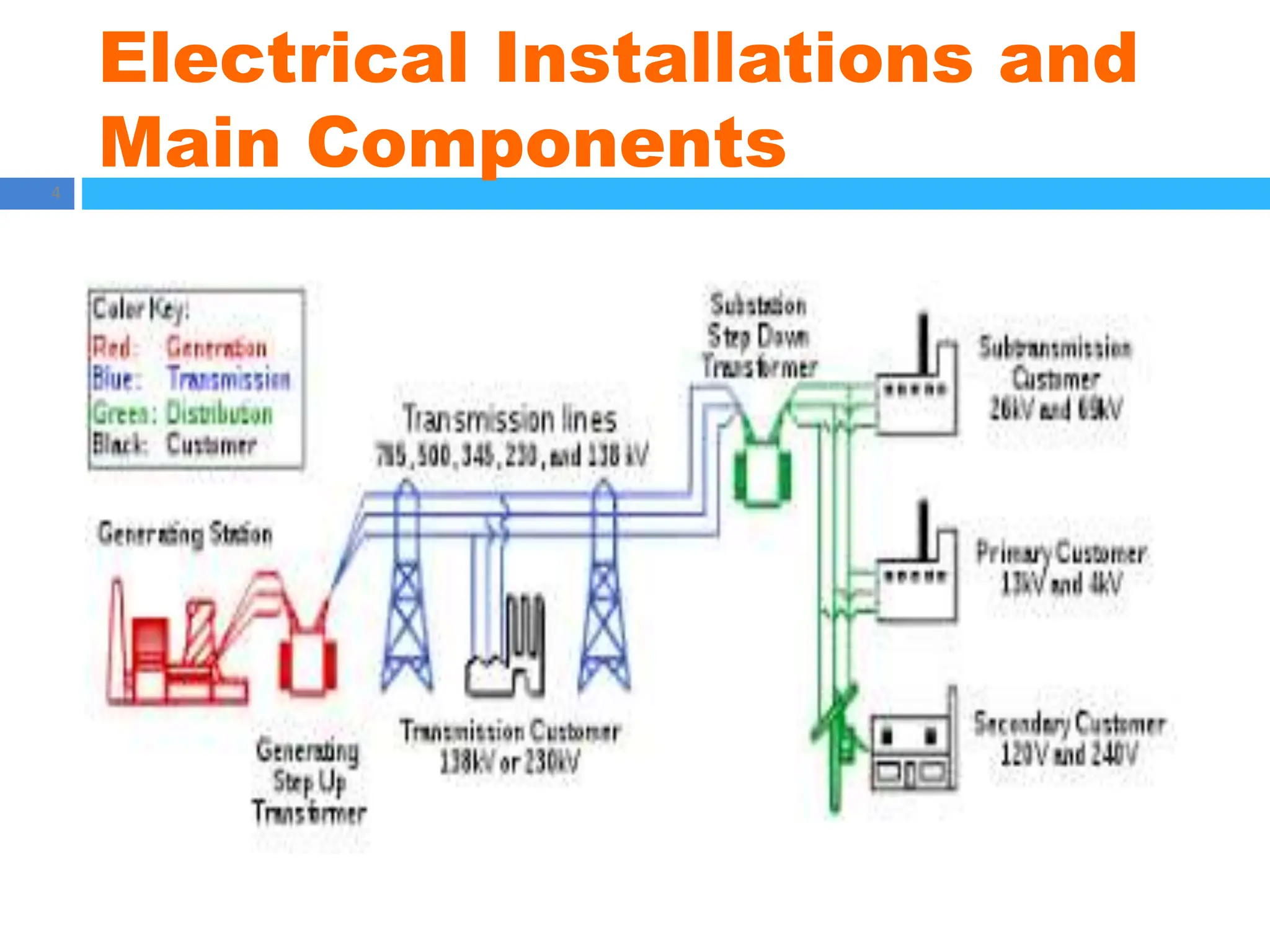
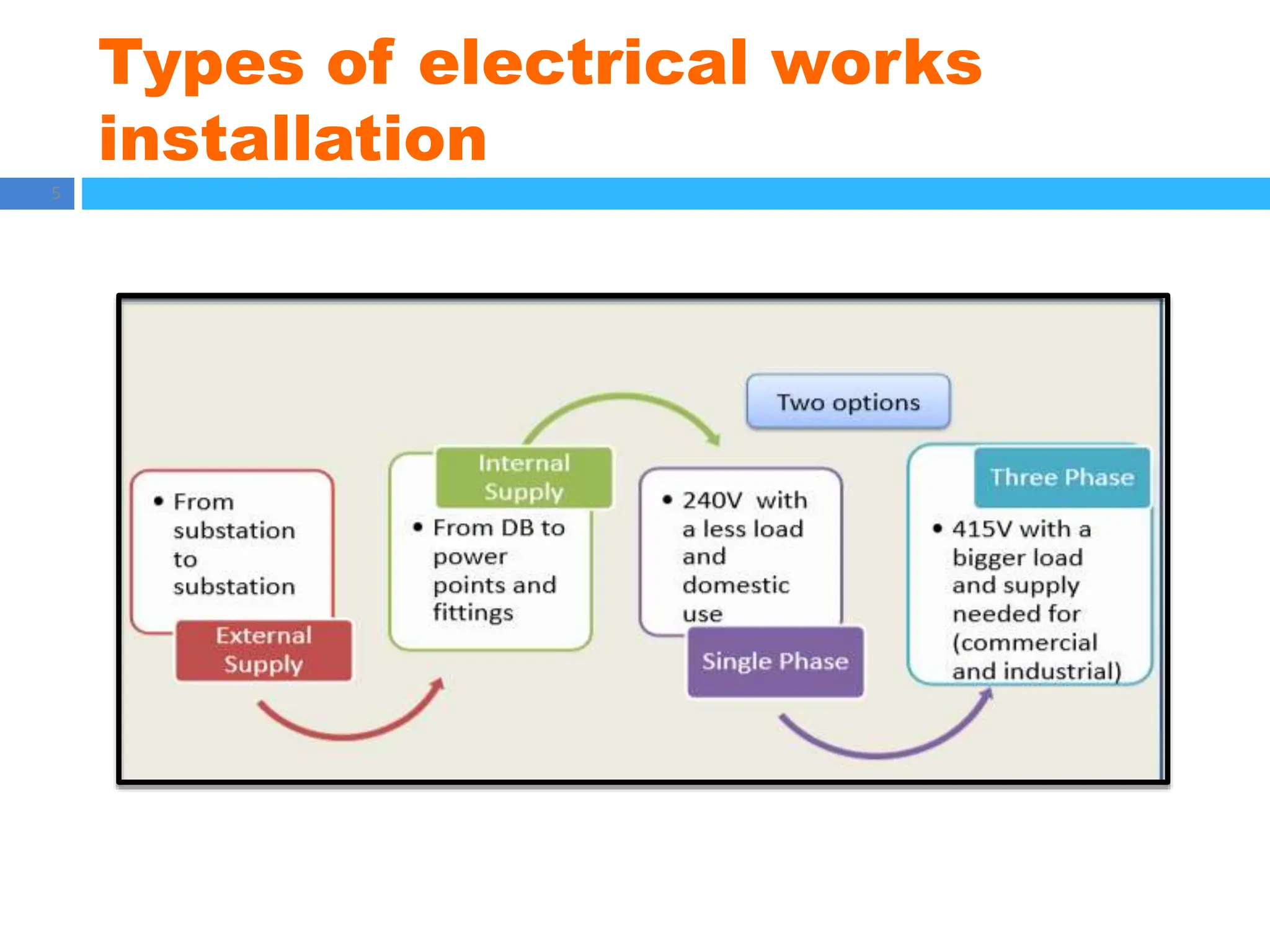
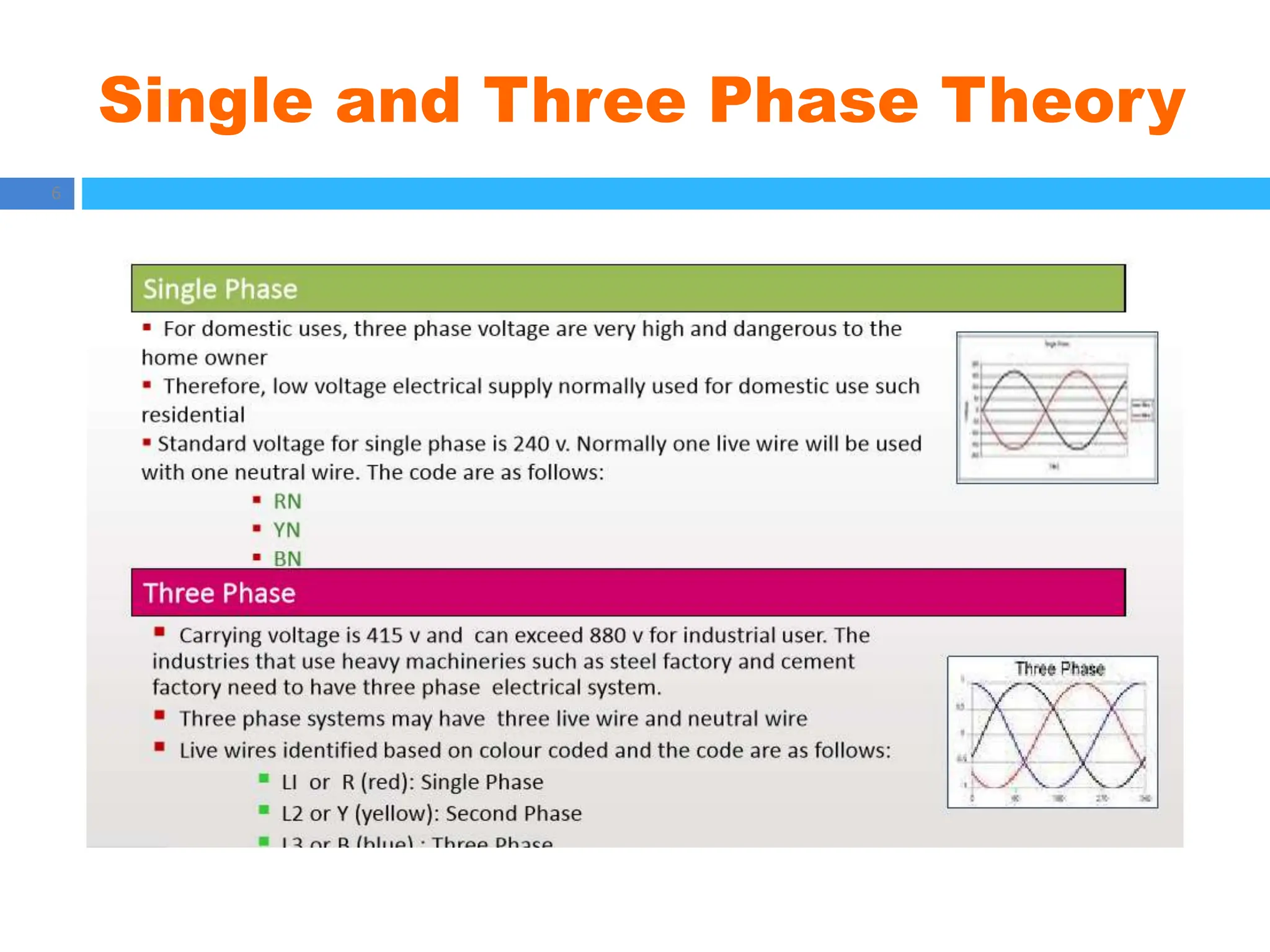
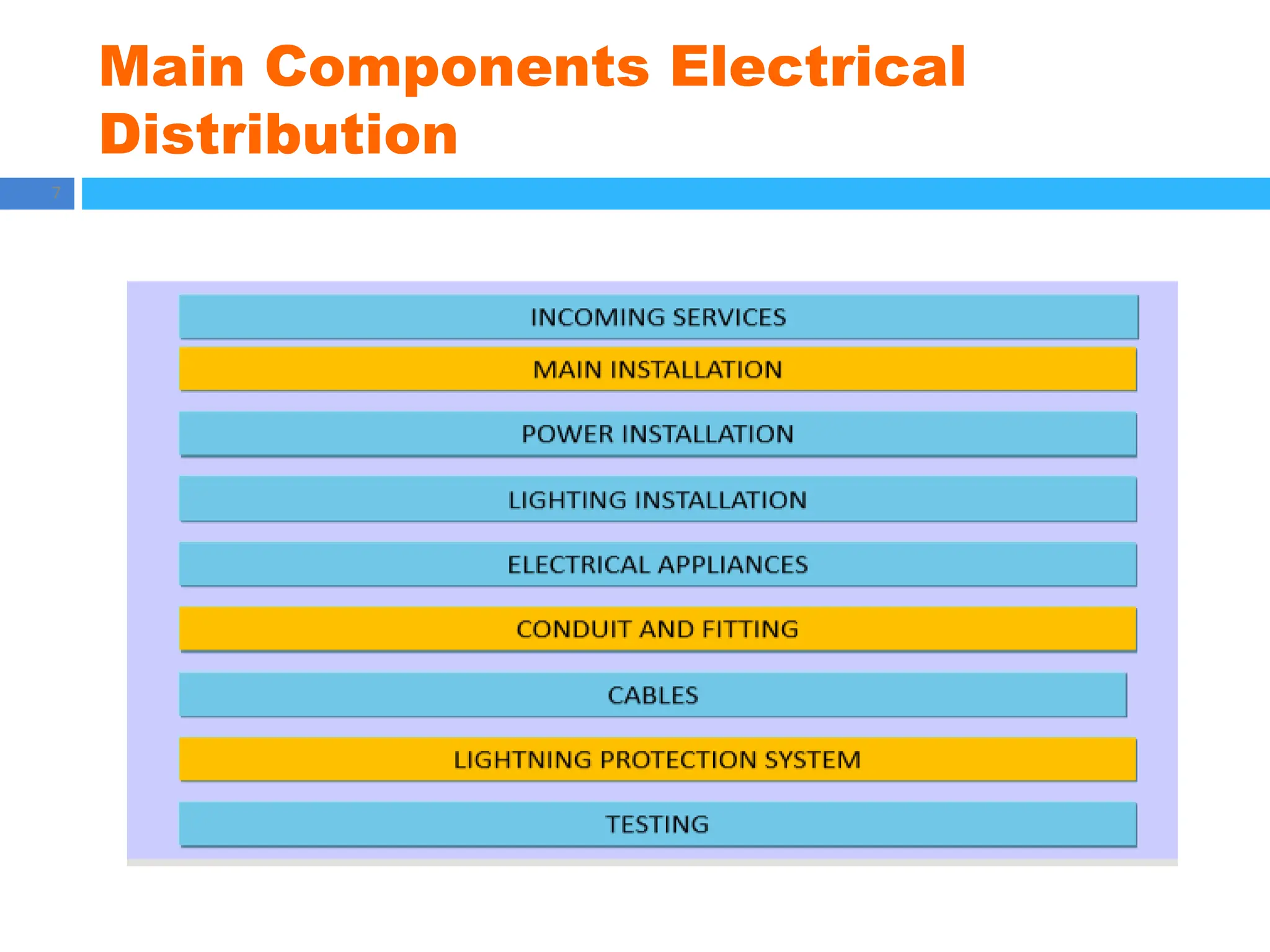
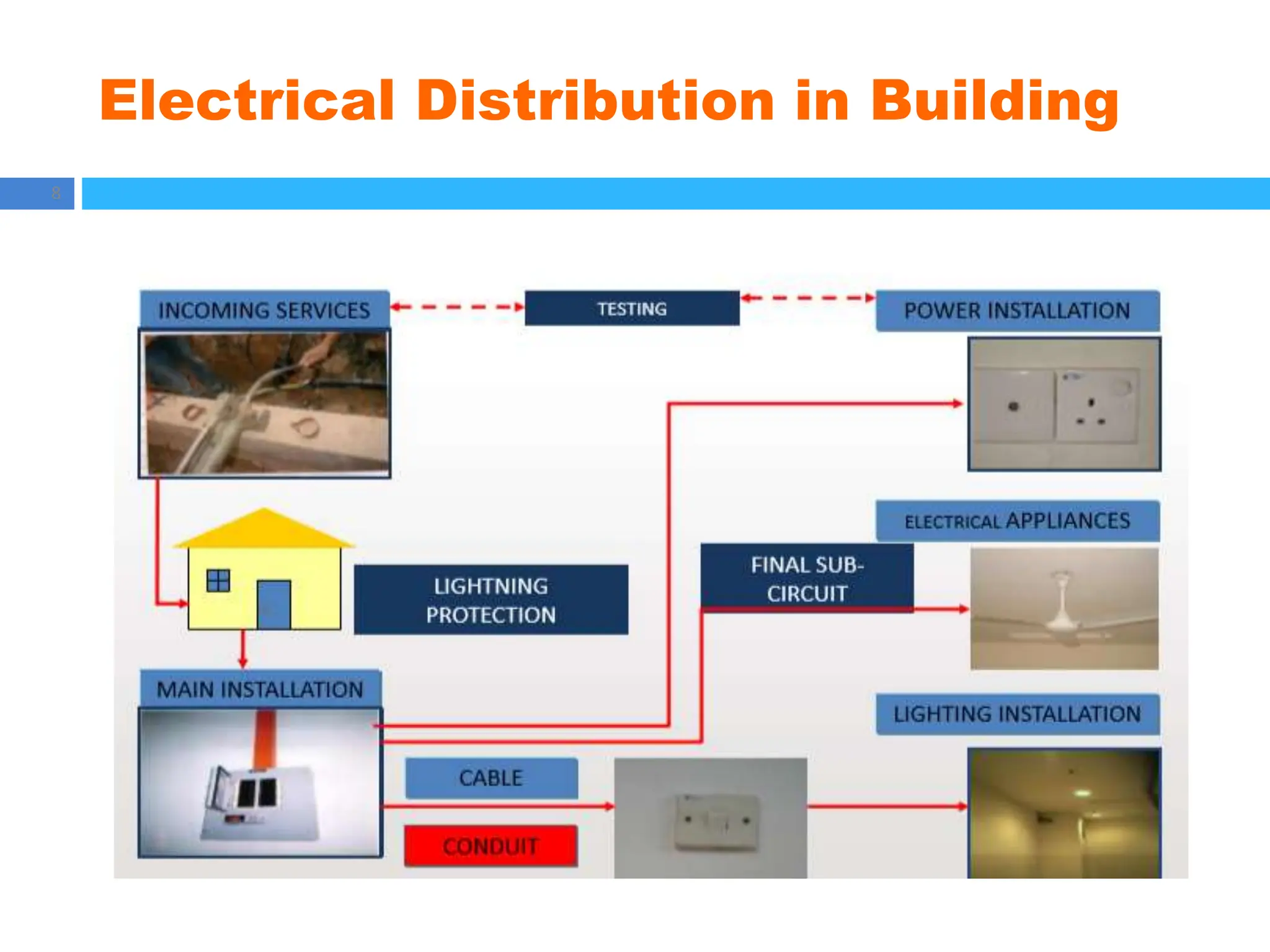
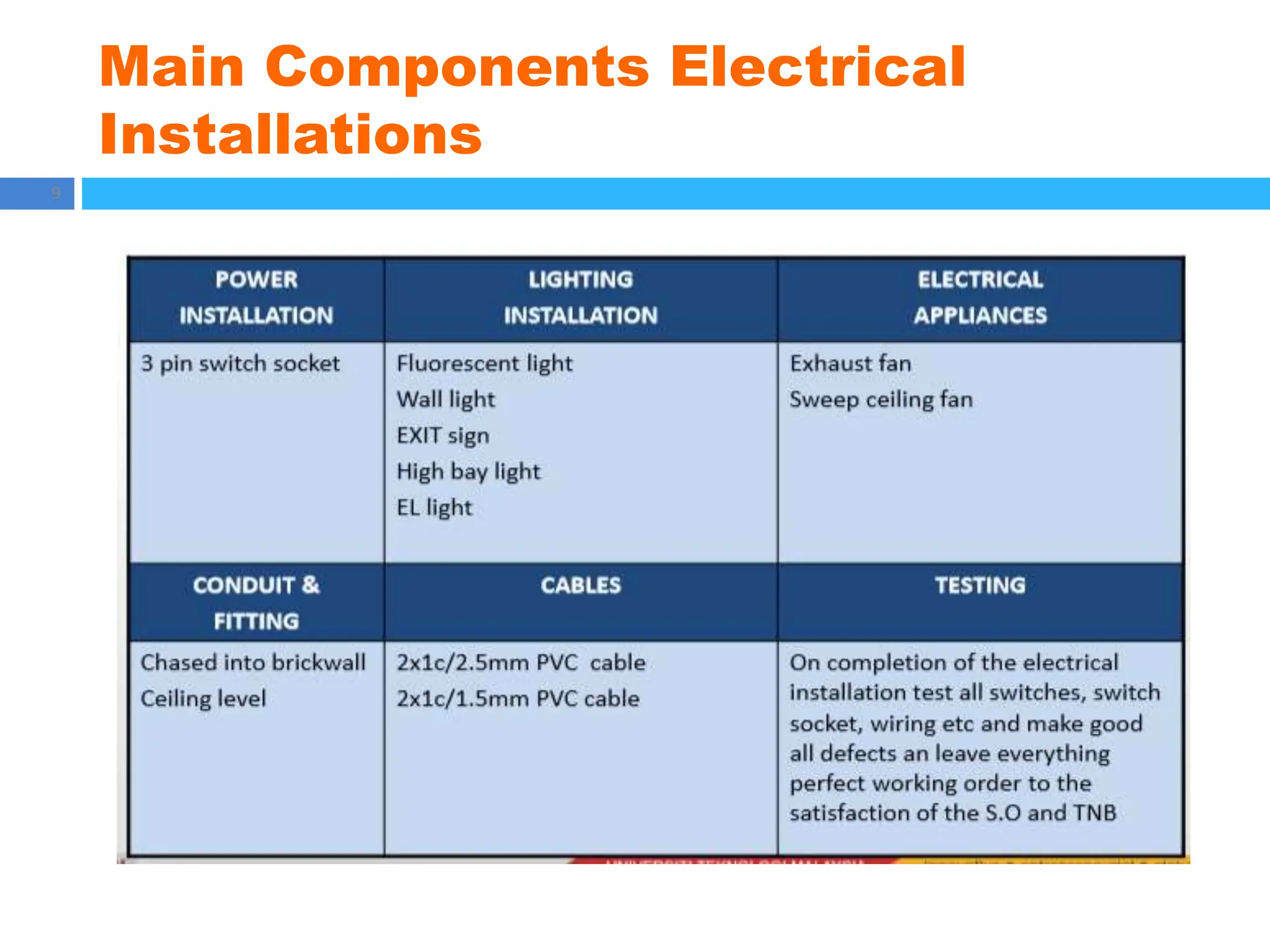
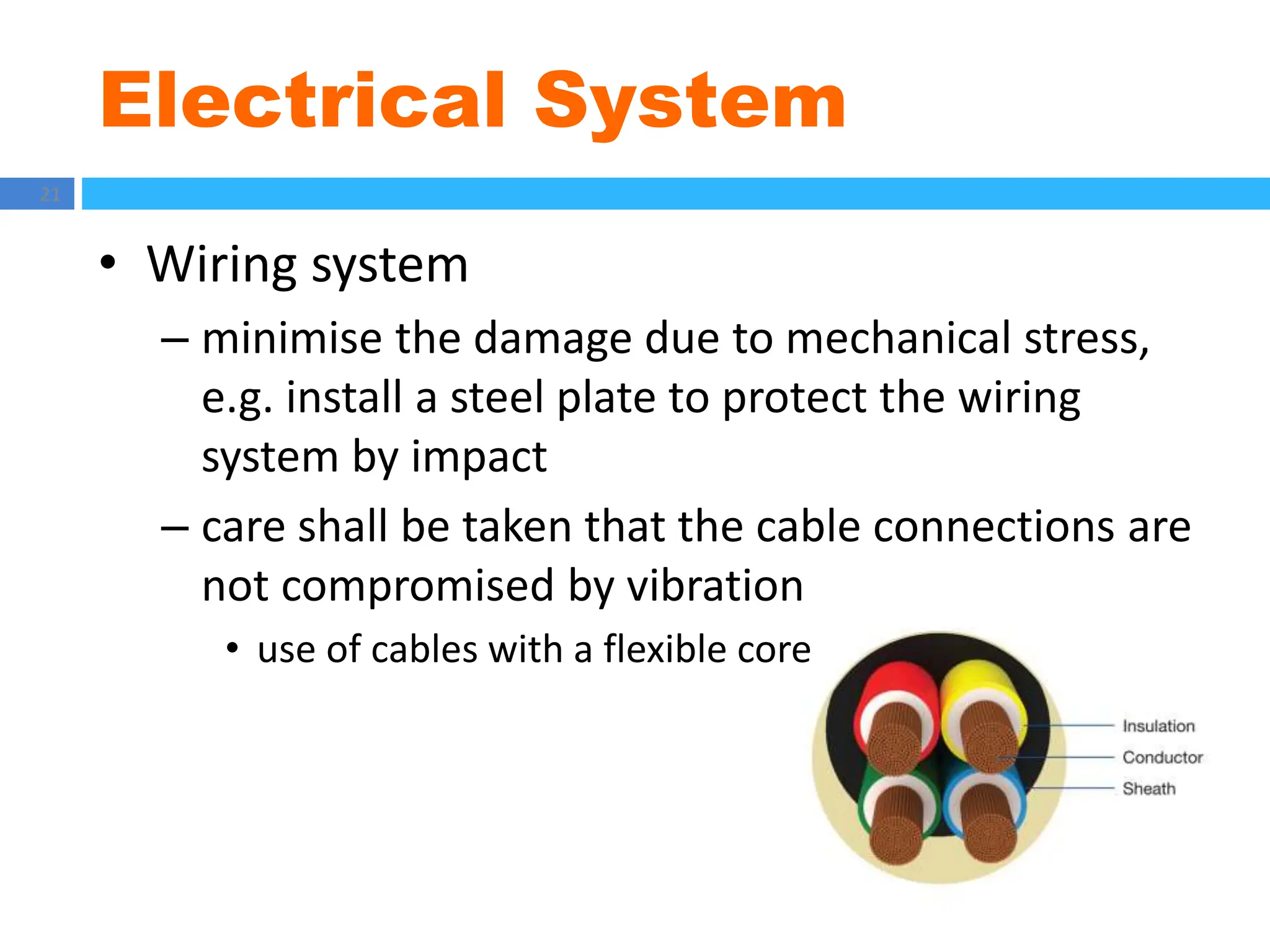
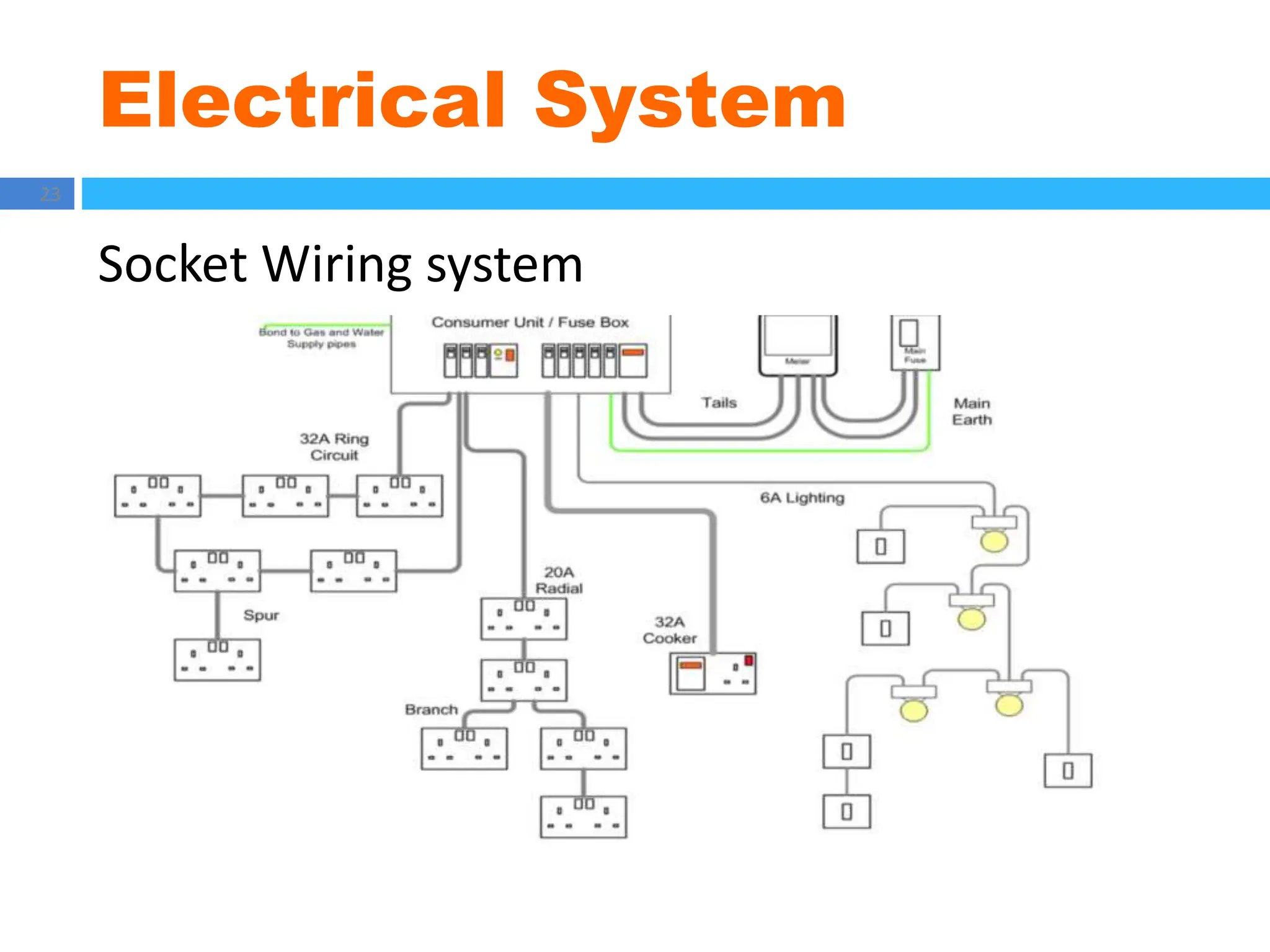
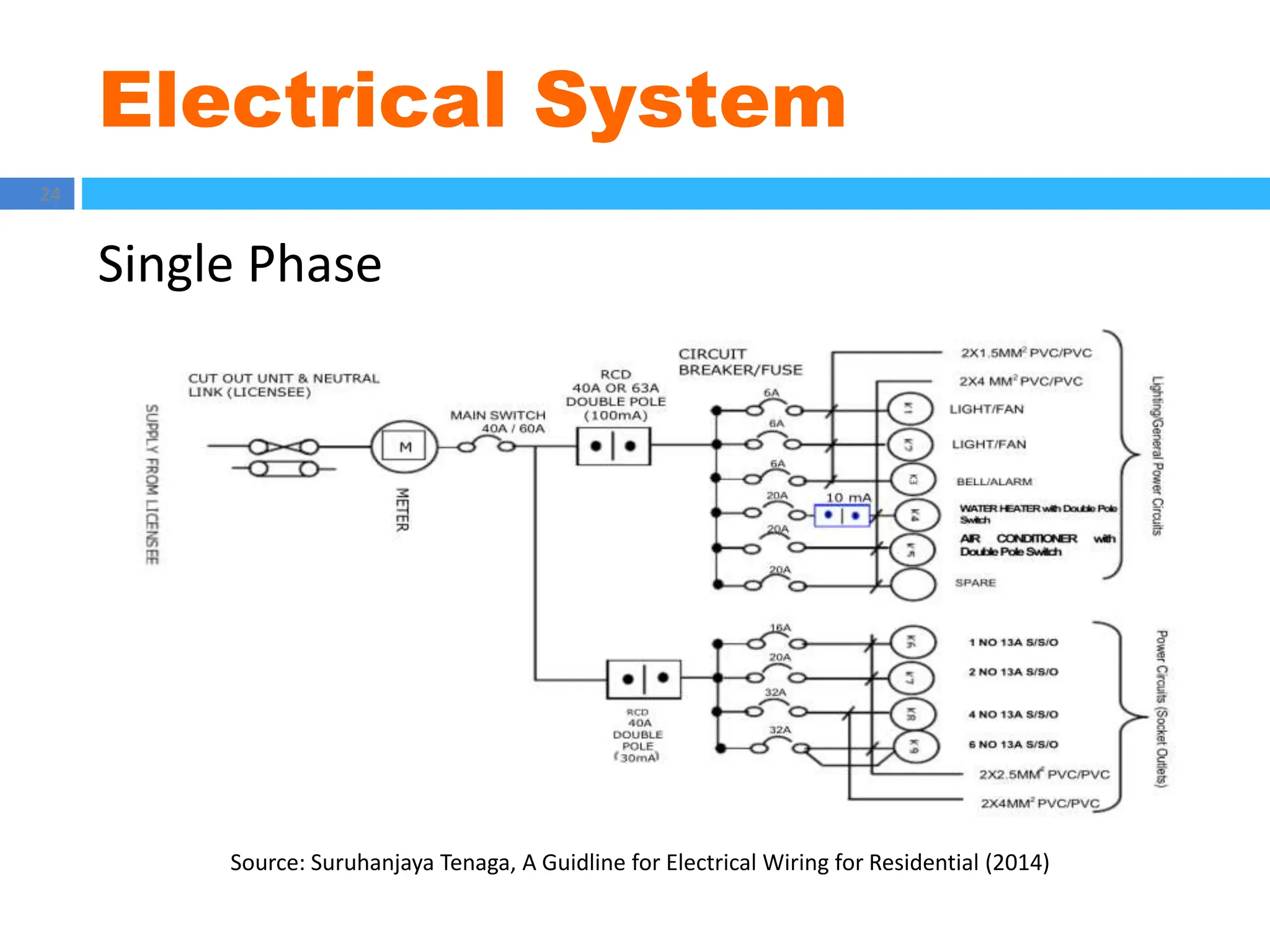
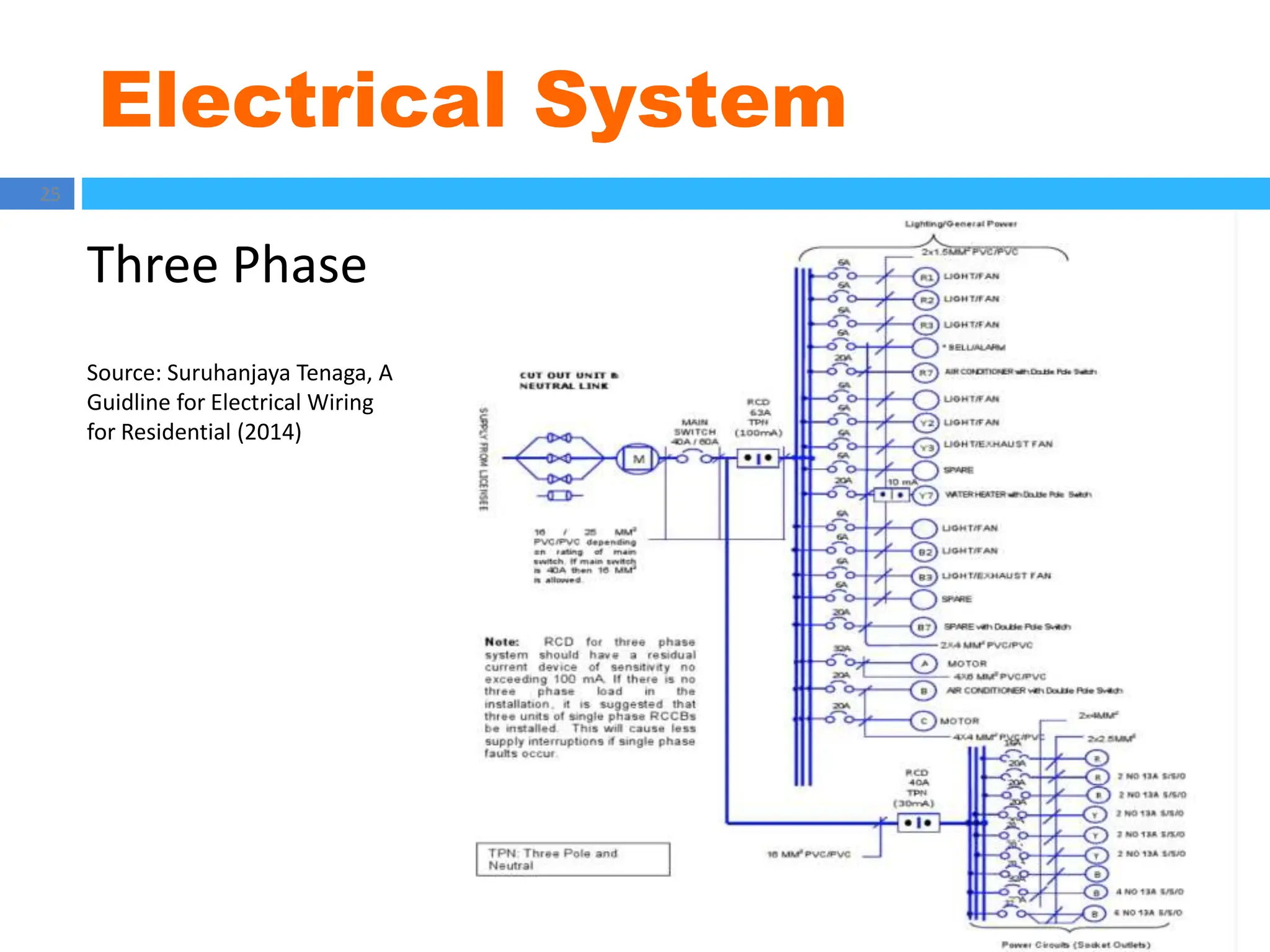
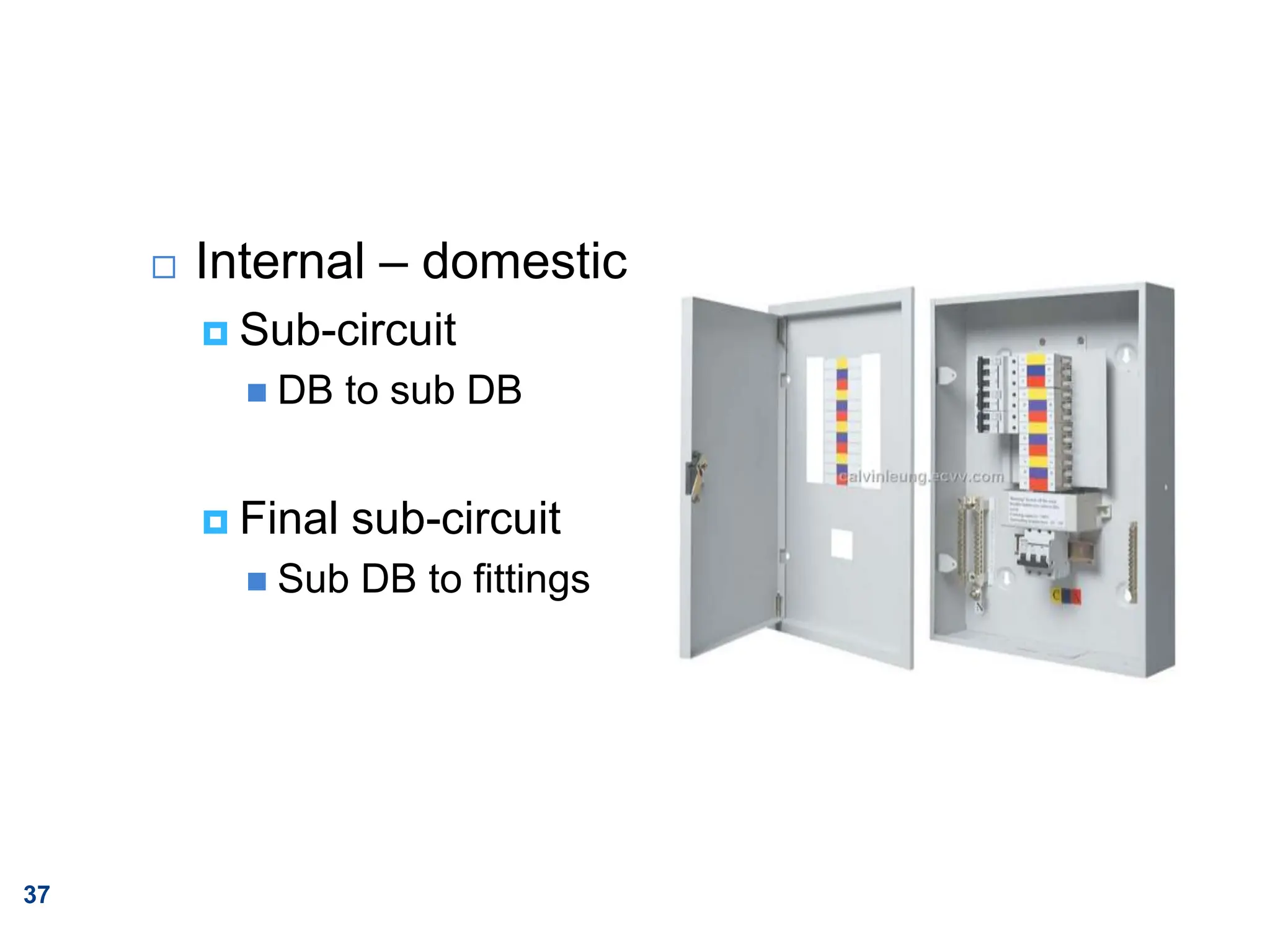
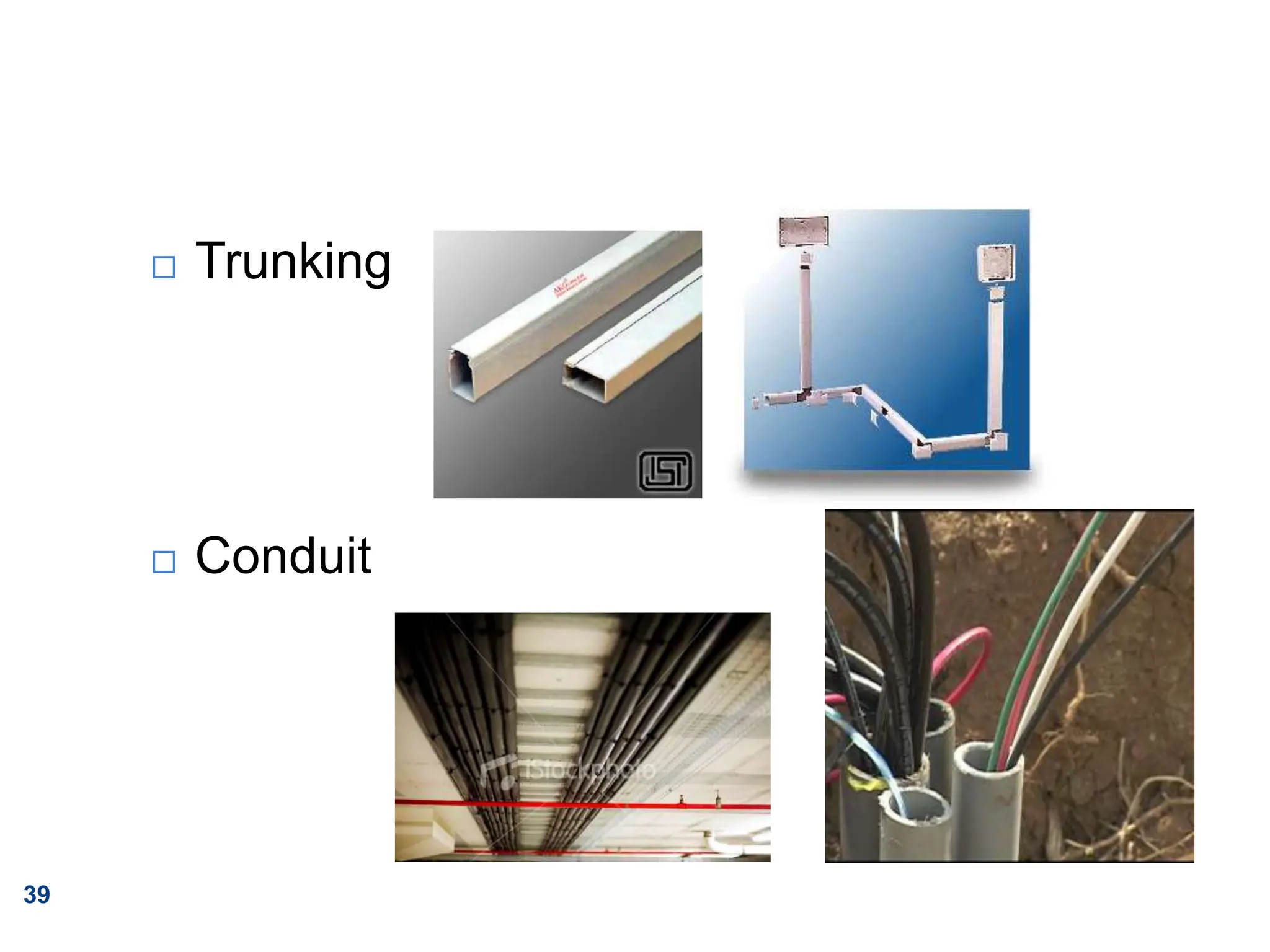
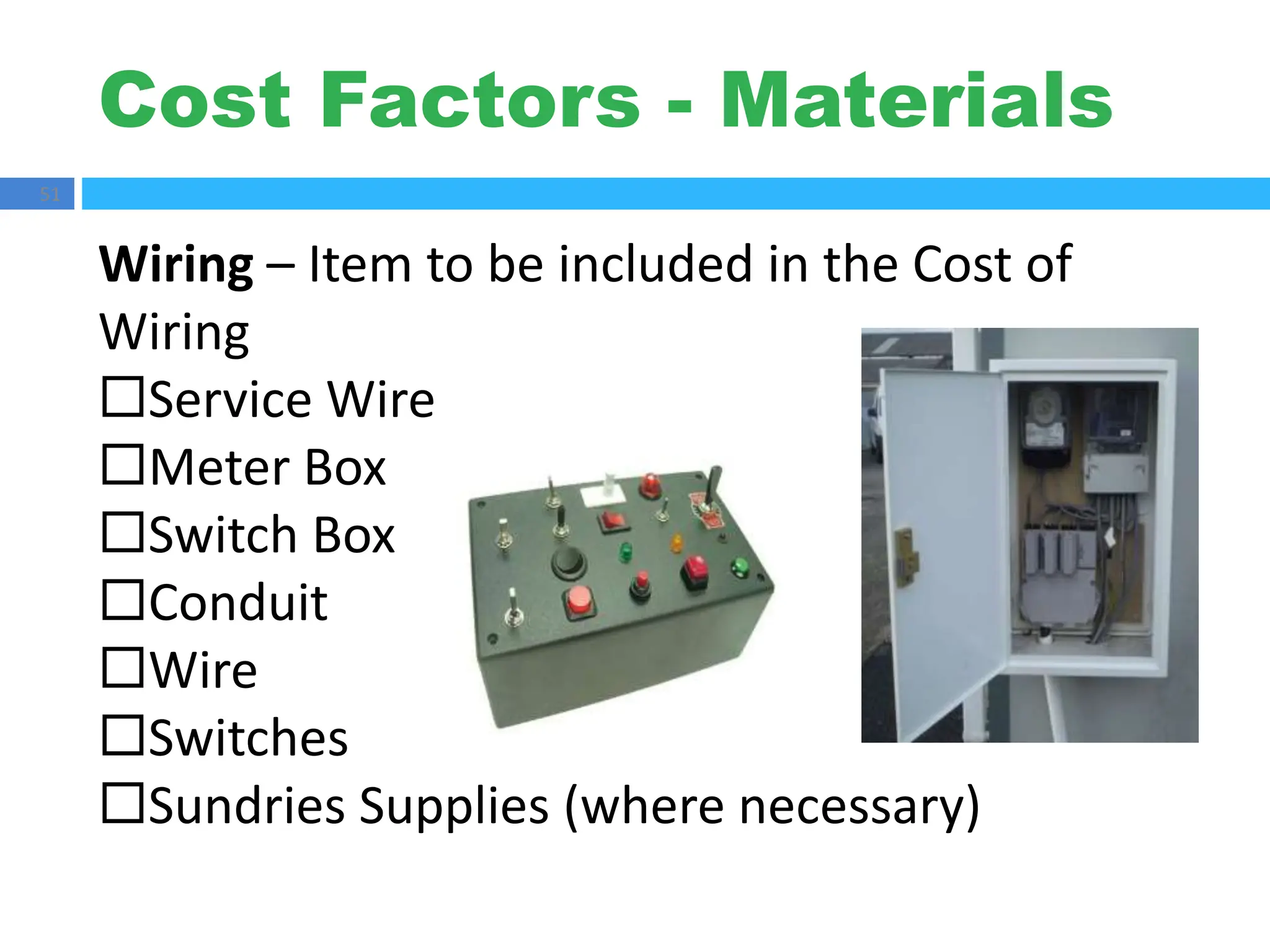
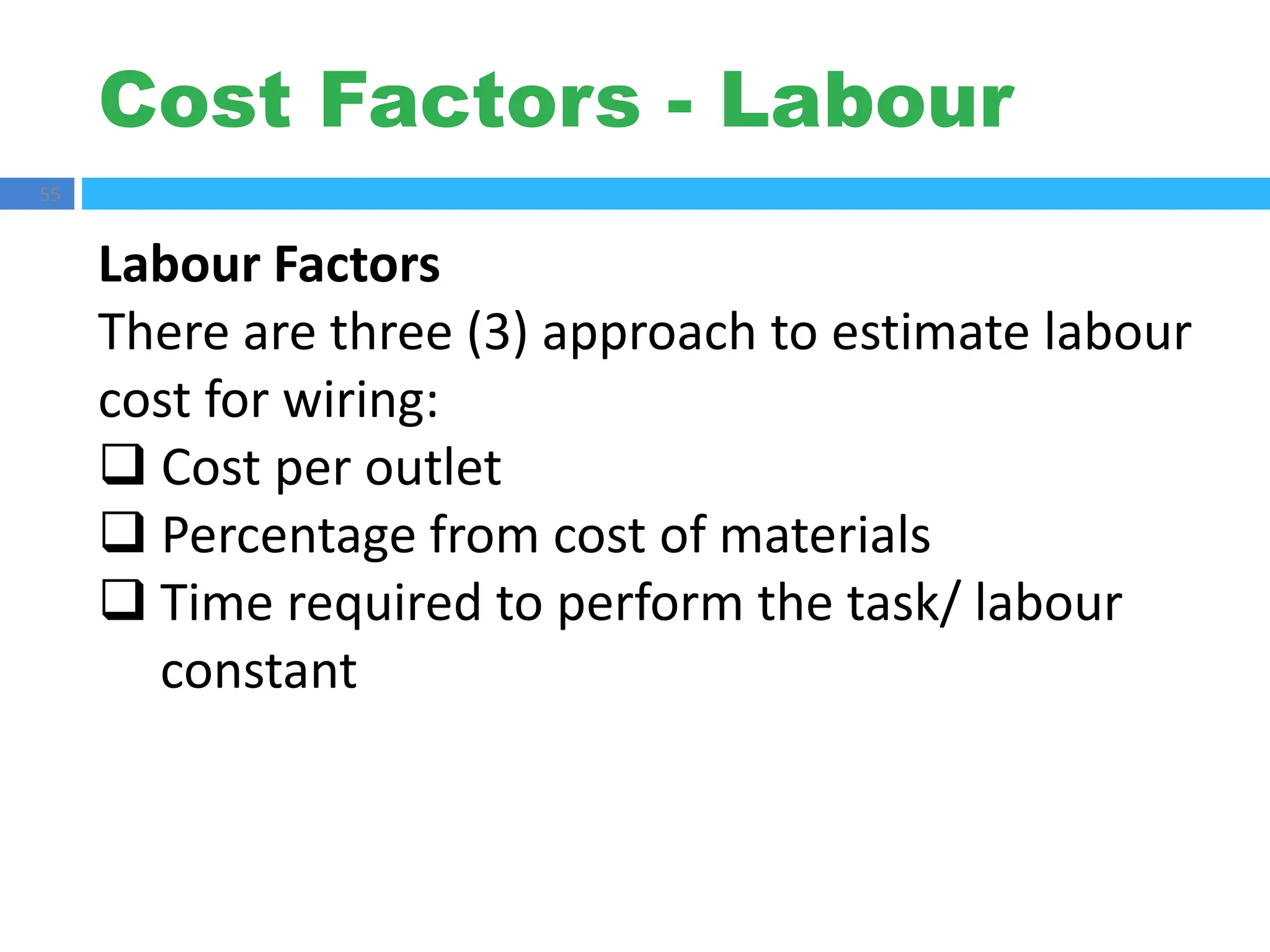
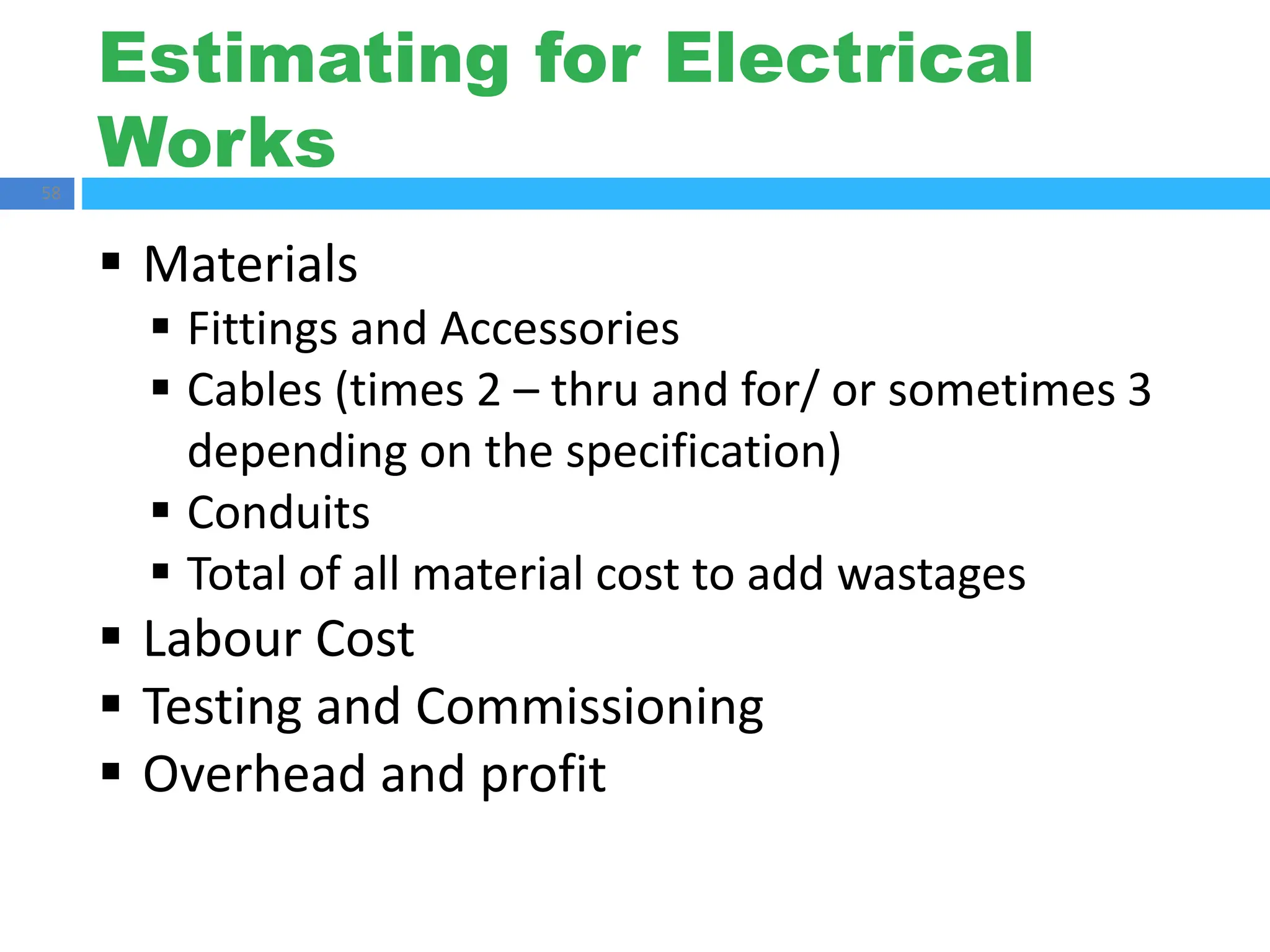
The document outlines principles of estimating for electrical works, focusing on installation types, system components, and safety measures. It emphasizes the importance of accurate measurement for cost control, detailing various factors affecting material and labor costs. Additionally, it provides guidelines for lighting system design and considerations for electrical installations.