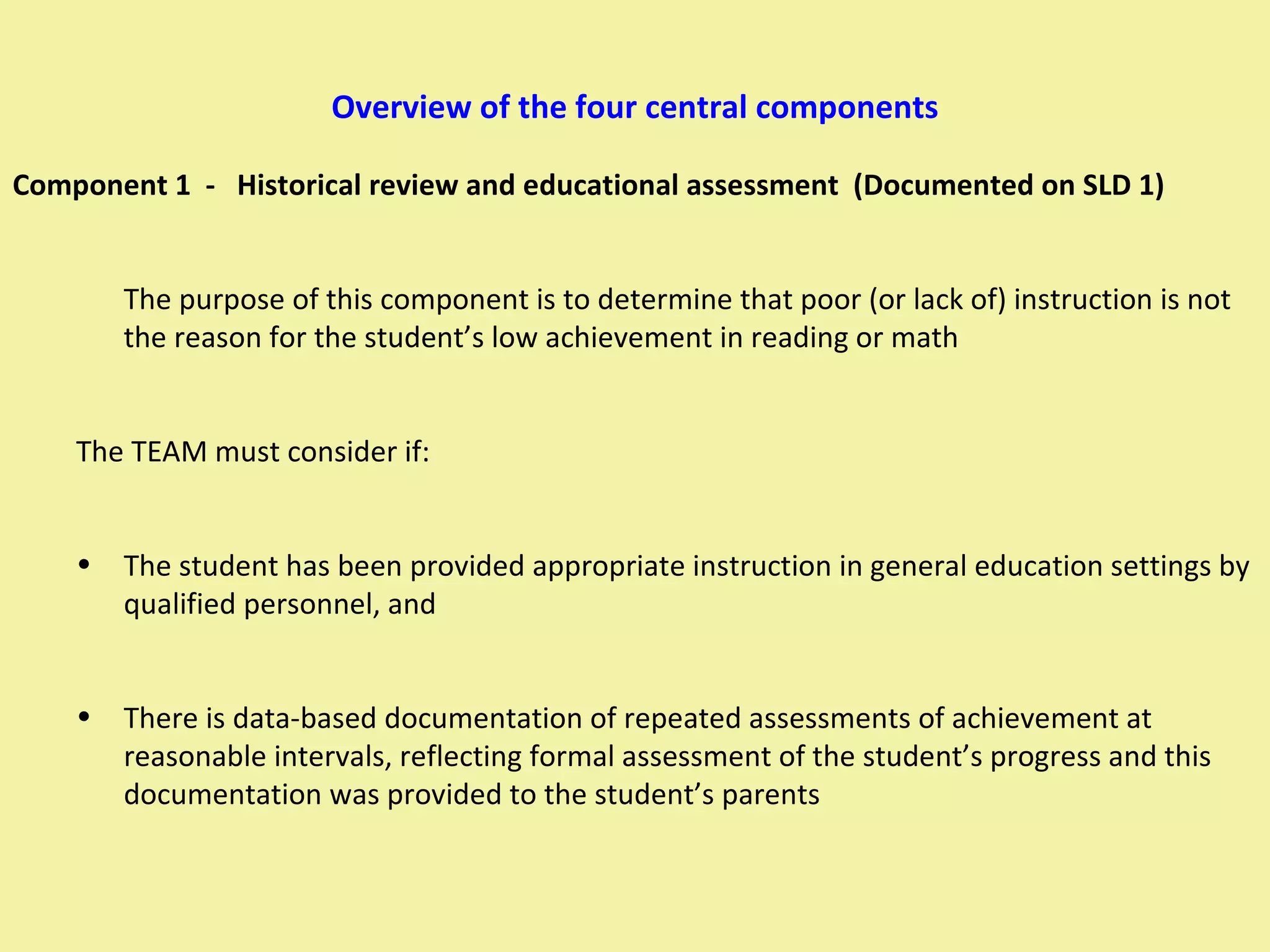
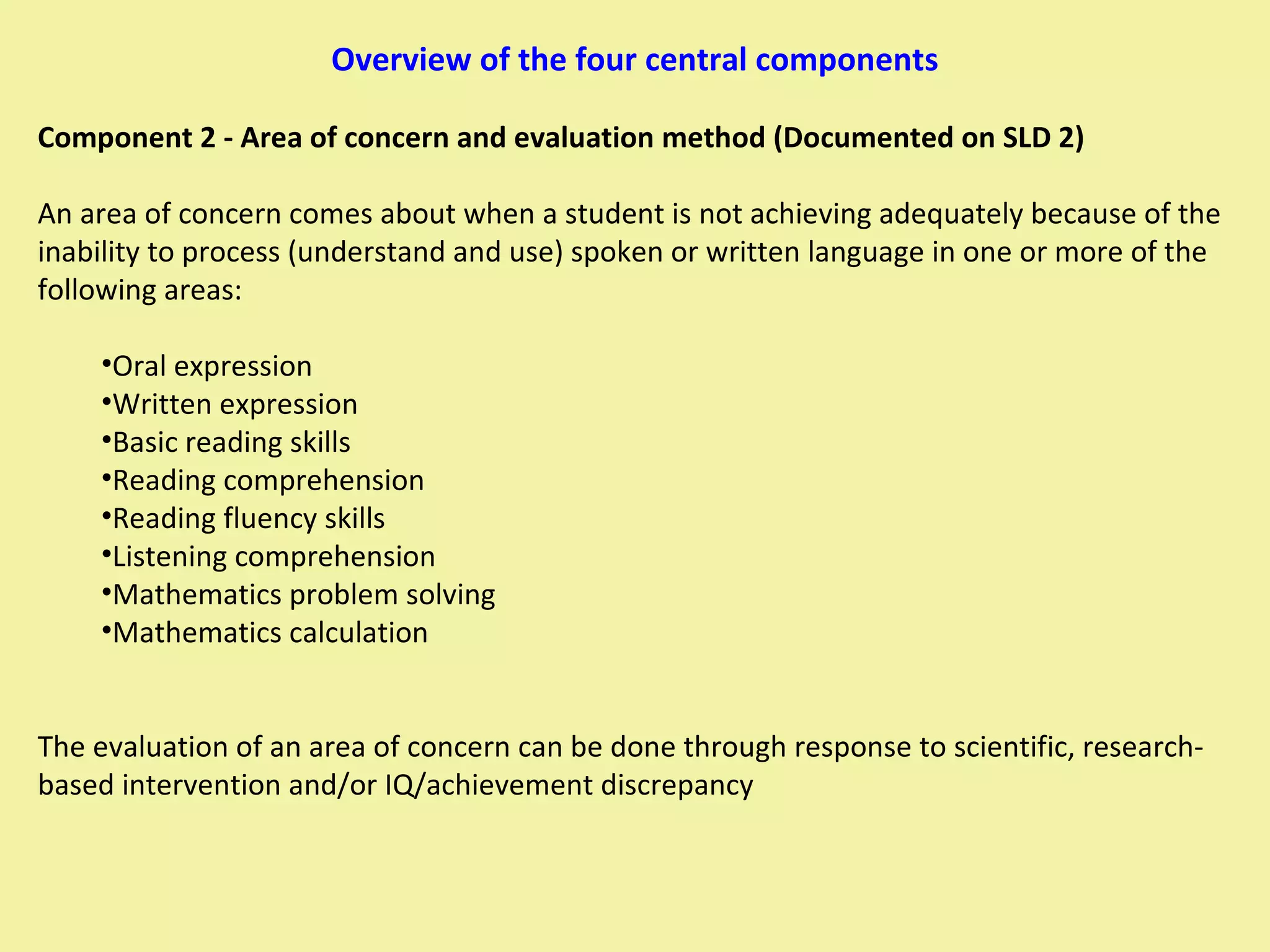
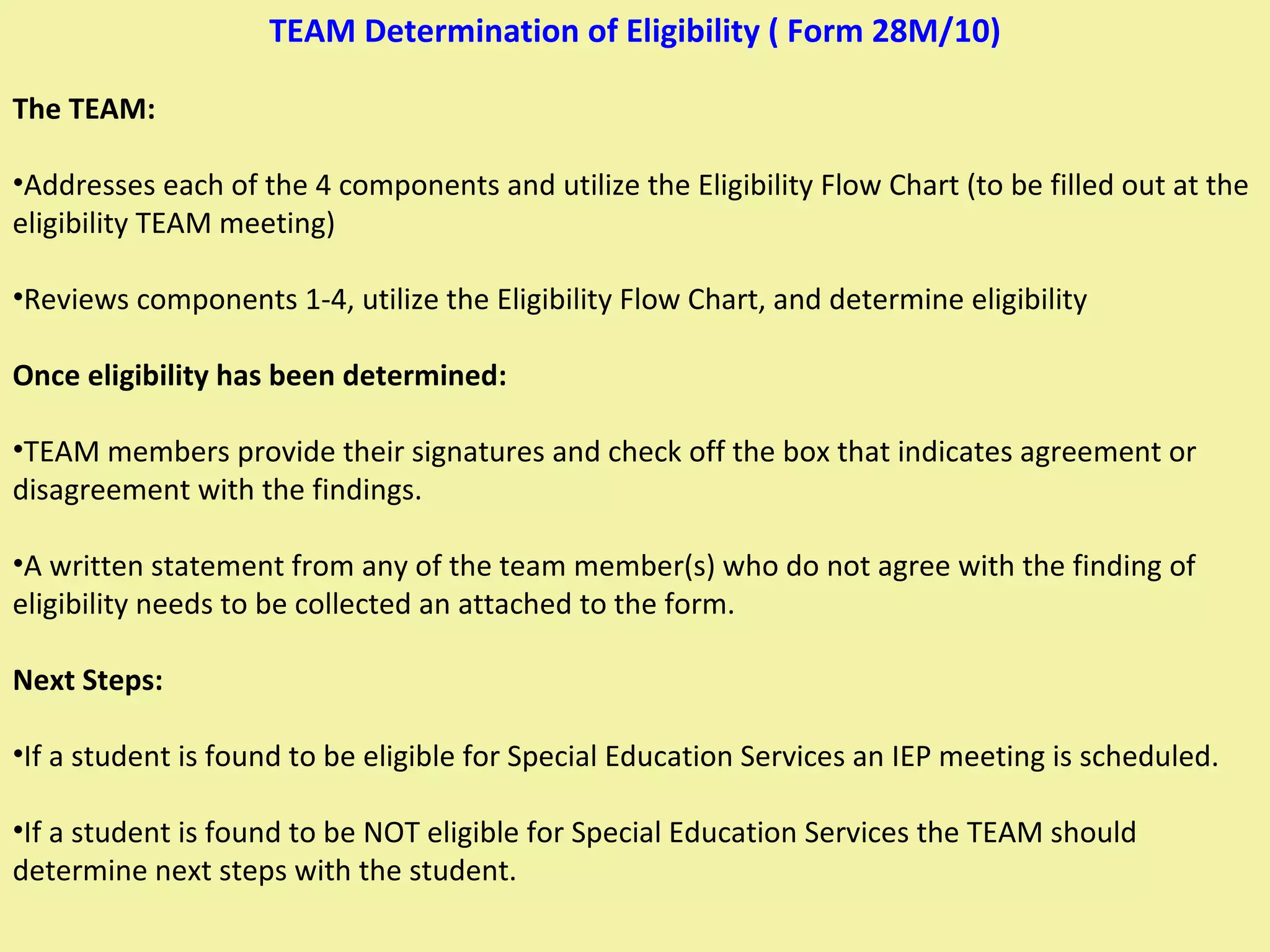
1) The document outlines the 4-component process used to determine if a student has a Specific Learning Disability (SLD) and is eligible for special education services.
2) The 4 components are: historical review/educational assessment, area of concern/evaluation method, exclusionary factors, and observation.
3) All parts of all 4 components must be completed and reviewed at an eligibility meeting to determine if the student qualifies for an IEP under the SLD category.