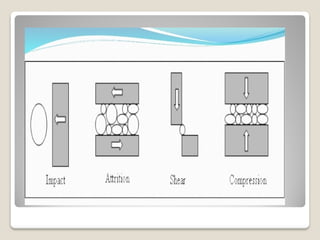
The document discusses various methods of size reduction used in pharmaceutical processing. It describes the objectives, principles, construction and working of common size reduction equipment such as hammer mills, ball mills, fluid energy mills, edge runner mills, and end runner mills. Size reduction is achieved through mechanisms like cutting, compression, impact and attrition. Factors like speed, material properties, and construction of the equipment affect the efficiency of size reduction. The summary provides an overview of the key information covered in the document.