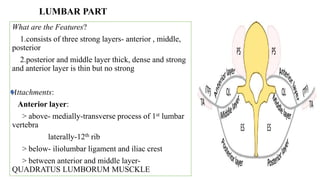
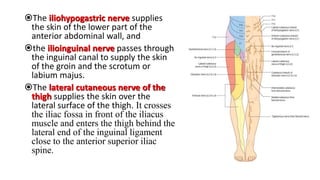
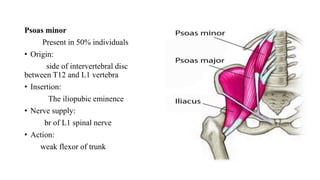
This document provides information on the thoracolumbar fascia, lumbar plexus, and back muscles. It describes the thoracolumbar fascia as a large sheet of connective tissue made of thoracic and lumbar parts that binds muscles to the spinal column. It also details the layers, attachments and clinical correlations of the lumbar fascia. Regarding the lumbar plexus, it lists the nerves that emerge from the lateral side of the psoas major muscle. Finally, it outlines the origins, insertions, innervations and actions of four back muscles - psoas major, psoas minor, iliacus and quadratus lumborum.