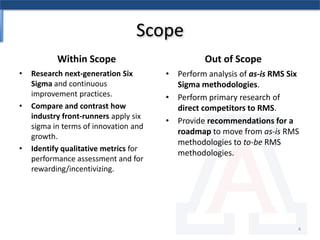
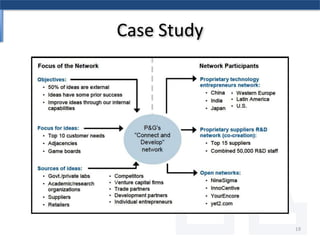
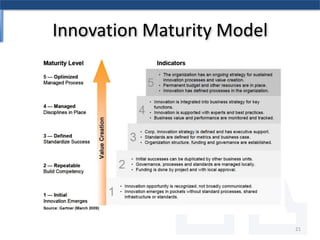
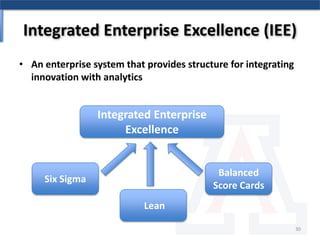
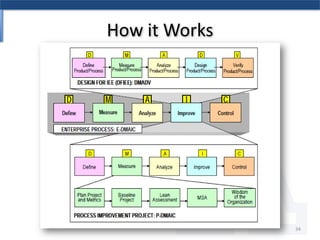
The document discusses the relationship between Six Sigma methodologies and innovation within organizations, emphasizing that Six Sigma should not be directly applied to innovation activities as it may hinder creativity. Recommendations include using Six Sigma to enhance processes that support innovation and adopting an integrated enterprise excellence model to align innovation with analytics. It also presents a research methodology and various frameworks for managing innovation effectively while fostering a collaborative organizational culture.