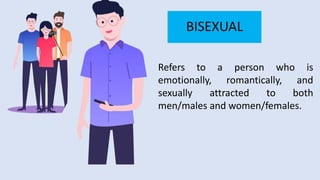
This document defines key terms related to sexual orientation, gender identity, and expression. It explains that every person has a sex assigned at birth based on biological traits, but also has a gender identity and expression. Gender identity is an internal sense of maleness, femaleness, or other, which may align with or differ from one's sex. Gender expression is how one presents gender externally through appearance and behavior. Sexual orientation refers to romantic and sexual attraction toward other genders. The document outlines common identities within the spectrum of gender and orientation.