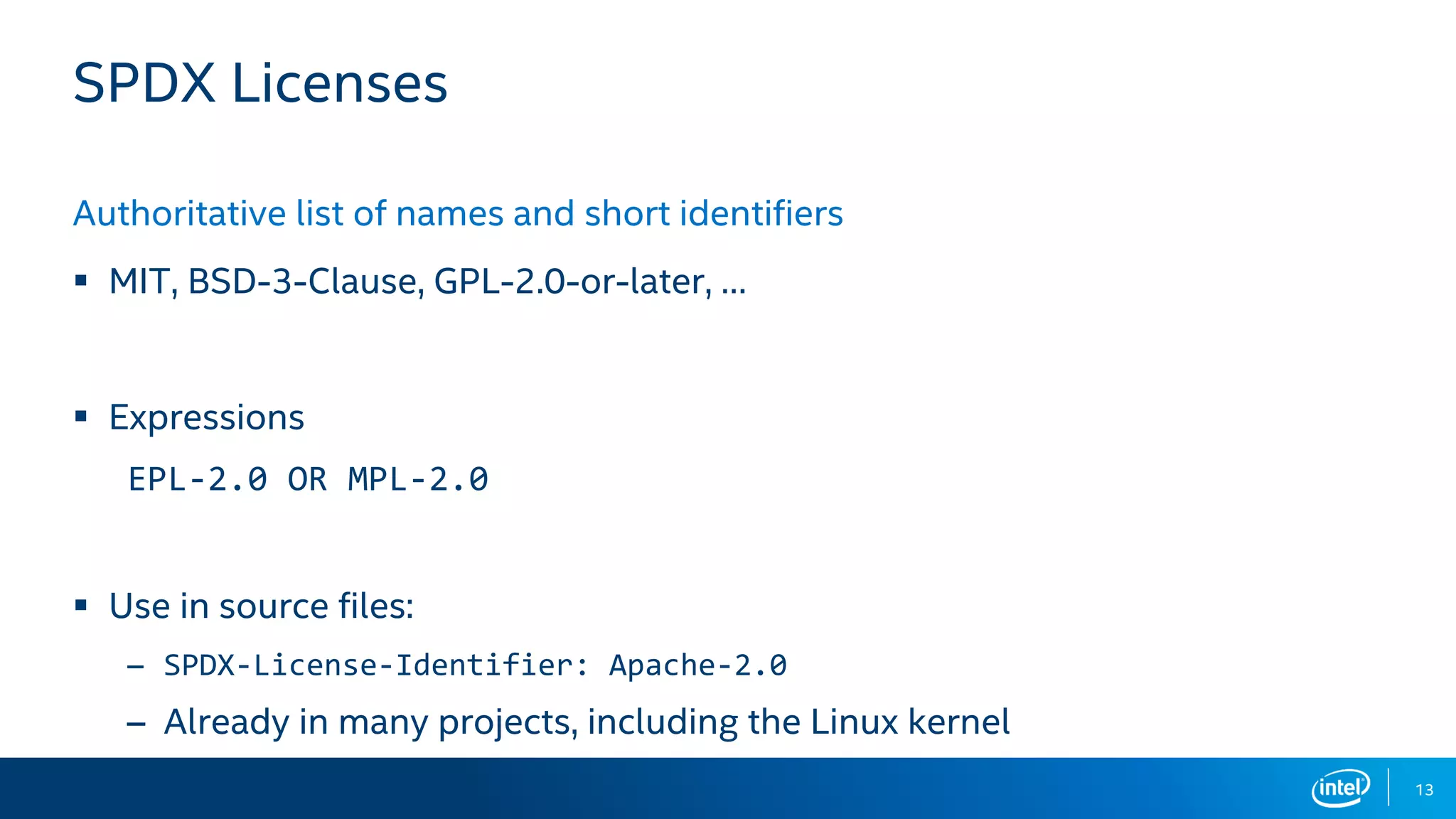
Alexios Zavras, a senior open source compliance engineer at Intel, discusses the company's extensive engagement with free software and the challenges it faces in compliance due to its large size and varied organizational structure. He emphasizes the importance of a governance and compliance program, mandatory training, and the use of supportive tools as strategies for managing open source obligations effectively. Zavras encourages the development of internal communities and collaboration to foster better compliance and community citizenship.