The document discusses three distribution methods for products mentioned as selling directly to customers over the internet, using independent distributors with vans, and direct selling to retail outlets. It also provides vocabulary words and their definitions and questions about obstacles founders faced and strategies used to promote their brands.













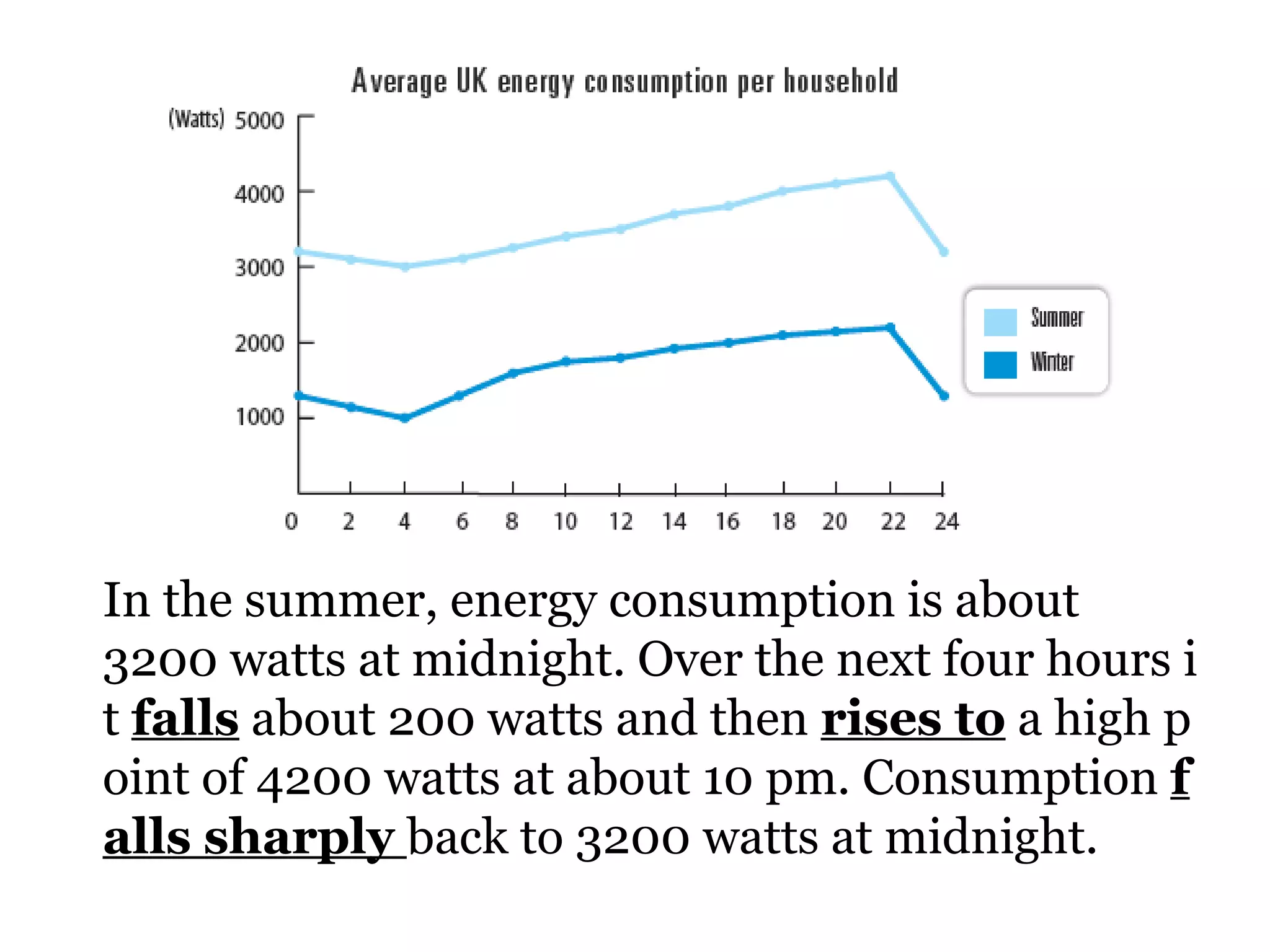
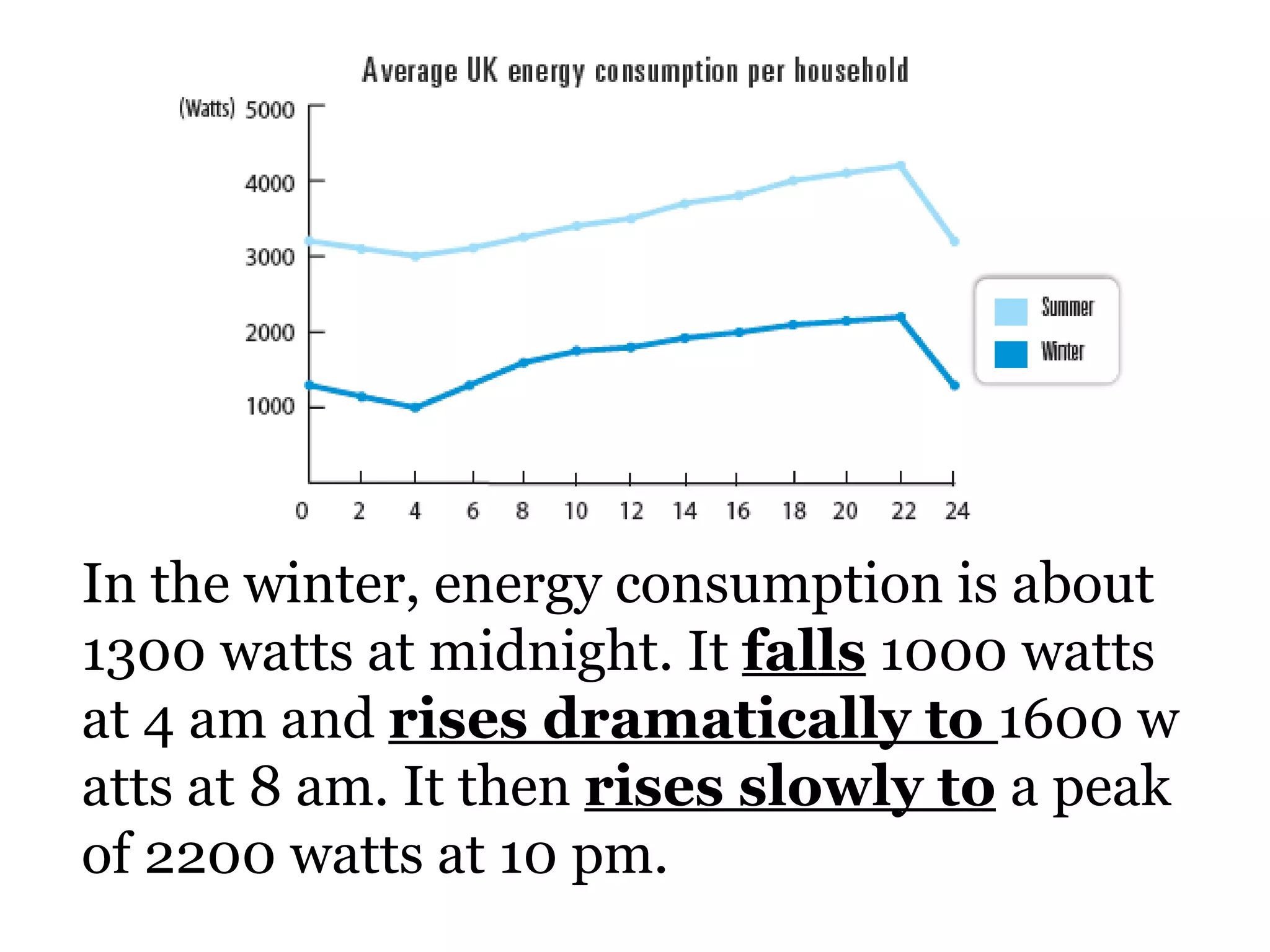
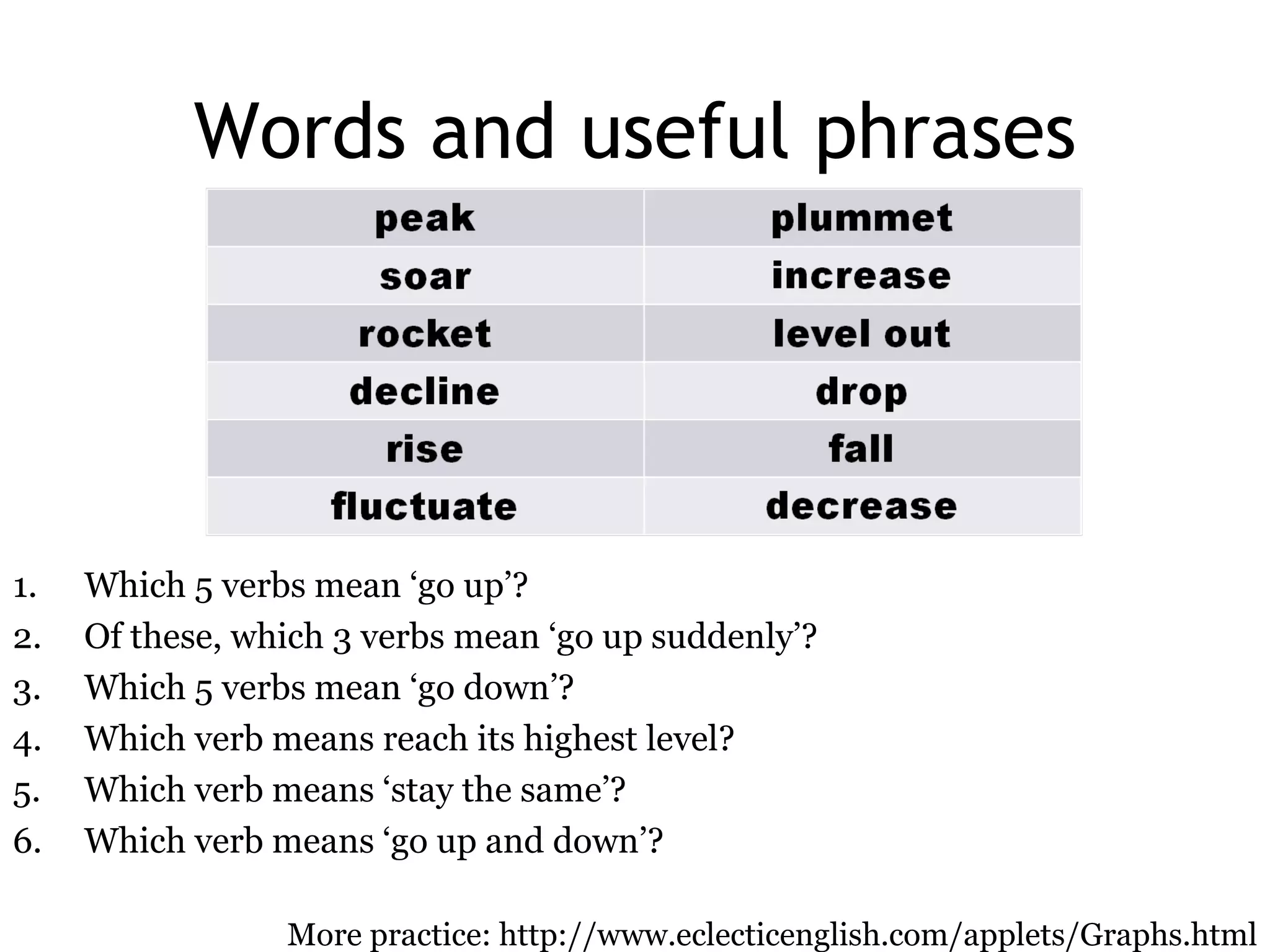
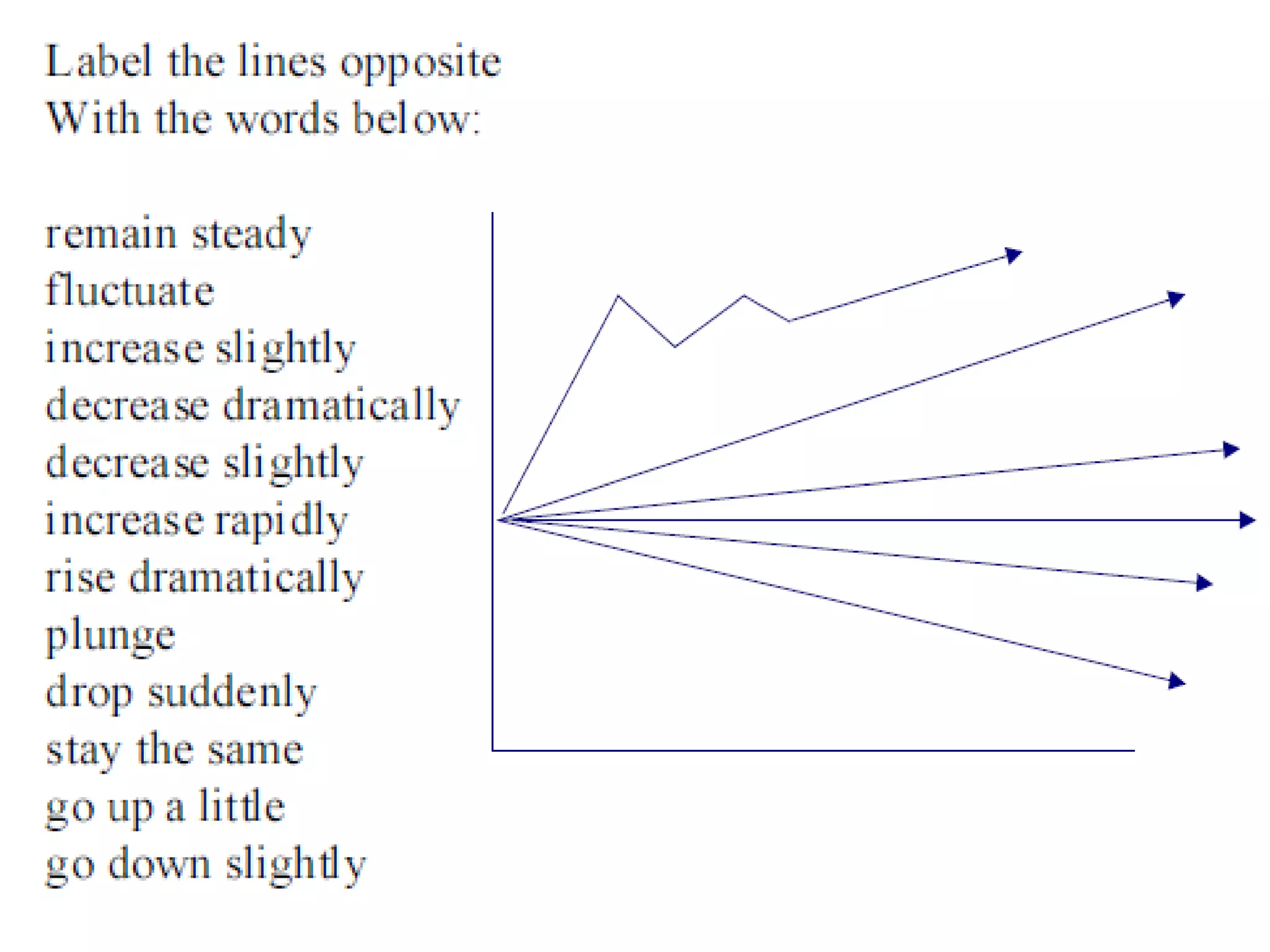
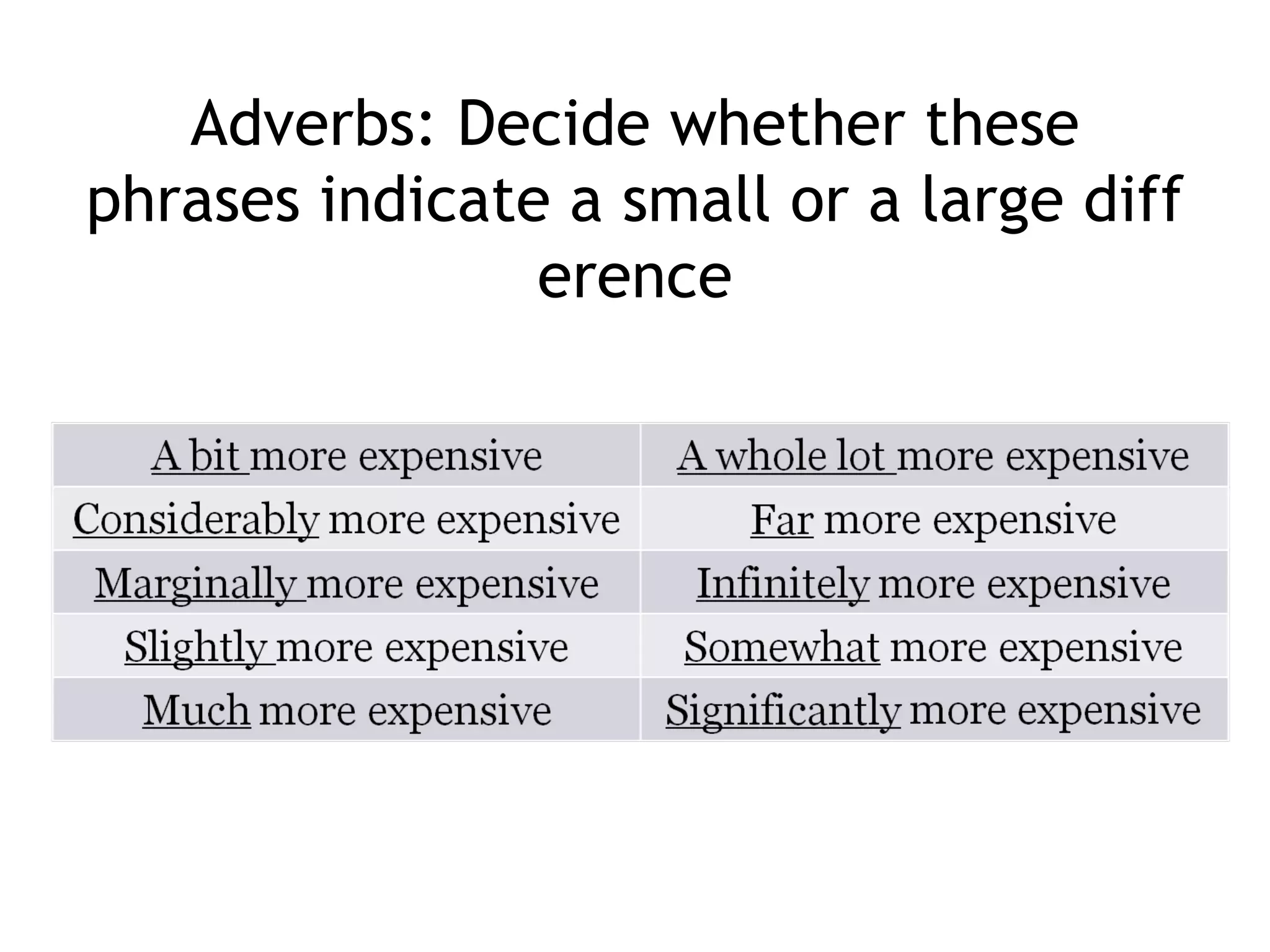

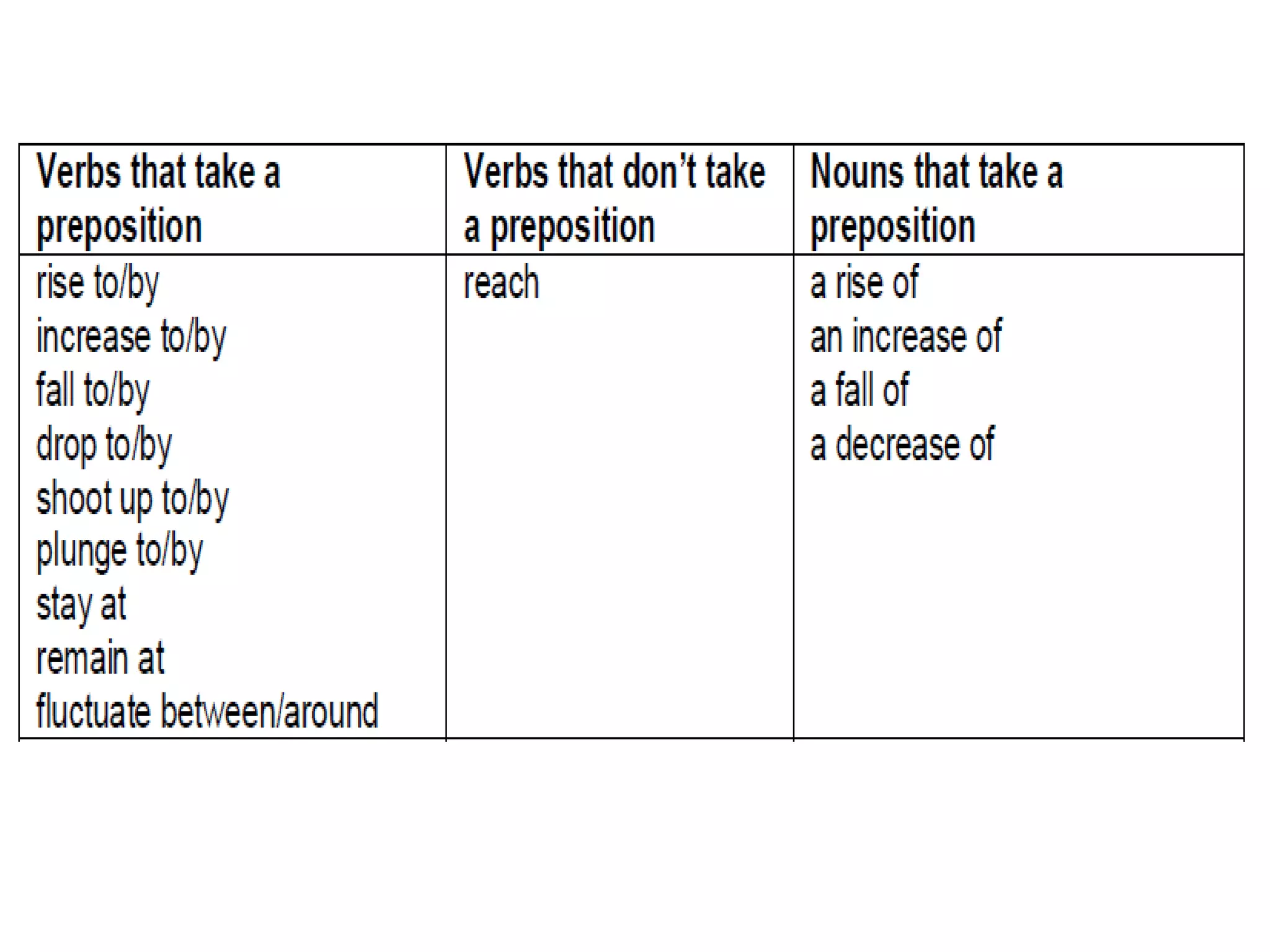


![2 ways of expressing the same idea 1 SUB + verb + [adverb] For example: The unemployment rate rose rapidly . The cost of living fell dramatically . 2 There is/are + [adj] + noun + in + something For example: There was a rise in unemployment. There has been an increase in the cost of living.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shelfspaceabstractfactassumption-110813050414-phpapp01/75/Shelf-space-abstract-graph-fact-assumption-26-2048.jpg)