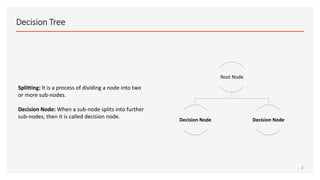
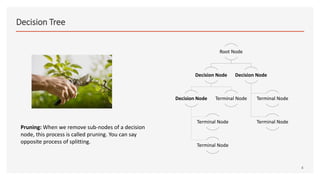
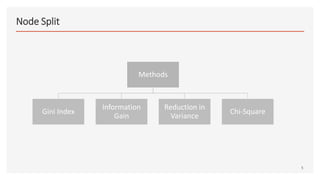
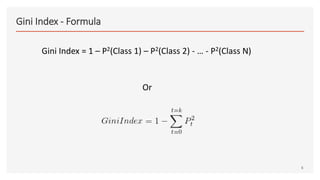
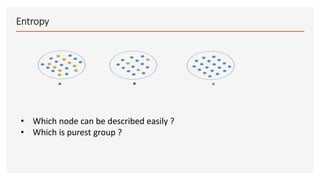
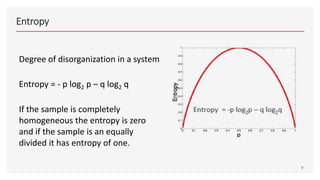
This document provides an overview of decision trees, including the key components and concepts. It defines the root node, decision nodes, terminal nodes, branches, and the relationships between parent and child nodes. It describes the processes of splitting nodes and pruning trees. Finally, it explains several common methods for splitting nodes, including Gini index, information gain, reduction in variance, and chi-square.



![Entropy - Example
10
Play Golf
Yes No
Outlook
Sunny 3 2 5
Overcast 4 0 4
Rainy 2 3 5
9 5 14
Entropy (Play Golf, Outlook) = 5/14 * [ - 3/5 log 3/5 – 2/5 log 2/5] + 4/14 [ - 4/4 log 4/4] + 5/14 [- 2/5 log 2/5 – 3/5 log
3/5]
= 0.46 * 0.971 + 0.28 * 0.0 + 0.56 * 0.971
= 0.693
Entropy (Play Golf) = Entropy (9/14, 5/14)
= - 9/14 log 9/14 – 5/14 log 5/14
= 0.95](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workingwithlogisticregressionv1-190103063213/85/Simple-Decision-Tree-10-320.jpg)