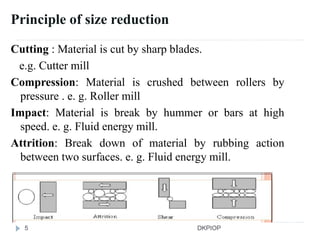
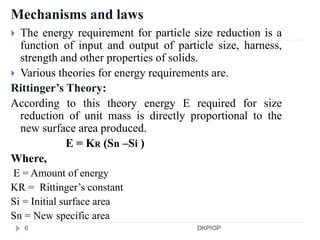
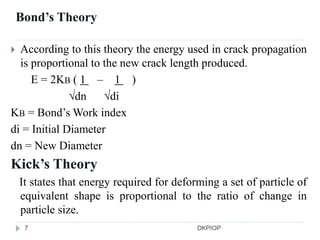
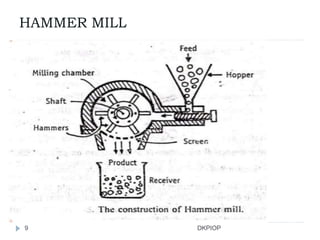
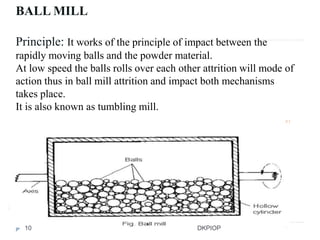
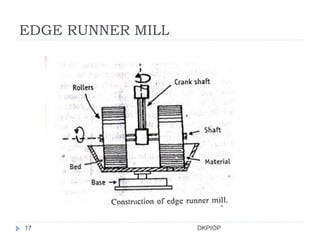
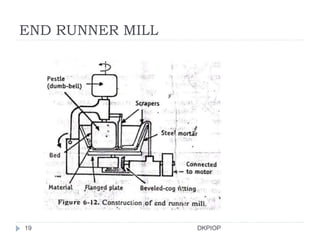
Size reduction is the process of reducing large solid units into smaller particles through mechanical or precipitation methods. It provides benefits like improved content uniformity, flow, extraction, drying, stability, dissolution, and absorption. Factors like hardness, moisture content, and required purity affect size reduction. Common size reduction equipment includes hammer mills, ball mills, fluid energy mills, and edge/end runner mills which employ mechanisms like cutting, compression, impact, and attrition. The energy required for size reduction is related to properties of the material and the surface area change according to theories by Rittinger, Bond, and Kick.