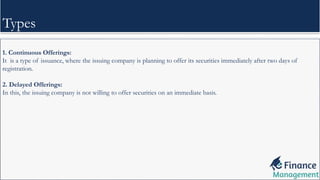
Shelf registration is a public offering process allowing companies to register securities once for multiple future offerings, enabling flexibility and reduced issuance timing. Advantages include minimized expenses and better market timing, while disadvantages consist of limited interest from major institutional investors. The document also discusses the 'baby shelf rule' for small companies with an equity value under $75 million, restricting stock offerings to one-third of total in a year.