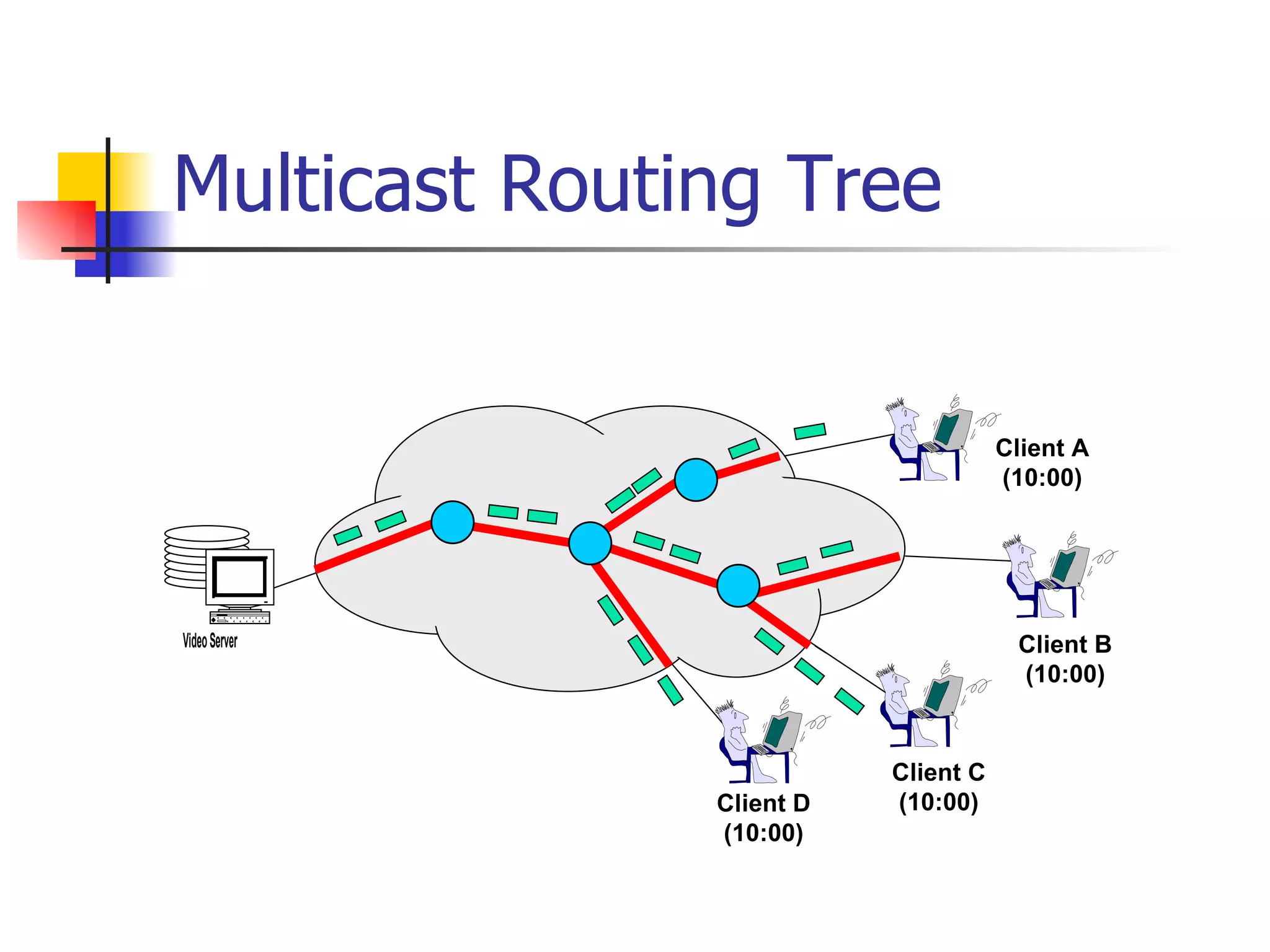
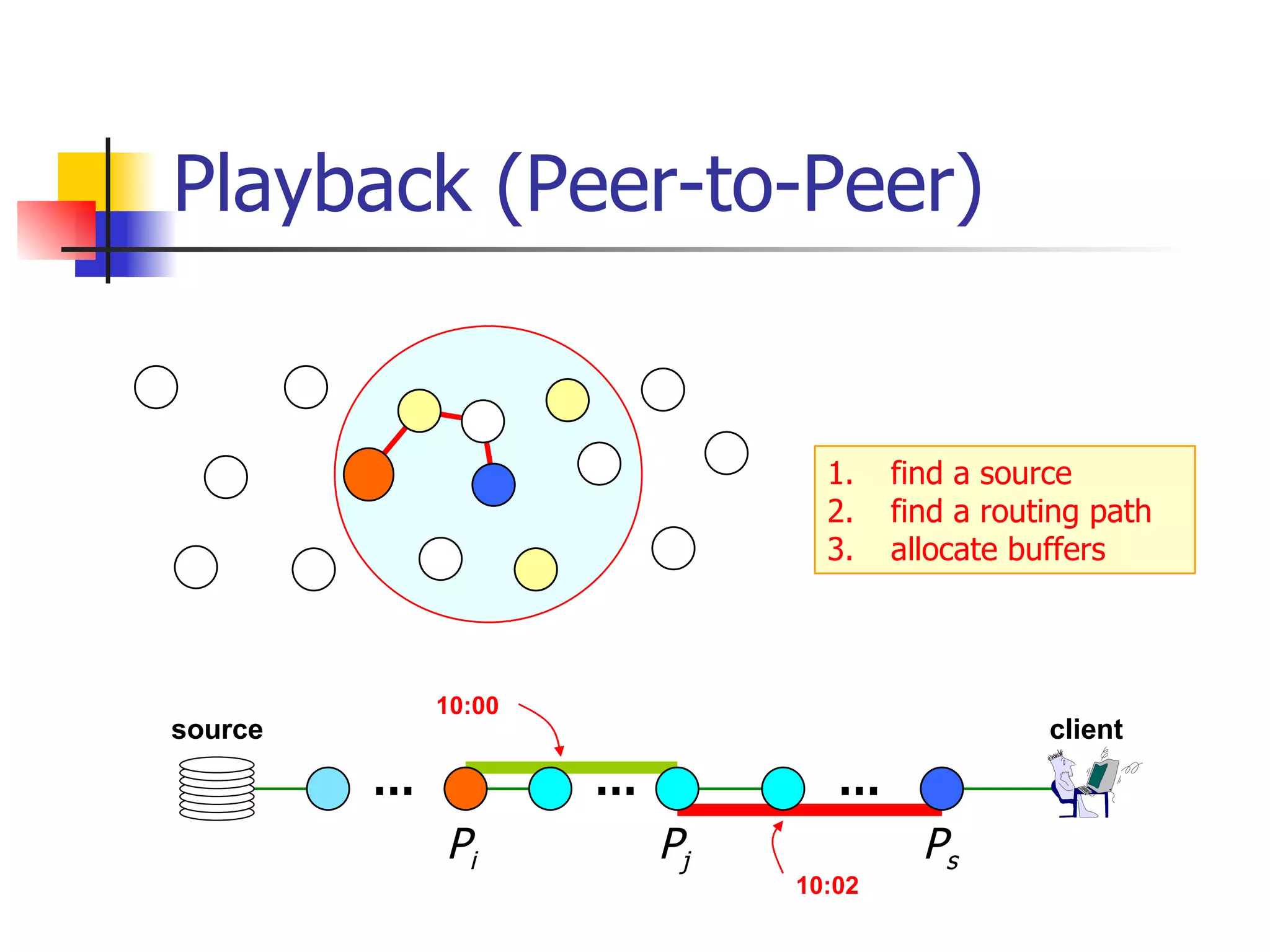
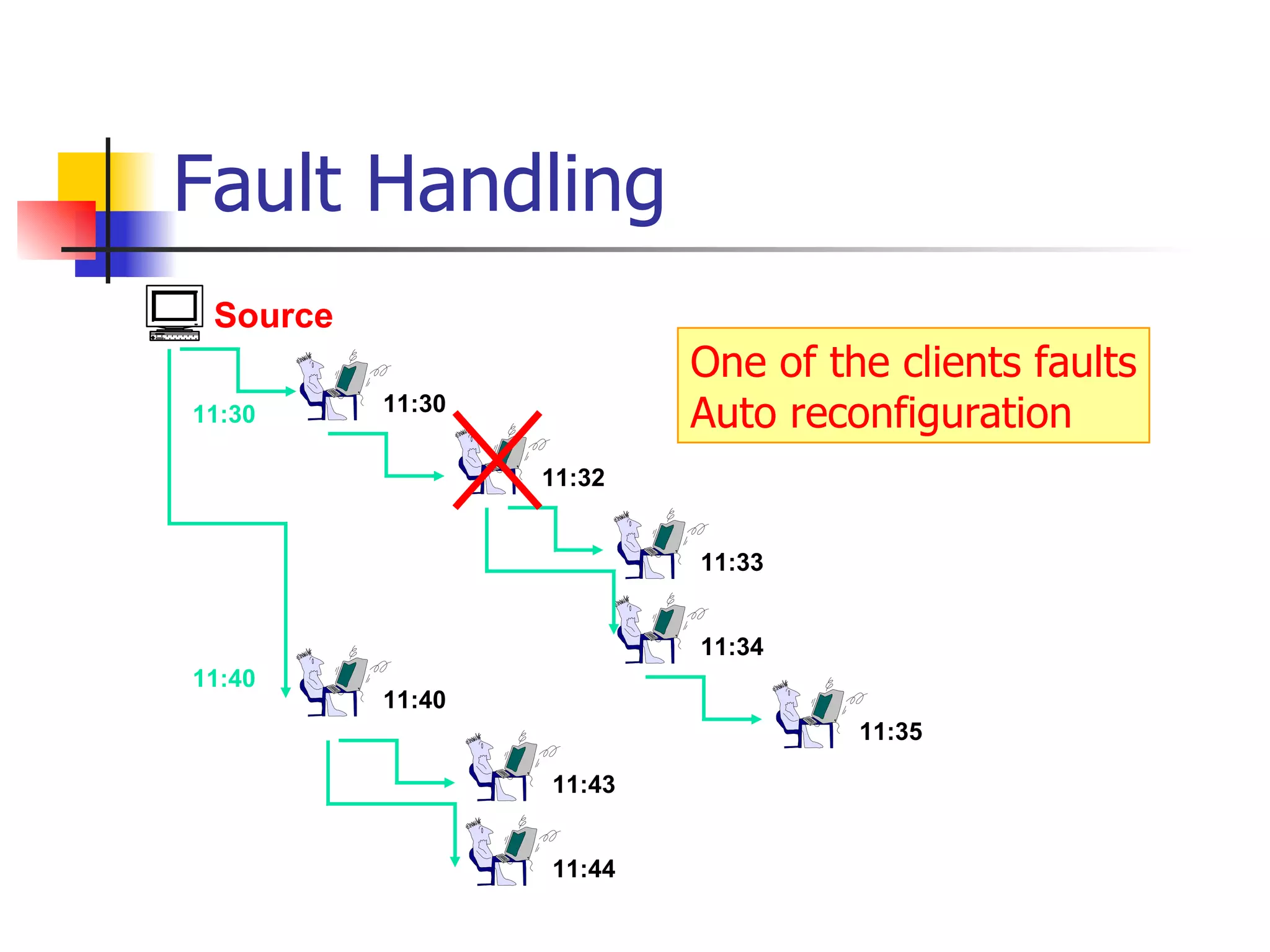
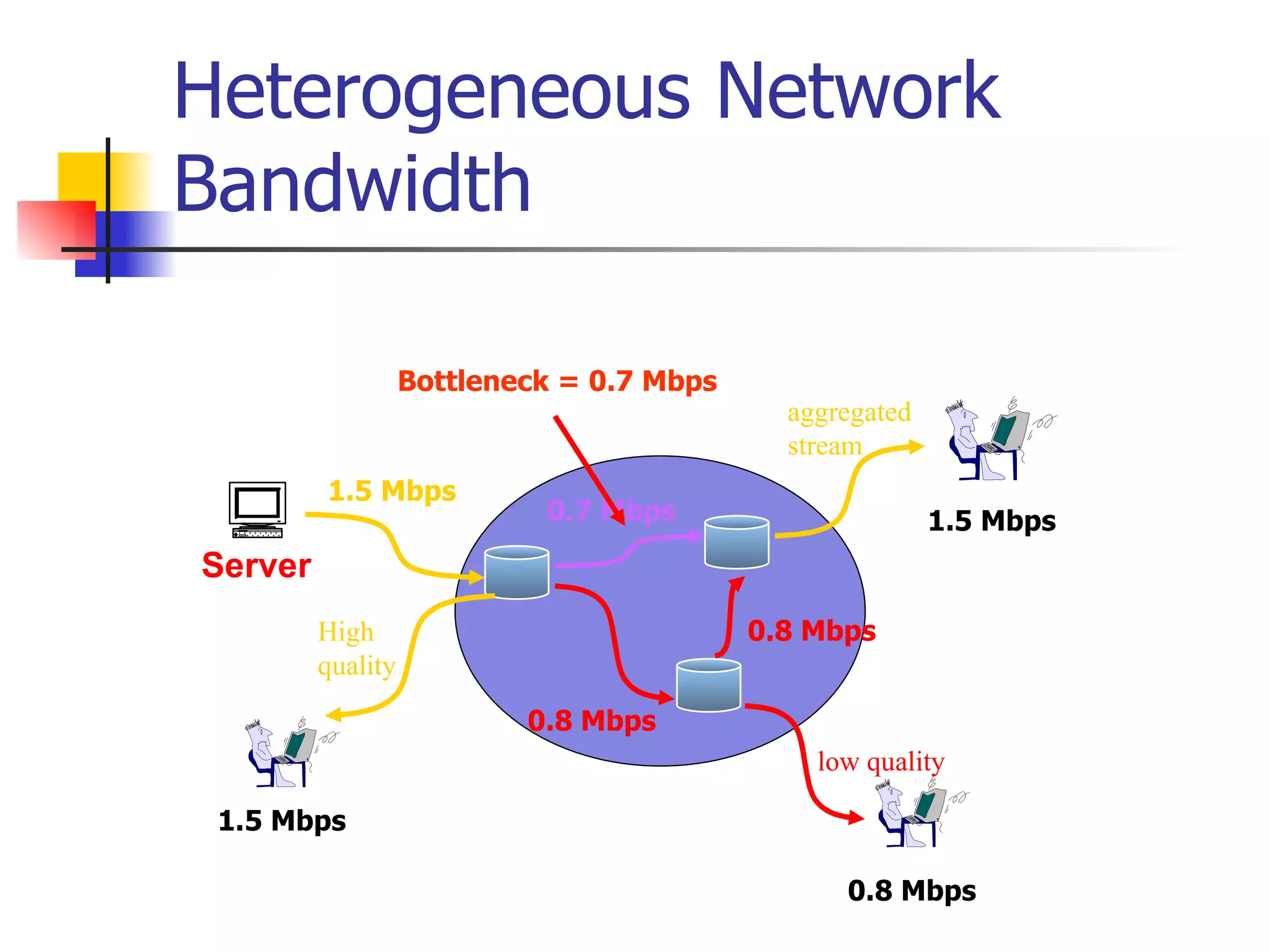
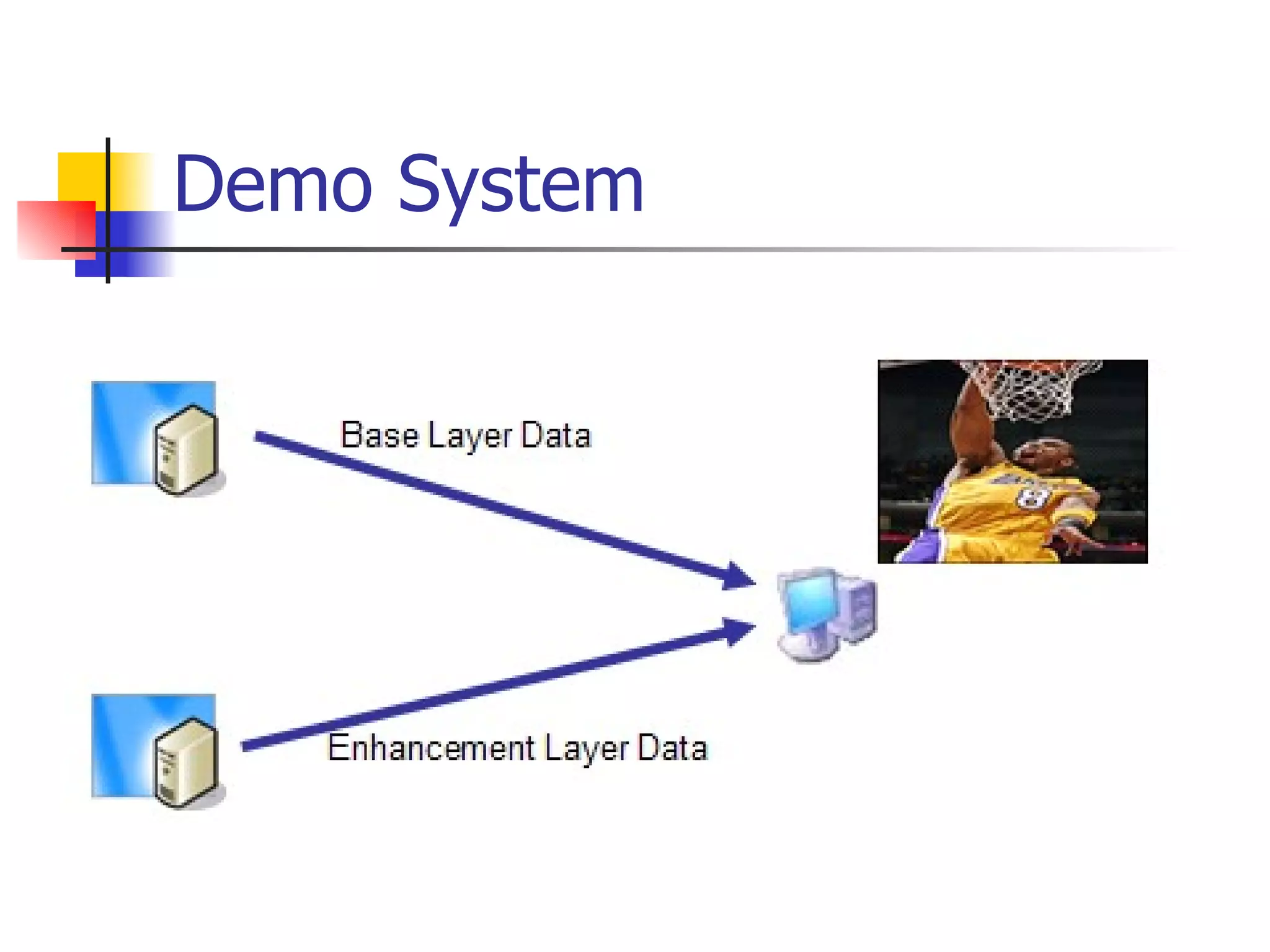
The document discusses the development of an overlay multicast infrastructure for live and on-demand video streaming to address limitations of traditional multicast approaches. It outlines previous work on peer-to-peer streaming video delivery and multicast platforms for layered videos. The proposed approach involves using an overlay network and peer-to-peer techniques to construct multicast trees and cache video segments for streaming live and on-demand video with improved performance and reliability.