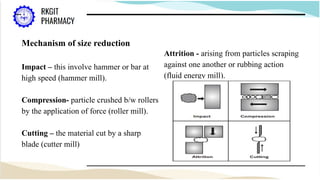
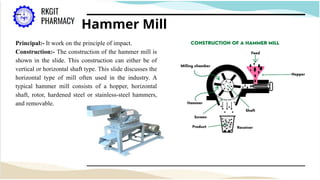
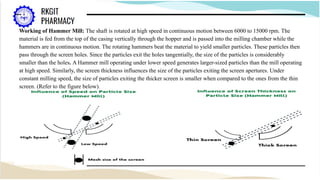
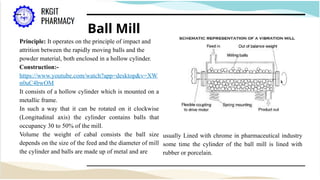
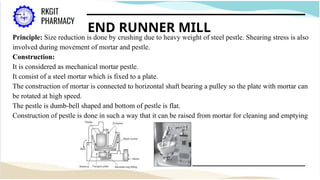
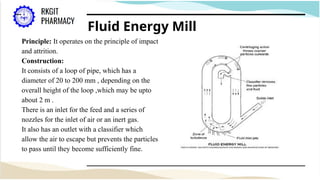
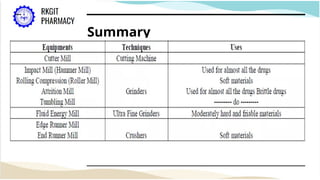
The document outlines the size reduction process in pharmaceutical engineering, detailing various methods such as hammer mills, ball mills, edge runner mills, and fluid energy mills. Key objectives include increasing surface area for therapeutic effectiveness and producing particles within a narrow size range. Additionally, it discusses the mechanisms, laws governing size reduction, factors affecting it, advantages and disadvantages of each milling method, and their specific applications in drug formulation.