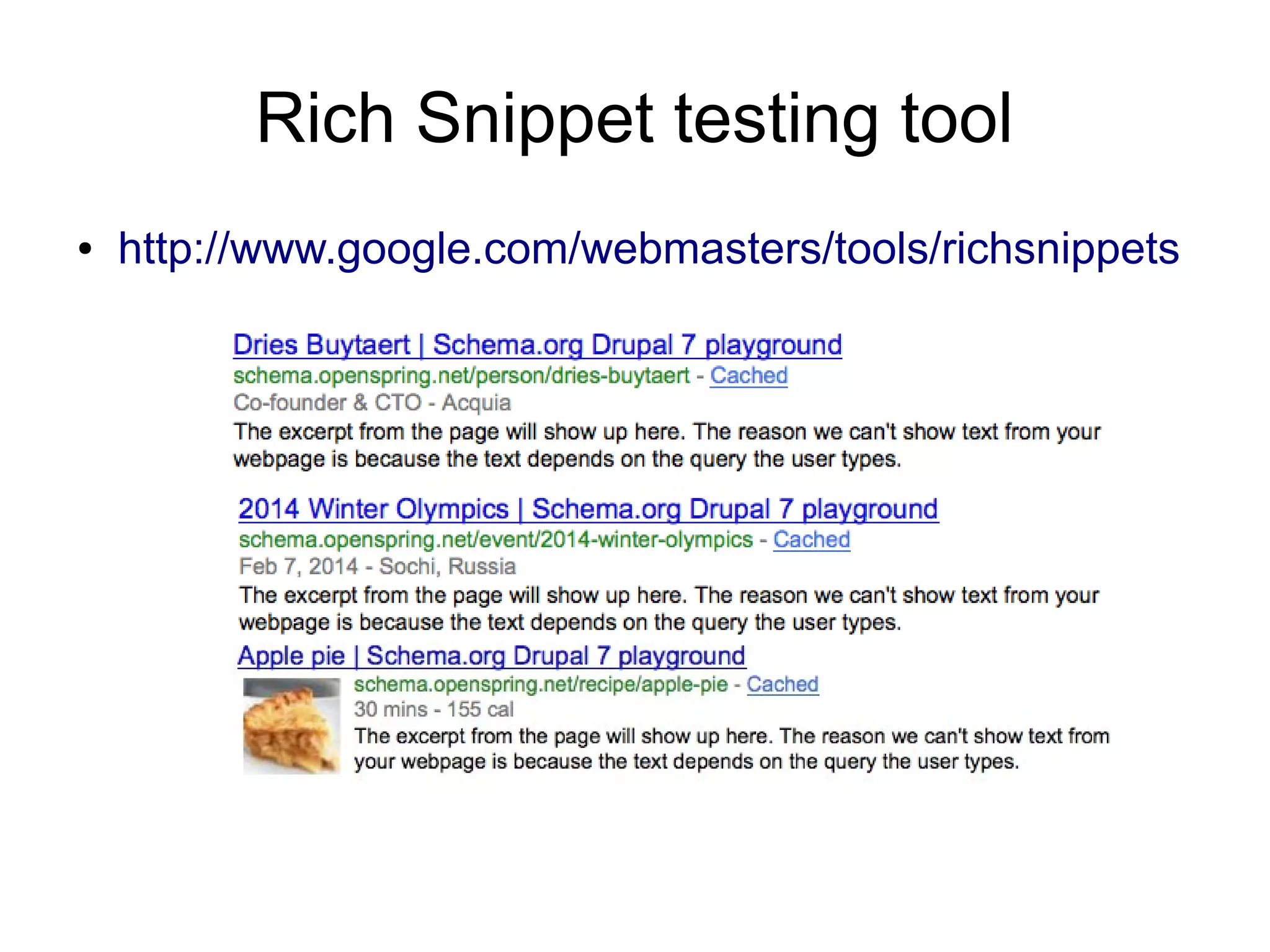
● Example: popular tags by comments
– http://openspring.net/sparql
PREFIX dc: <http://purl.org/dc/terms/>
PREFIX sioc: <http://rdfs.org/sioc/ns#>
SELECT ?tag sum(?replies) as ?total_replies
WHERE {
?post sioc:num_replies ?replies.
?post dc:subject [ rdfs:label ?tag ] .
}
GROUP BY ?tag
ORDER BY DESC(?total_replies)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slidessemanticwebdrupalesipjune13-130628134750-phpapp01/75/Drupal-and-the-Semantic-Web-ESIP-Webinar-49-2048.jpg)