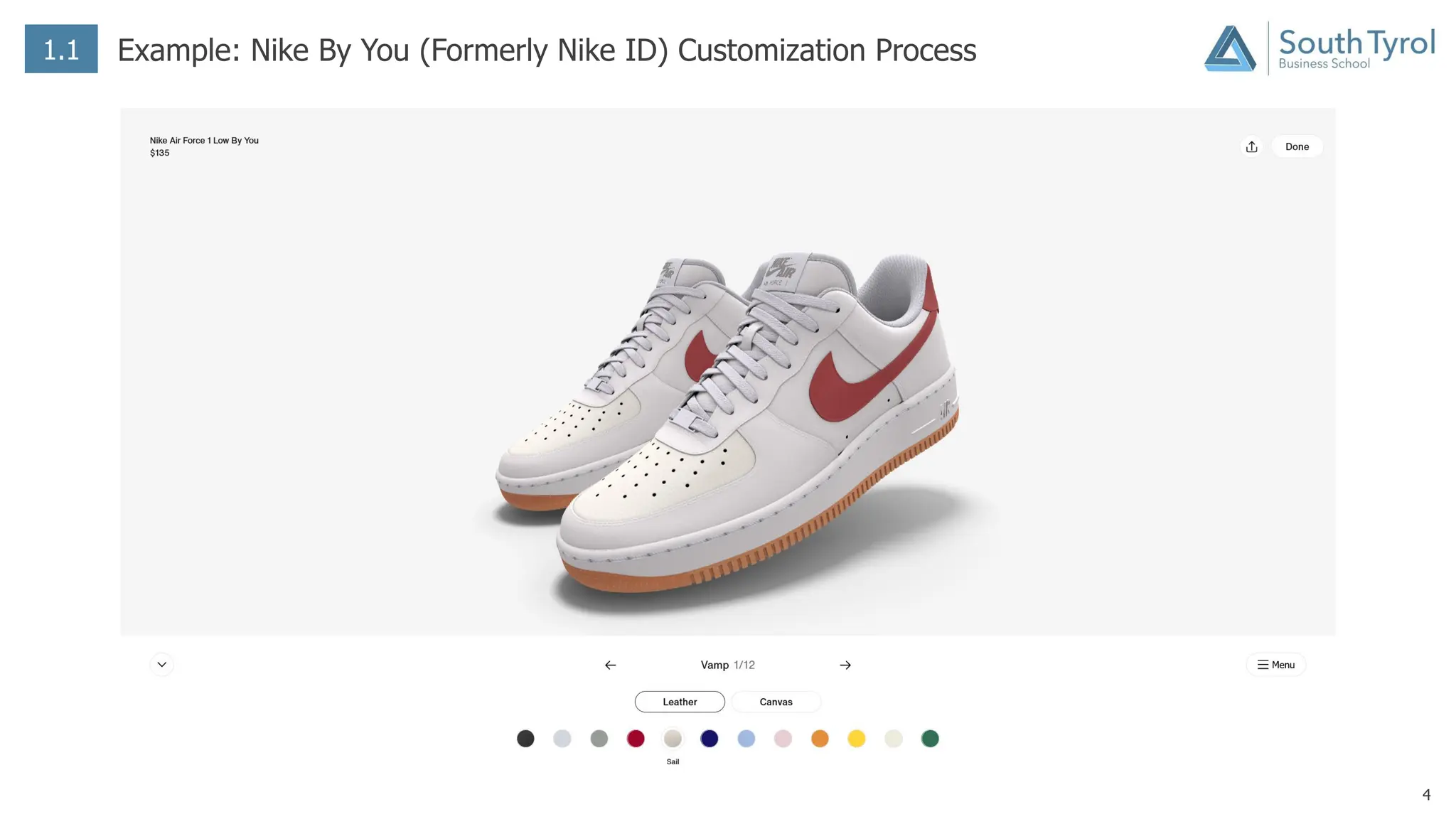
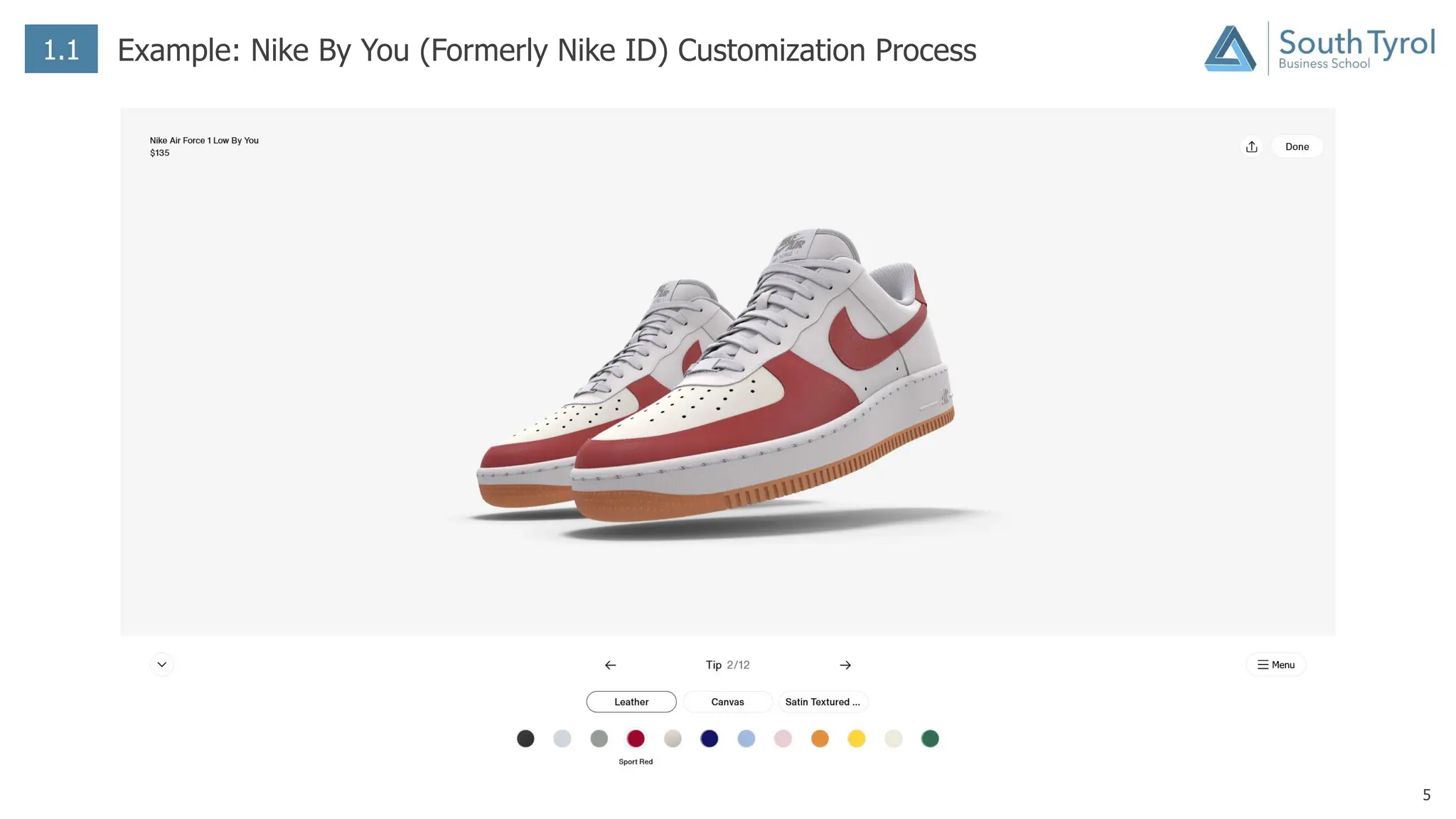
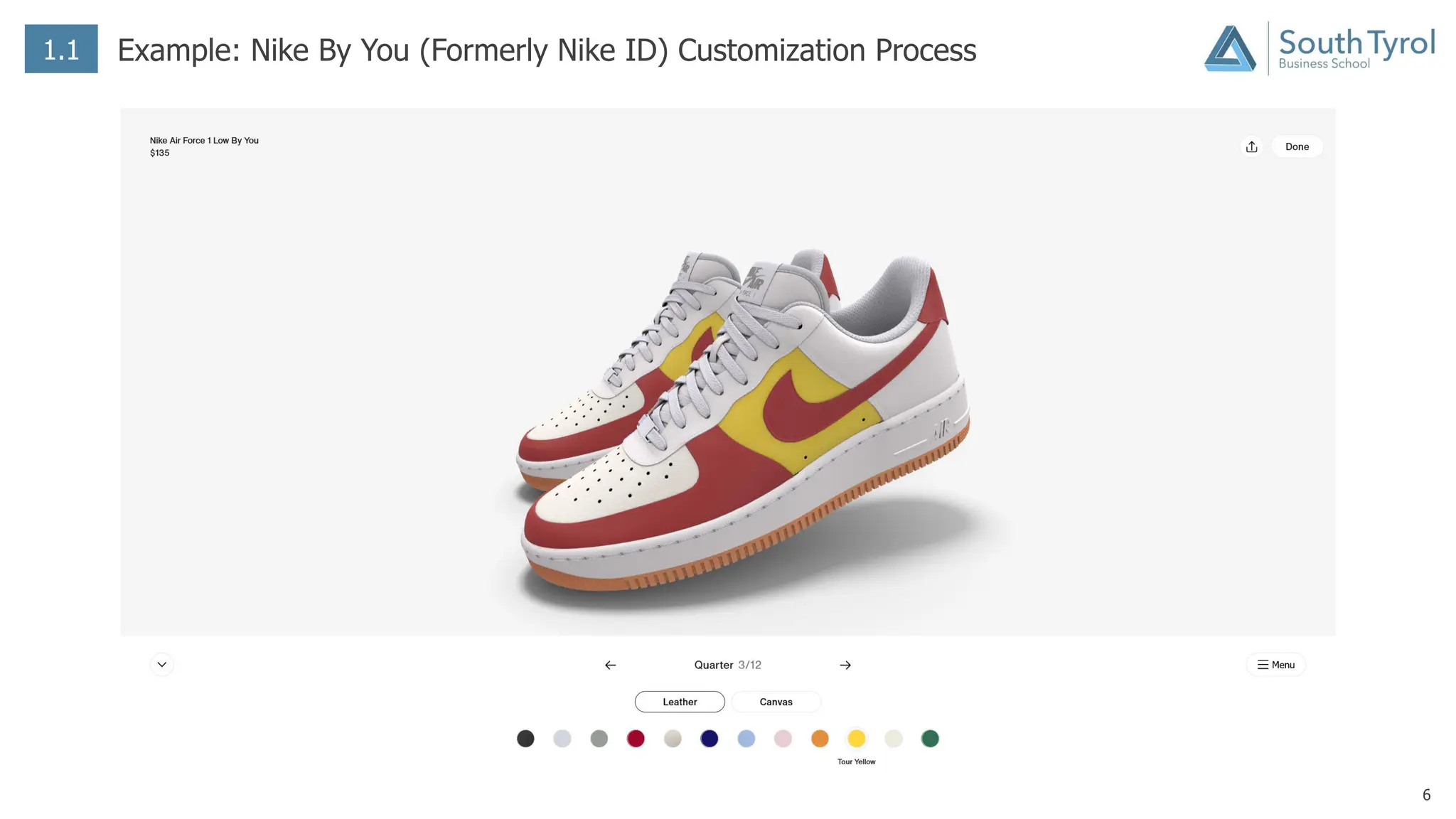
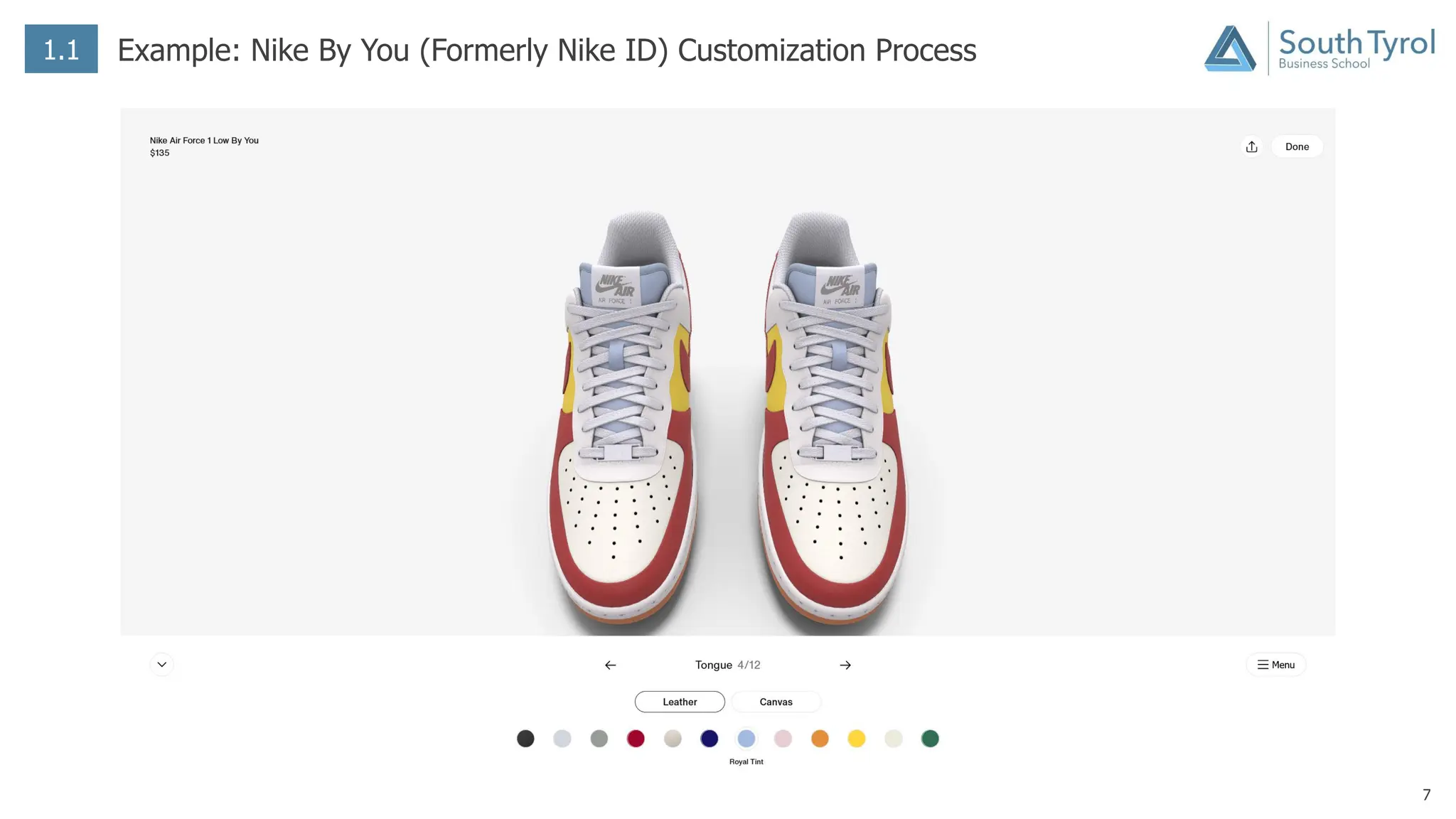
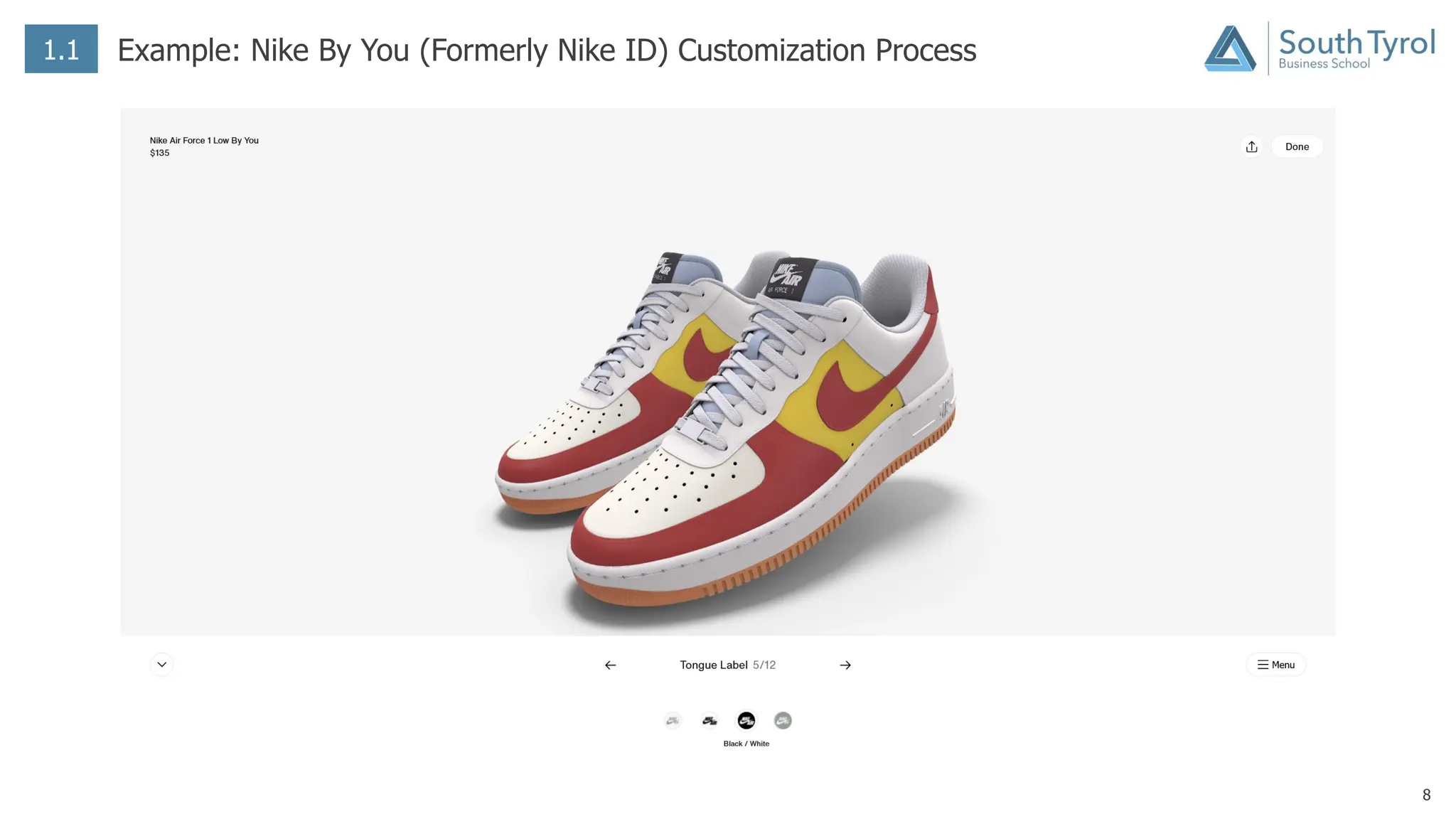
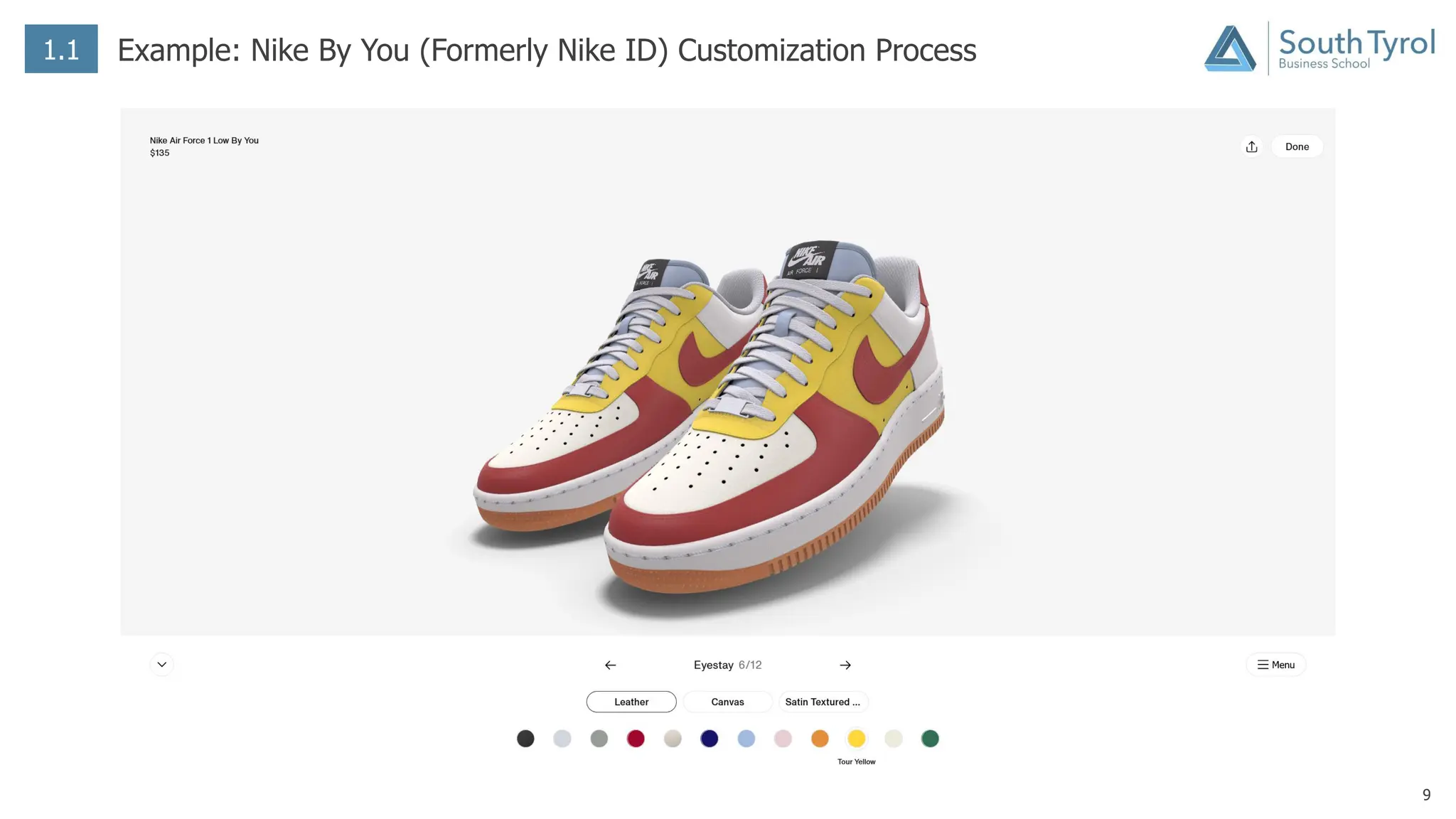
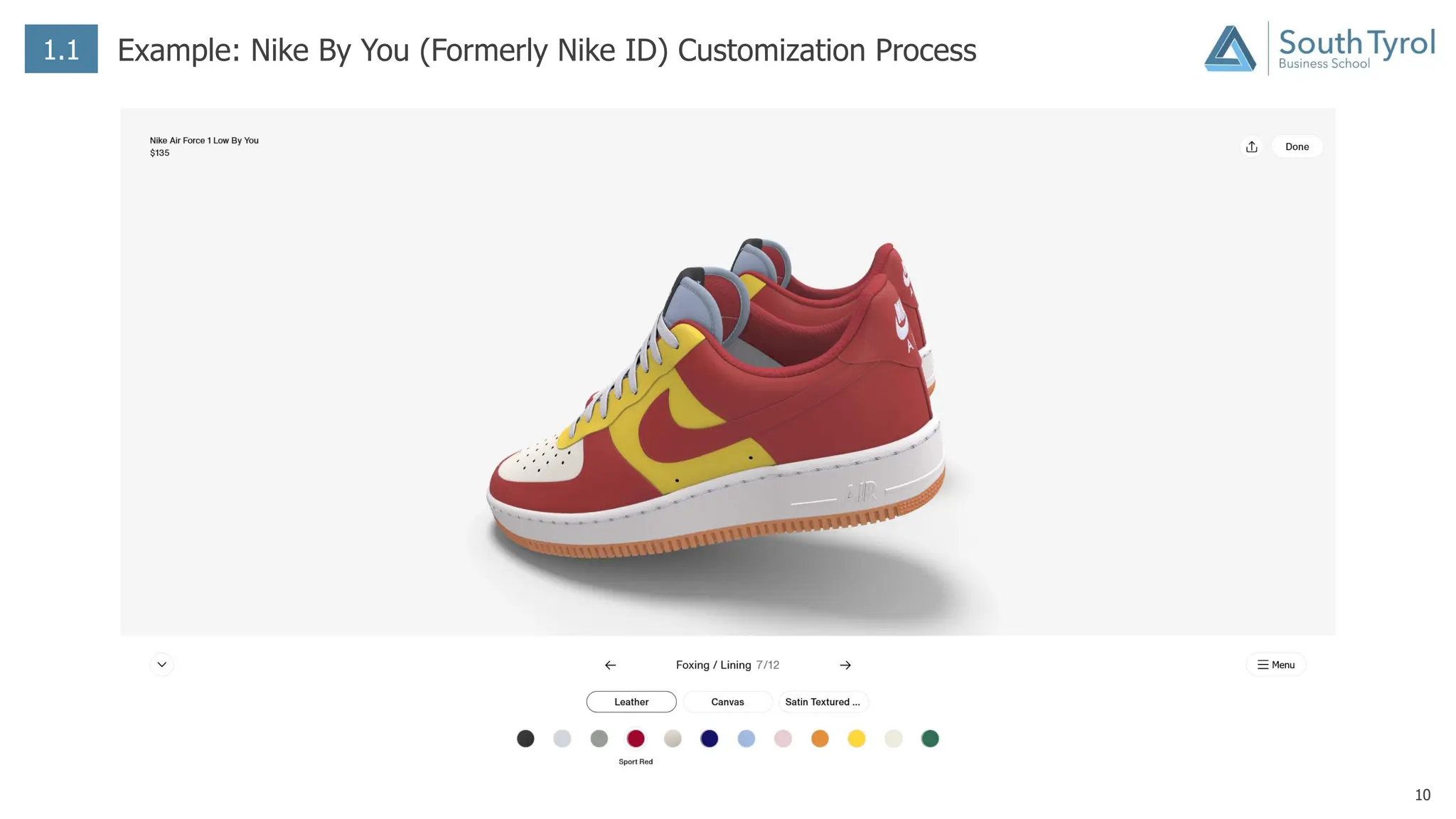
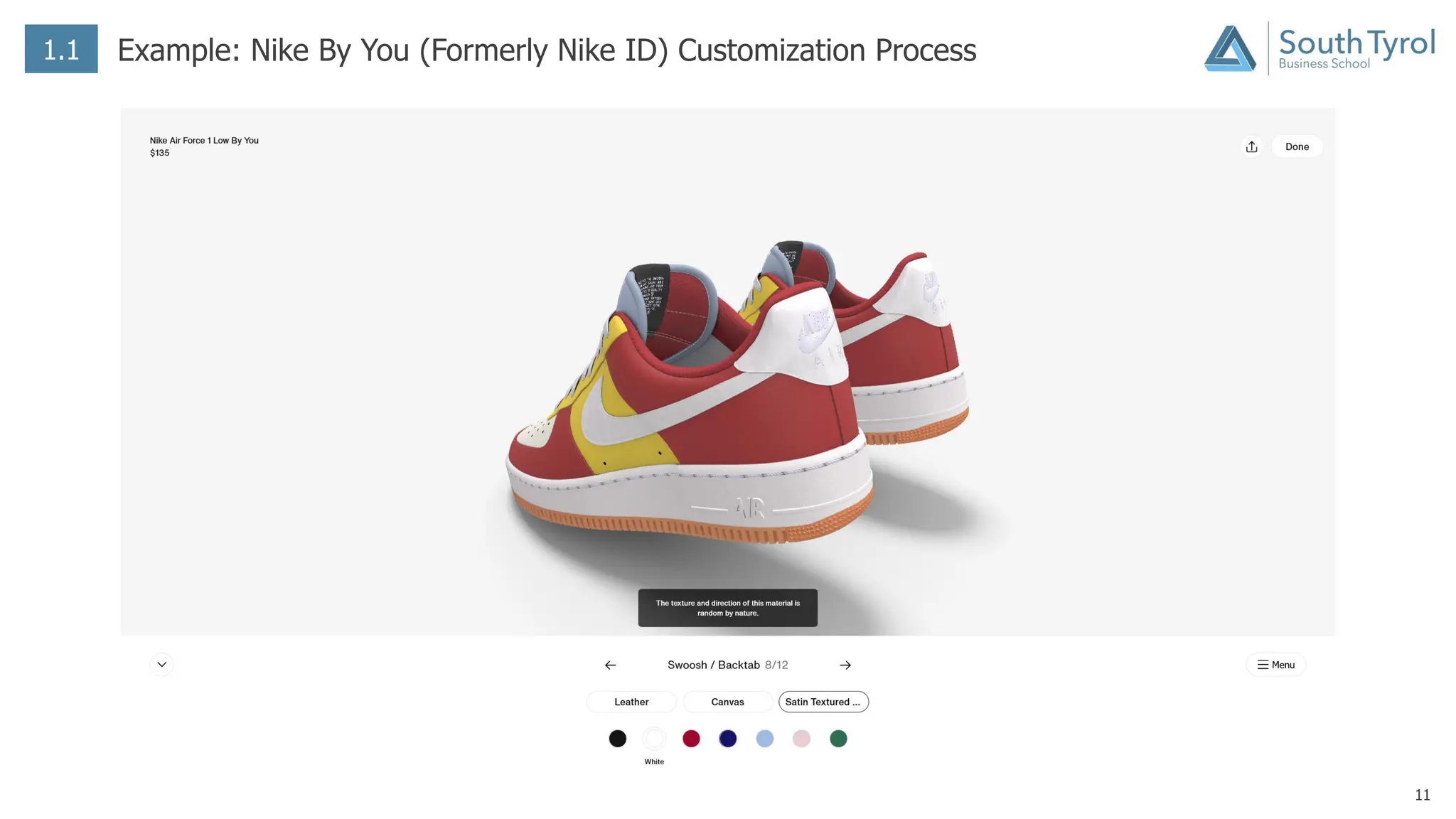
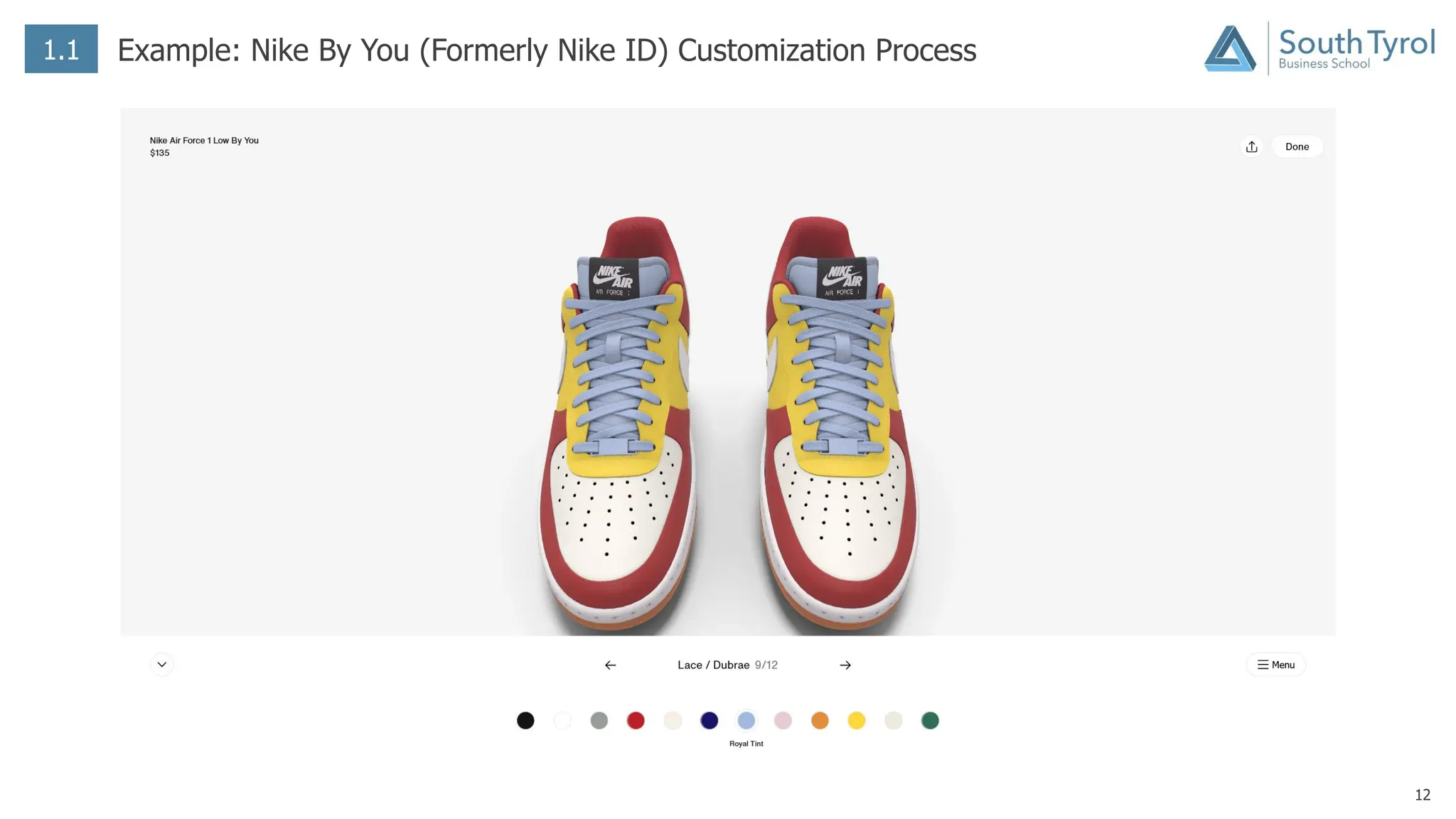
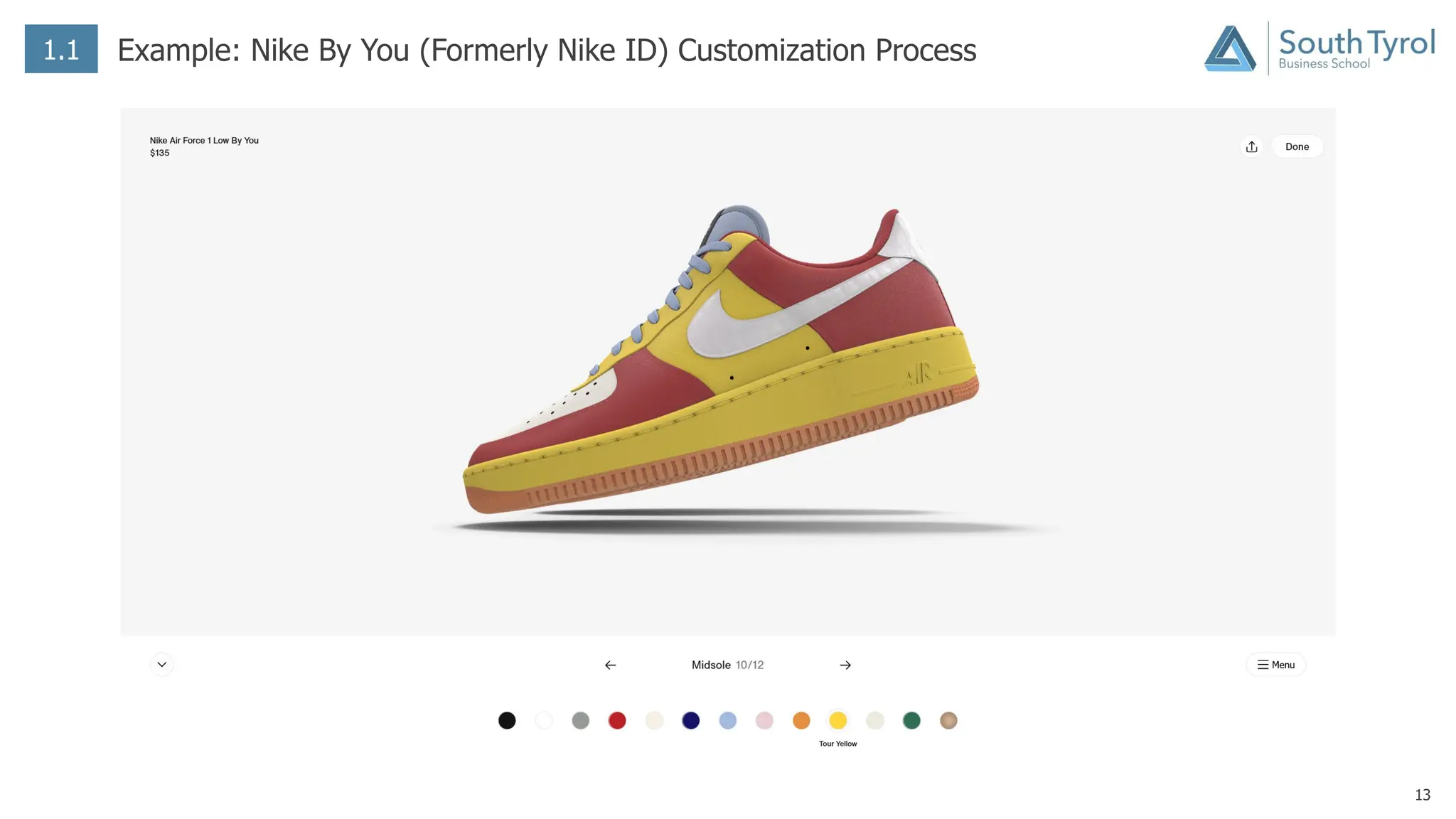
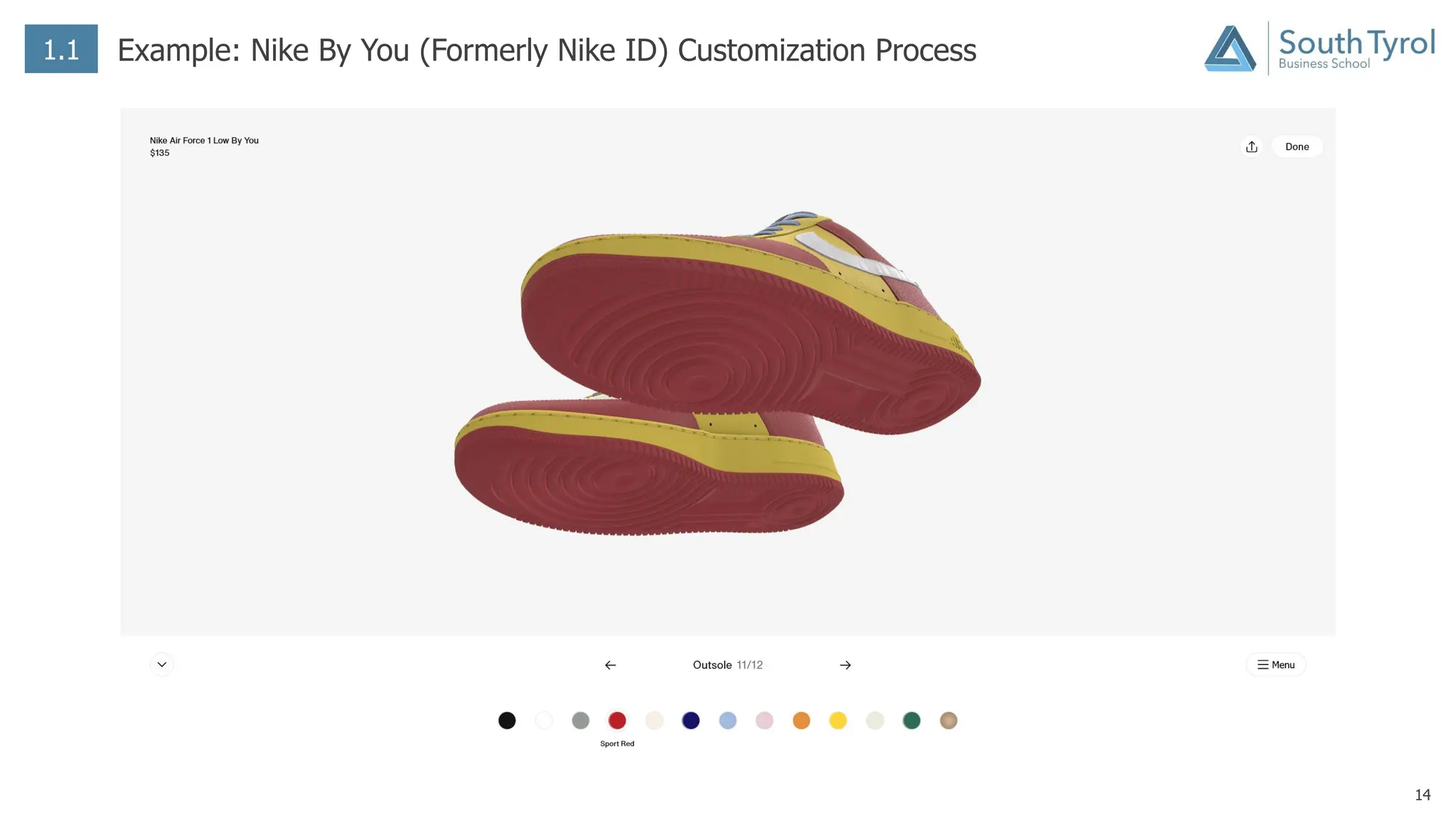
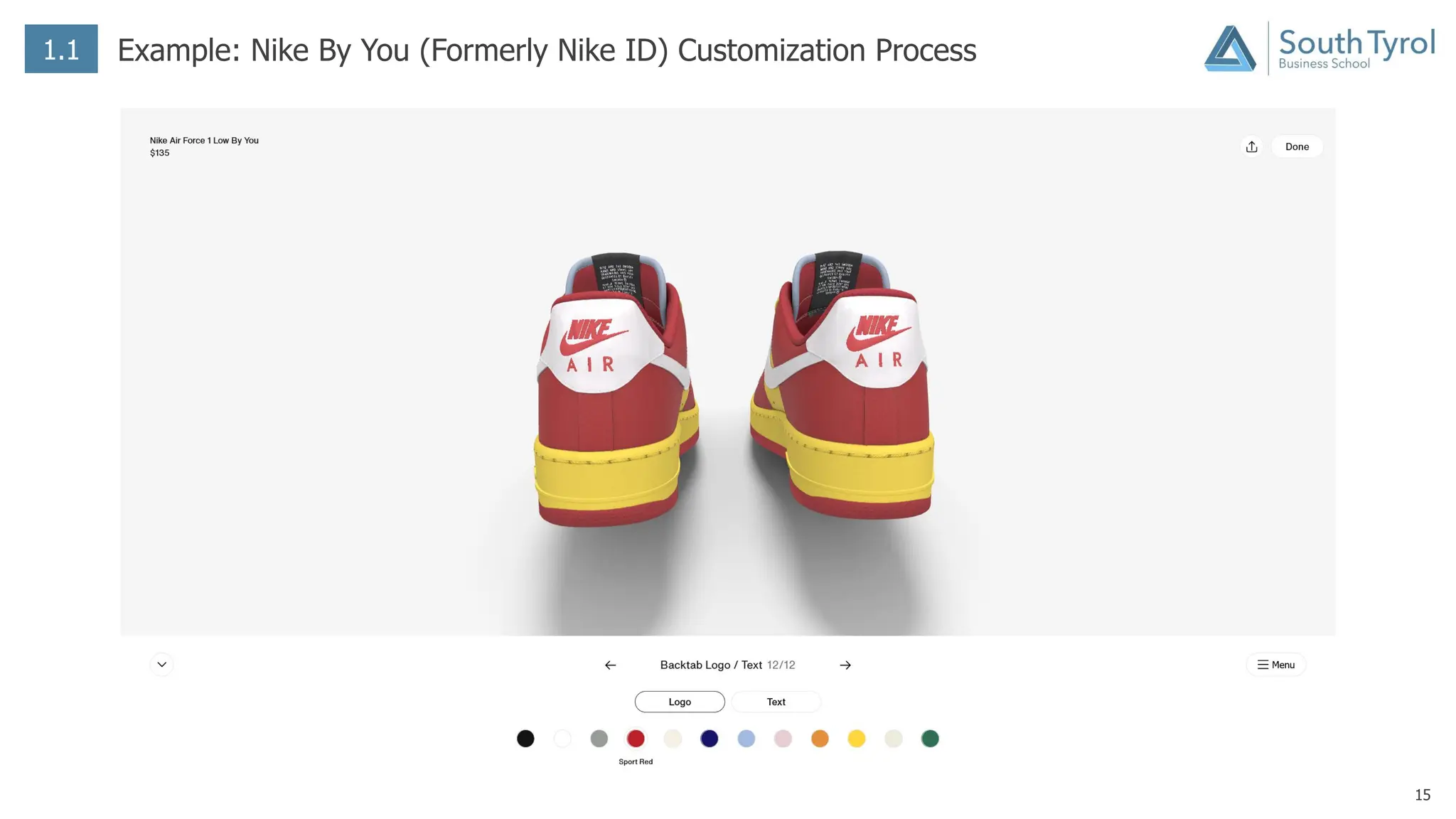
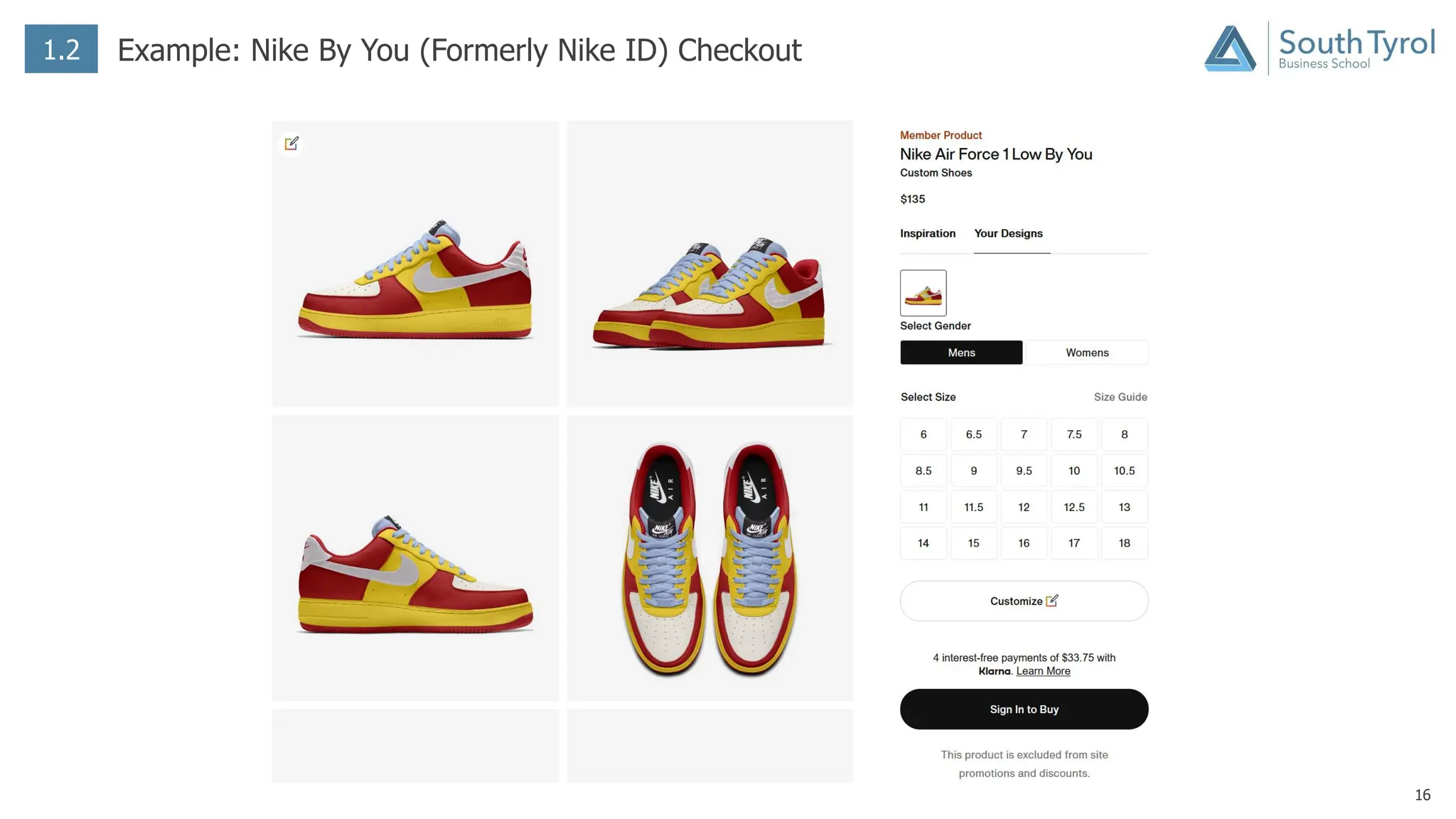
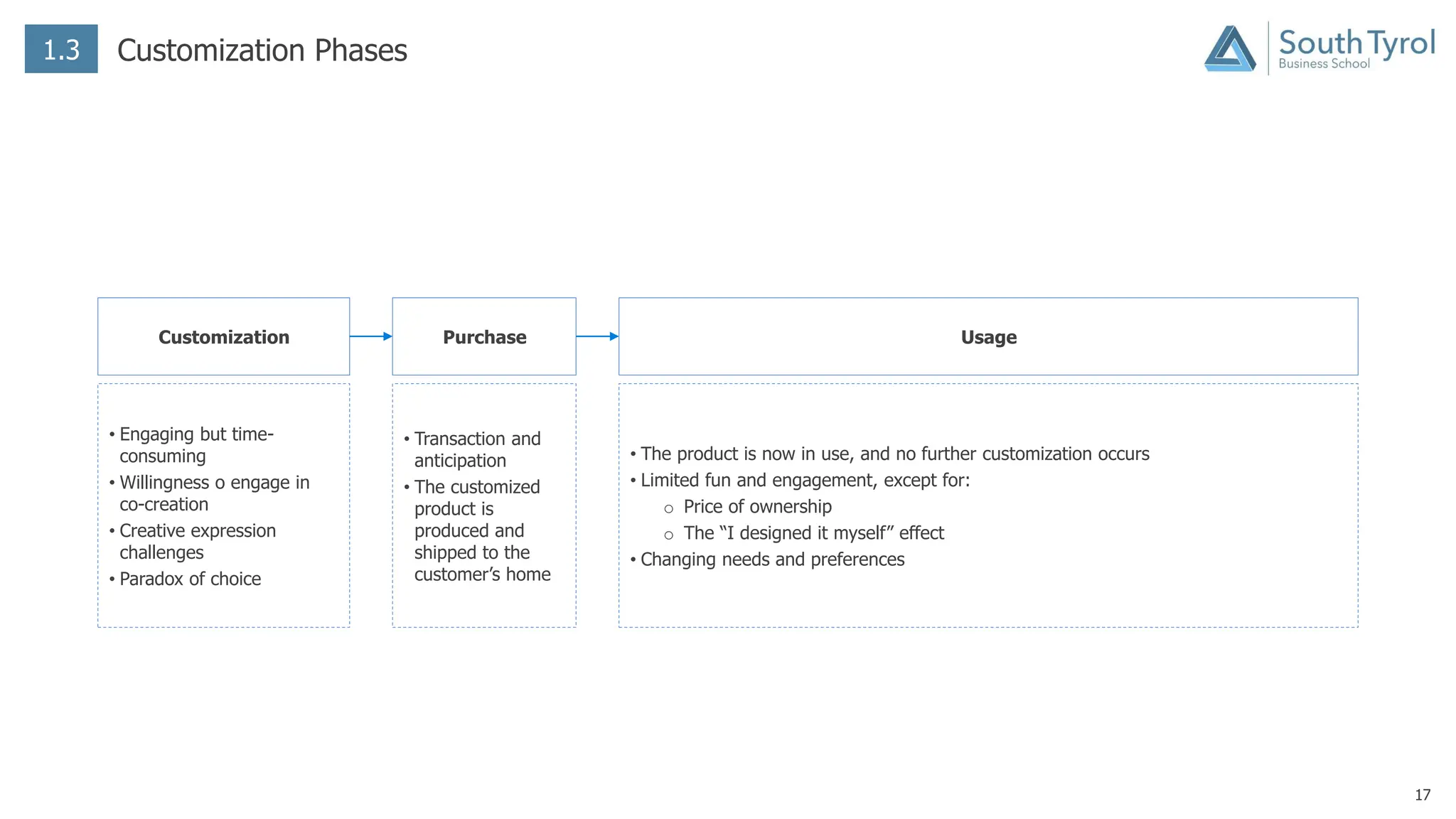
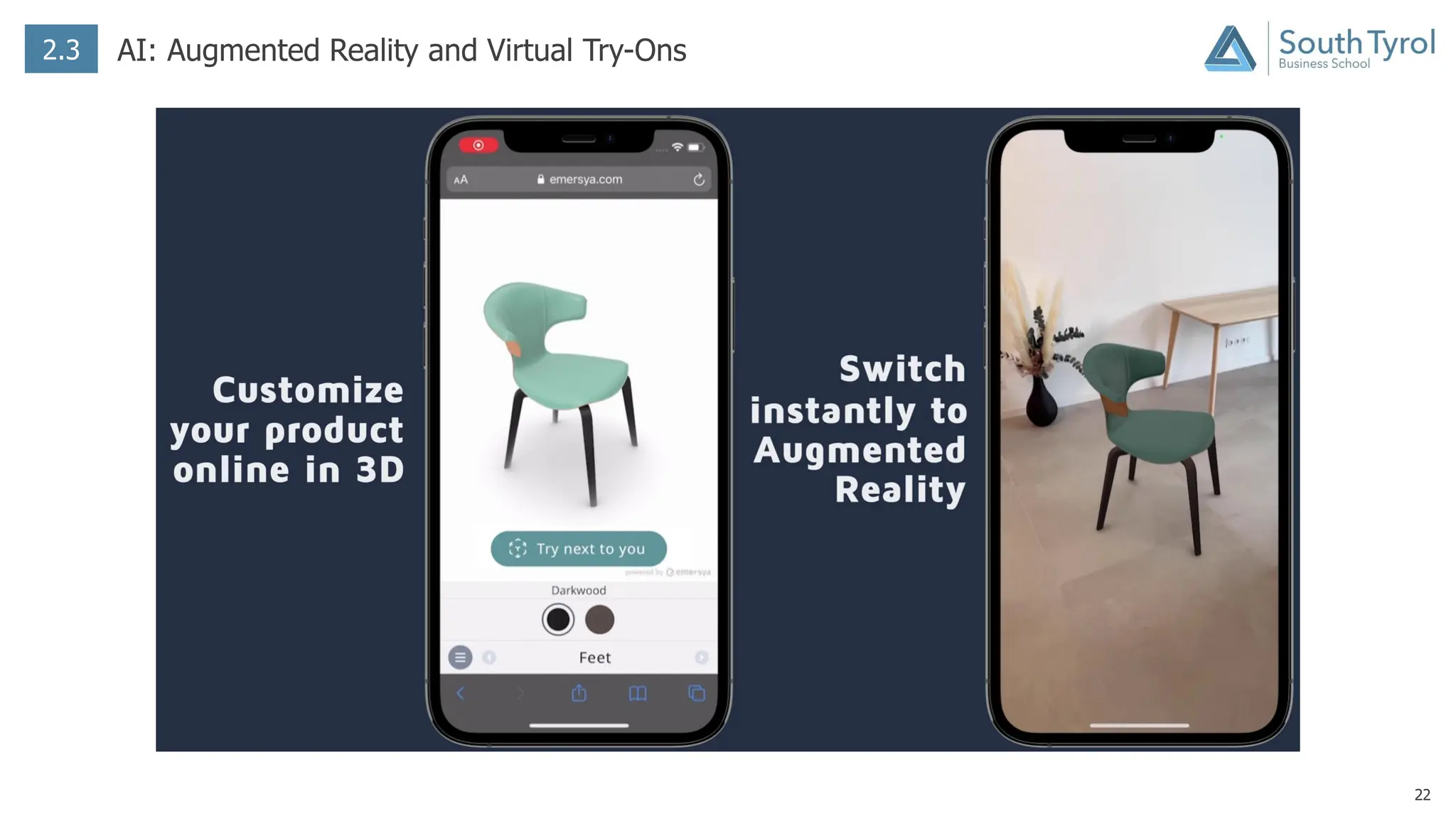
The document discusses how artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing mass customization. Traditional mass customization allows customers to customize products online through selection of options. AI enables more intuitive customization by learning customer preferences and offering dynamic, individual recommendations. IoT connects devices to customize the usage experience based on a person's context and needs. The integration of these technologies has the potential to transform mass customization by enabling mood-based and natural language processing for customization as well as products designed through AI with minimal user input.