This document provides a comprehensive overview of arrays in C programming, defining them as collections of elements of the same data type that facilitate efficient data manipulation. It discusses declaration, initialization, and various operations such as traversal, searching, and sorting, while also touching upon advanced concepts like dynamic arrays and multidimensional arrays. Additionally, real-world applications in areas like sorting algorithms and game development illustrate the practical relevance of arrays.



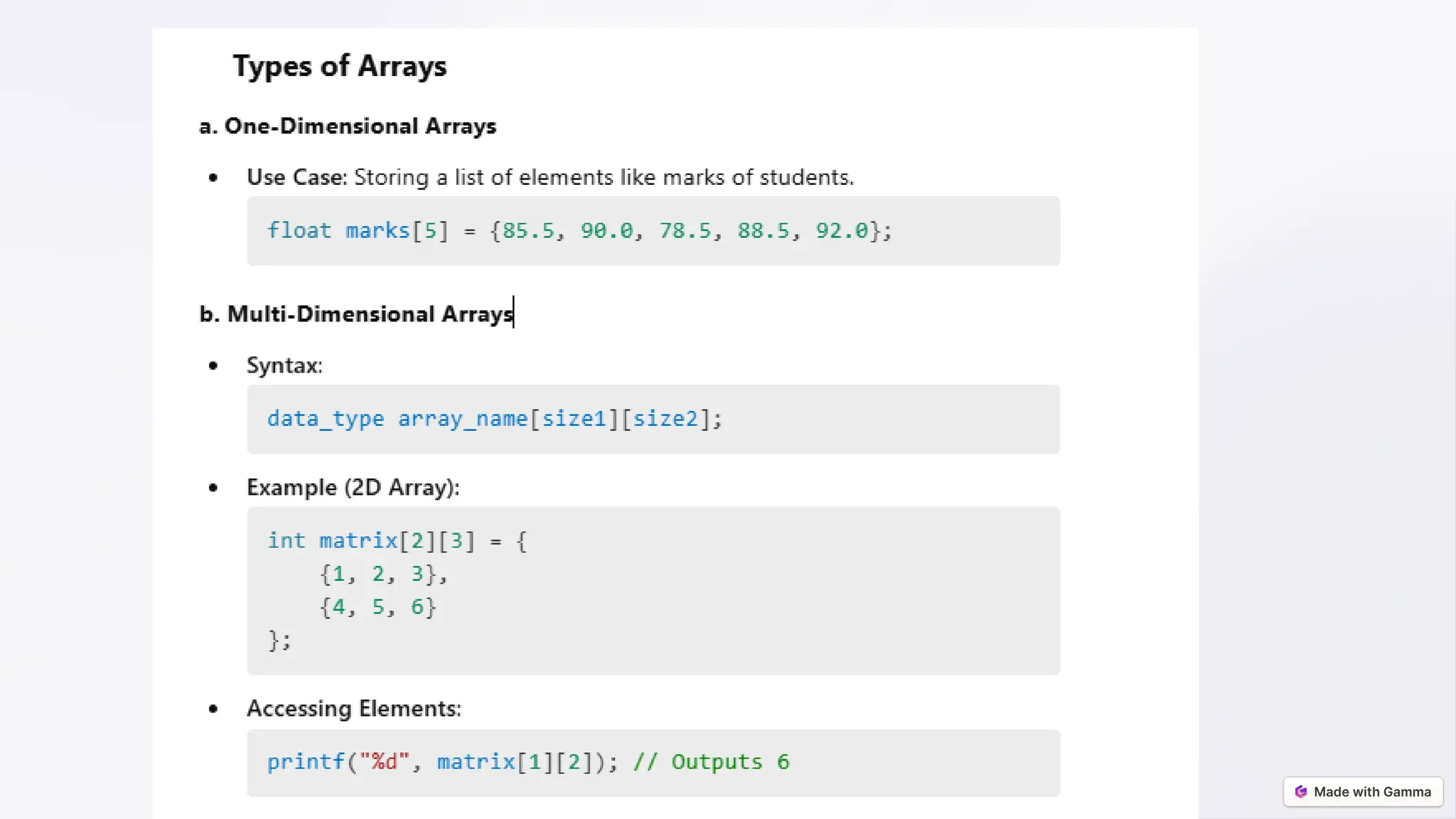
![Declaring and Initializing Arrays
Syntax
data_type array_name[size];
Examples
int numbers[5]; /* Declaration */
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; /* Initialization */](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-from-basics-to-advancedfinal-250105162248-4796559f/75/Arrays-from-Basics-to-Advanced-final-pptx-4-2048.jpg)
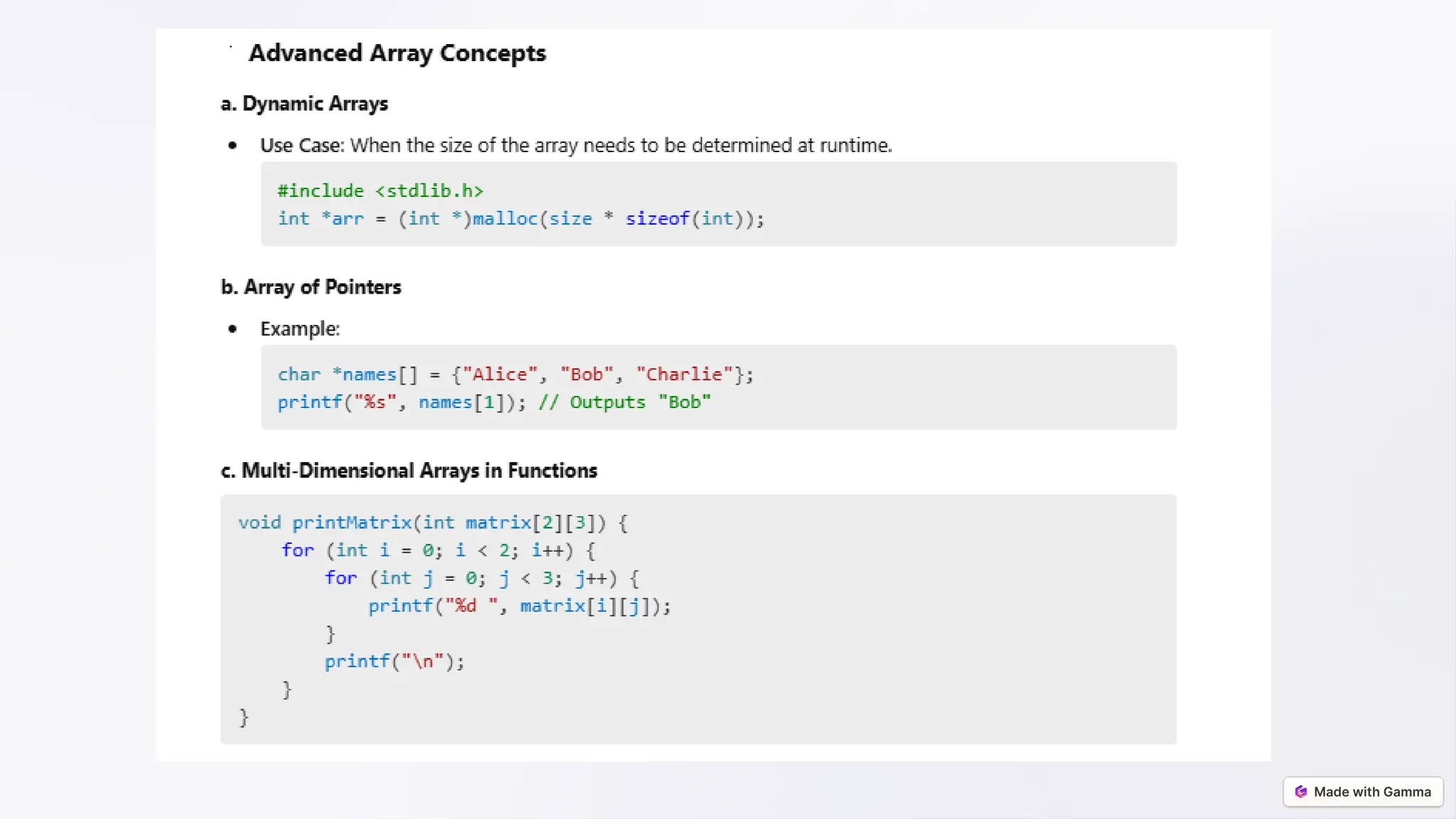
![Declaring and Initializing Arrays
Syntax:
data_type array_name[size];
Examples:
Declaration:
int numbers[5];
Initialization:
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
Partial Initialization:
int numbers[5] = {10, 20}; // Remaining elements are initialized to 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-from-basics-to-advancedfinal-250105162248-4796559f/75/Arrays-from-Basics-to-Advanced-final-pptx-5-2048.jpg)

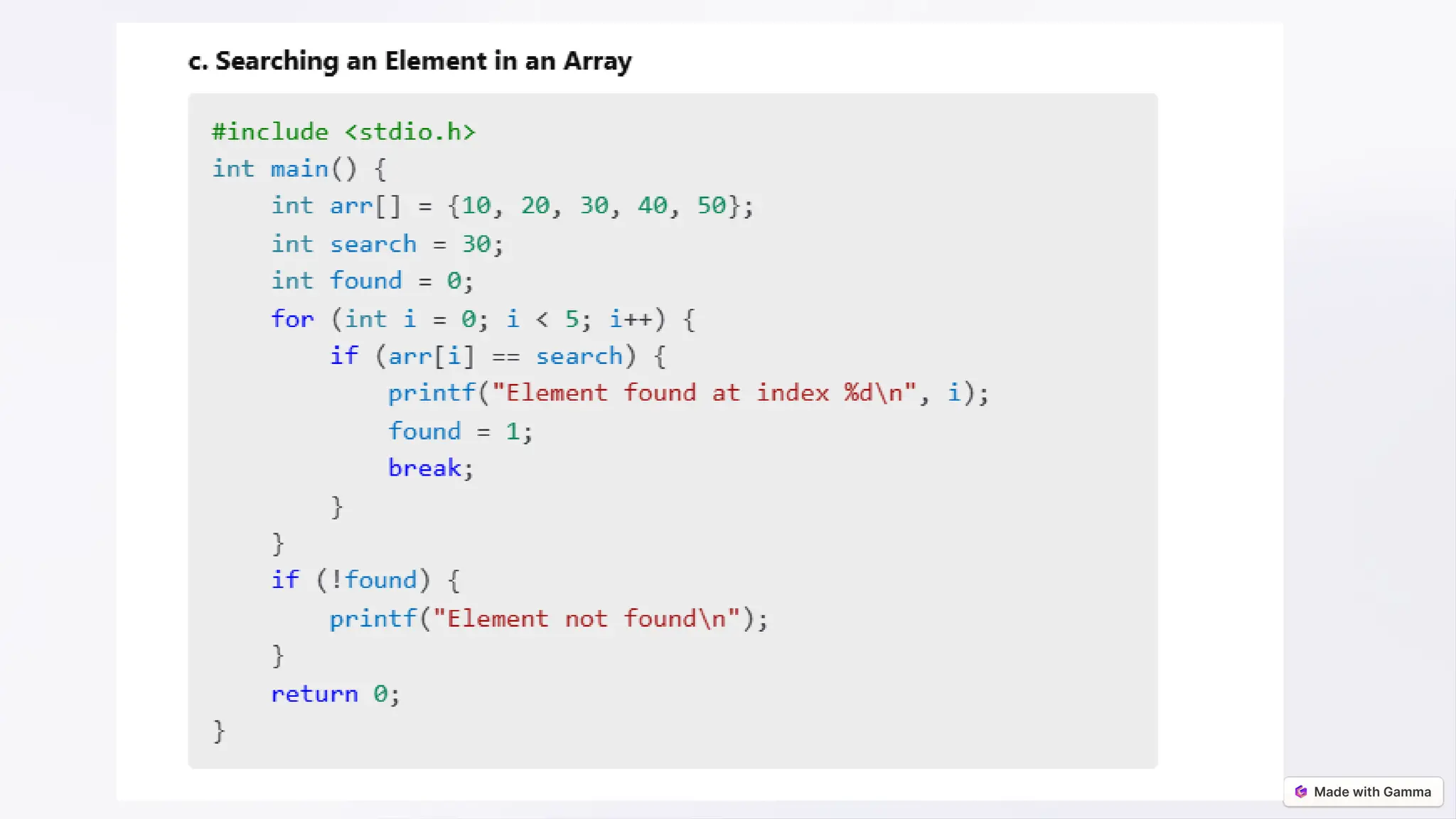
![Accessing Array Elements
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
Using Index: Array indexing starts from 0.
printf("%d", numbers[2]); // Outputs 30
Example Program:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("Element at index %d: %dn", i,
numbers[i]);
}
return 0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-from-basics-to-advancedfinal-250105162248-4796559f/75/Arrays-from-Basics-to-Advanced-final-pptx-8-2048.jpg)