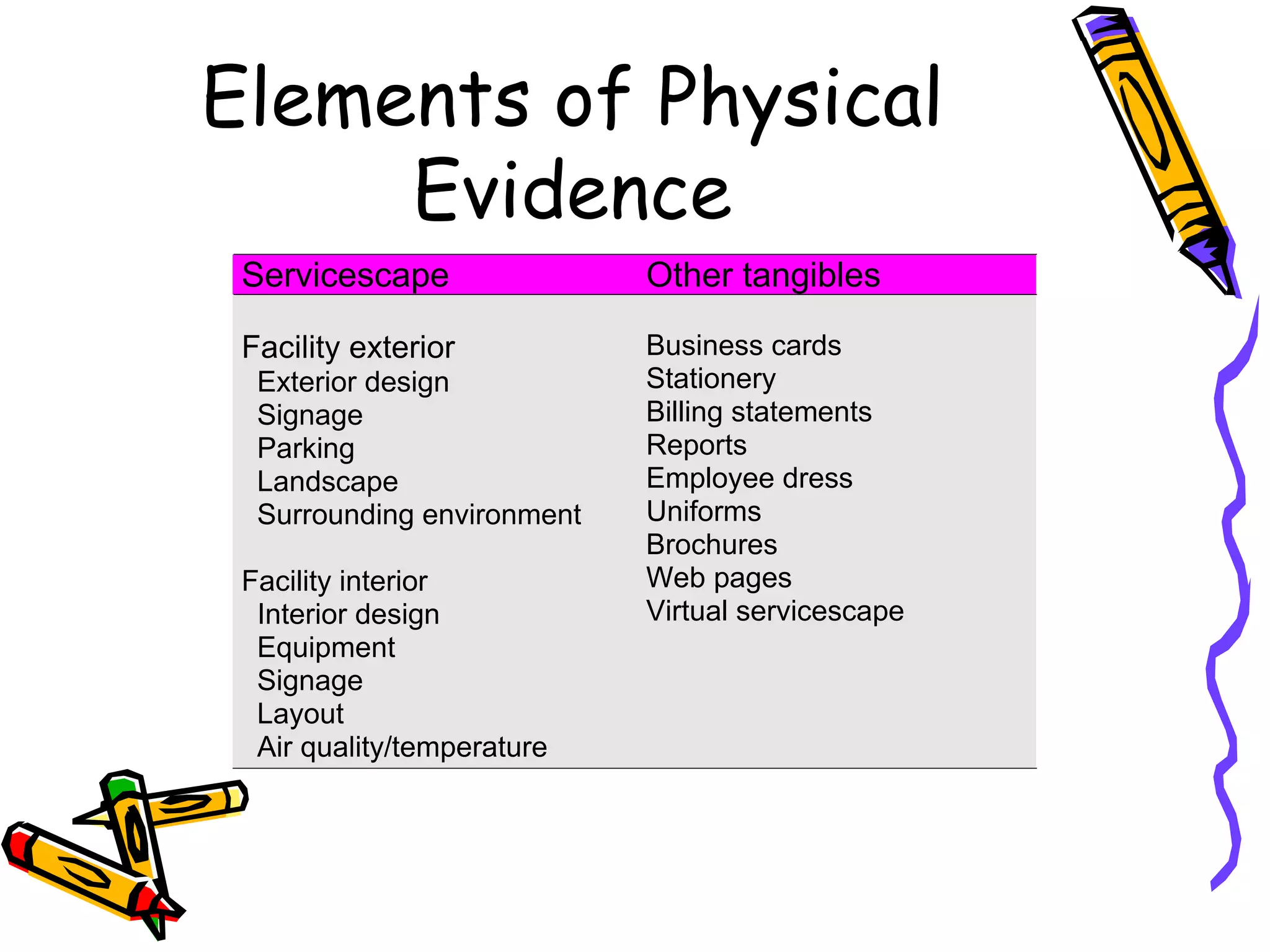
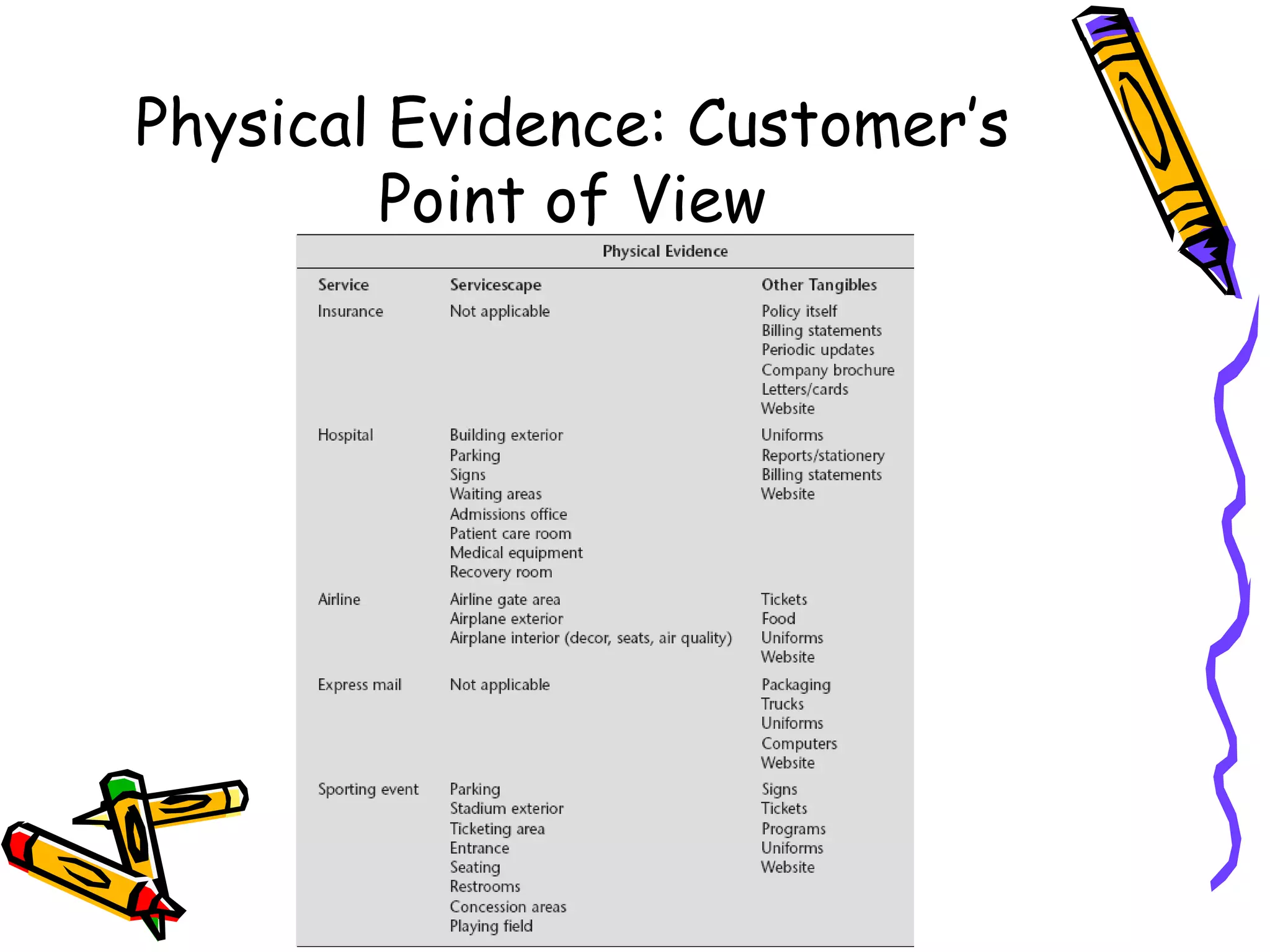
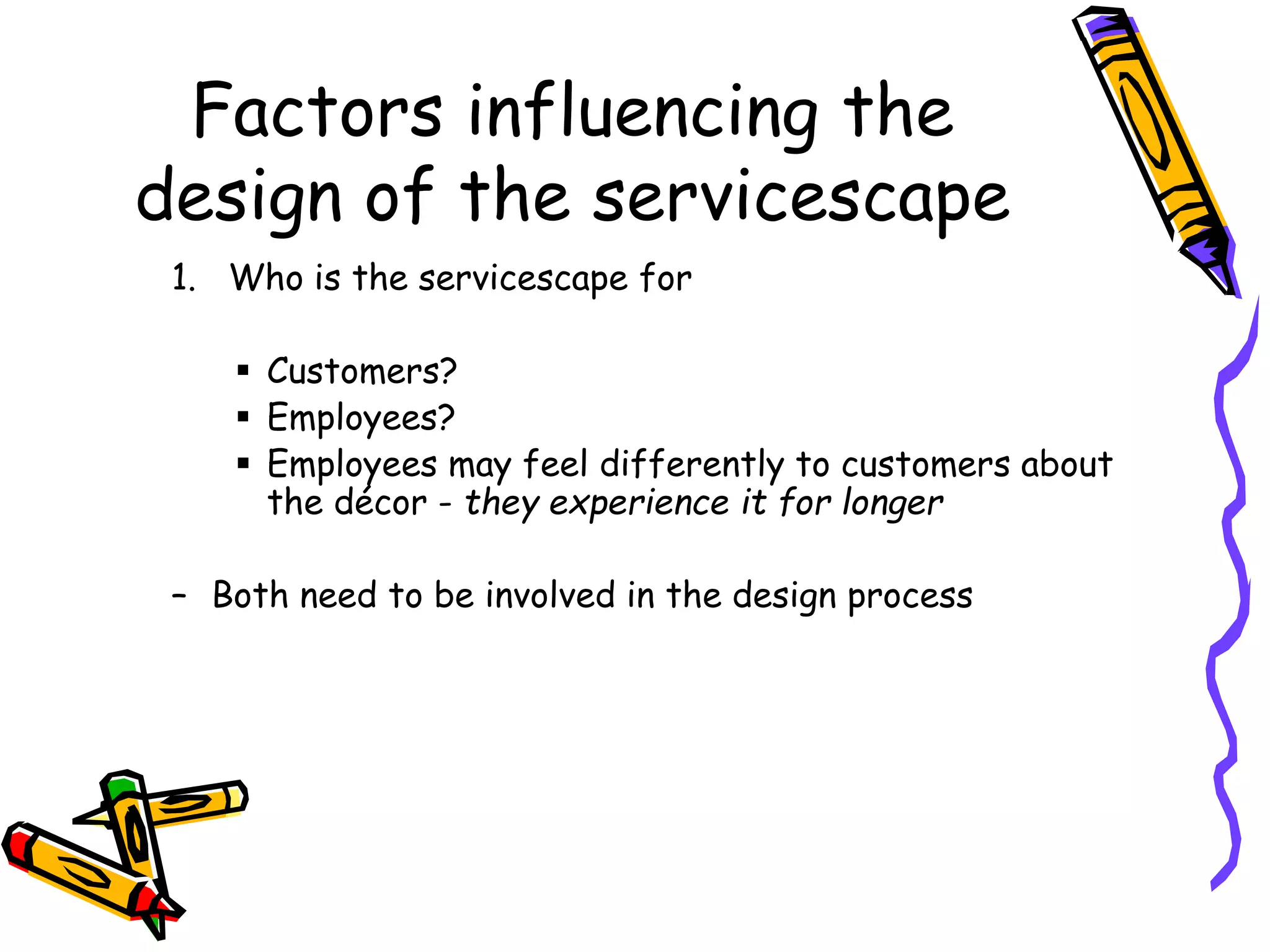
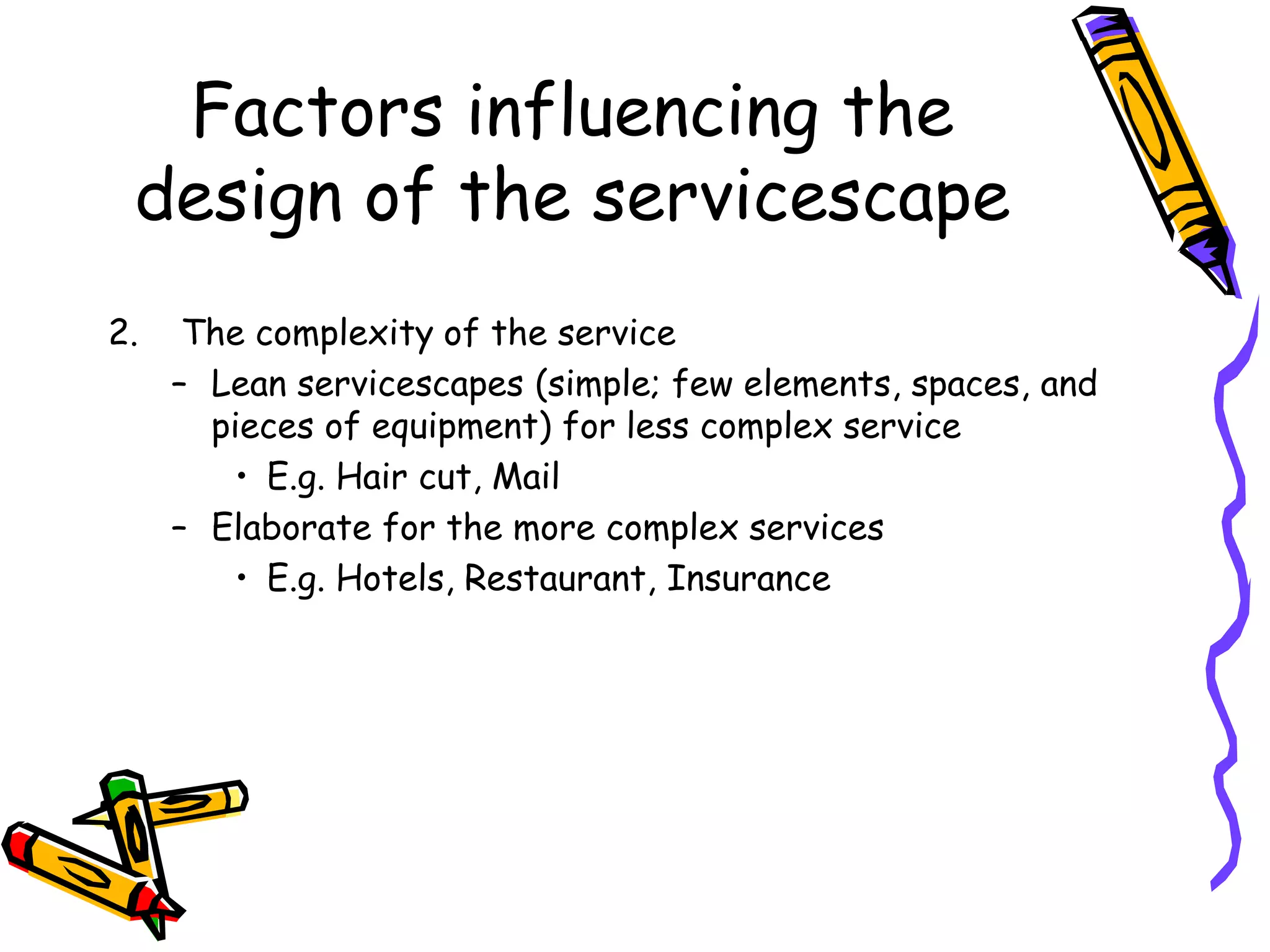
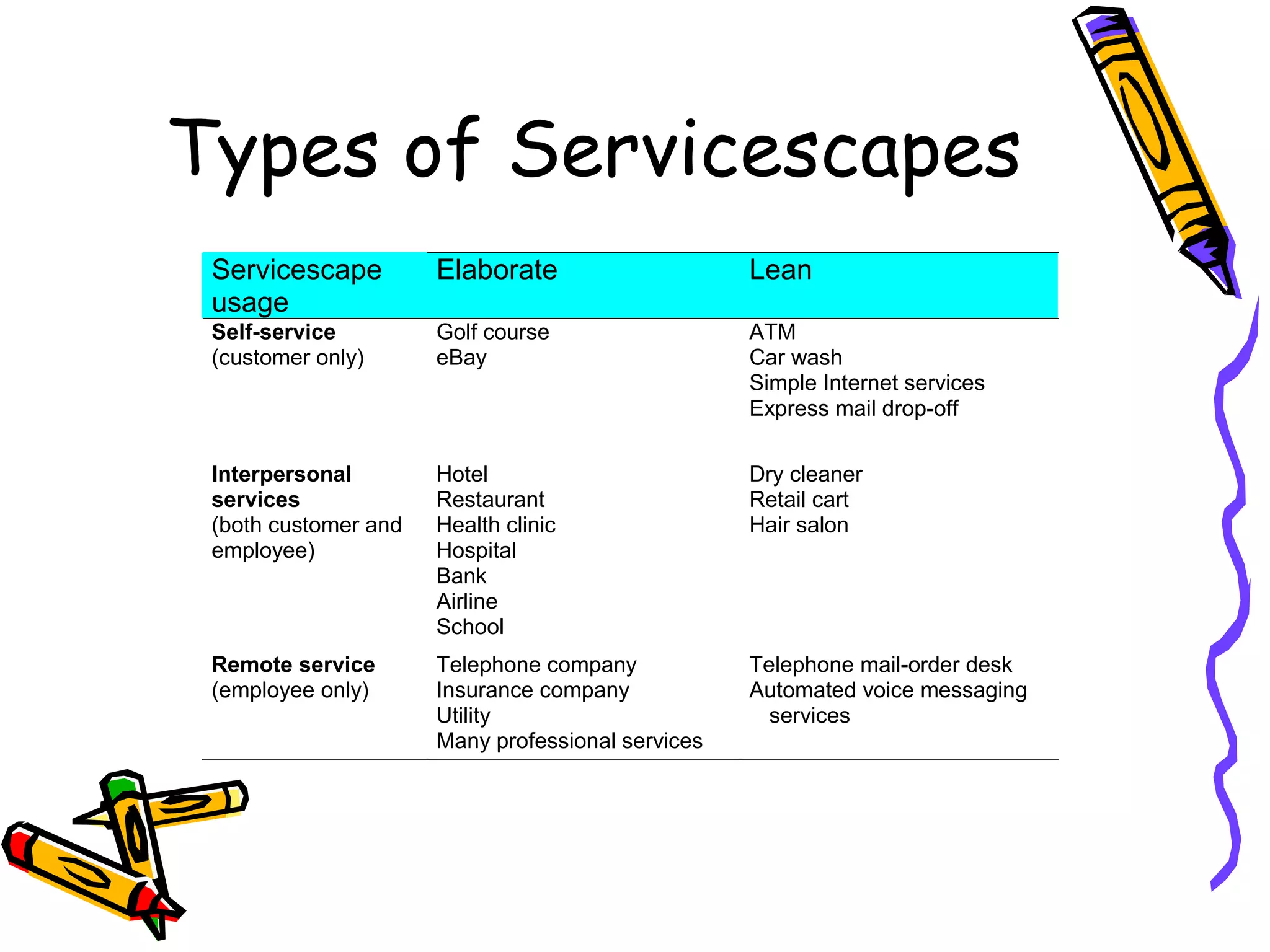
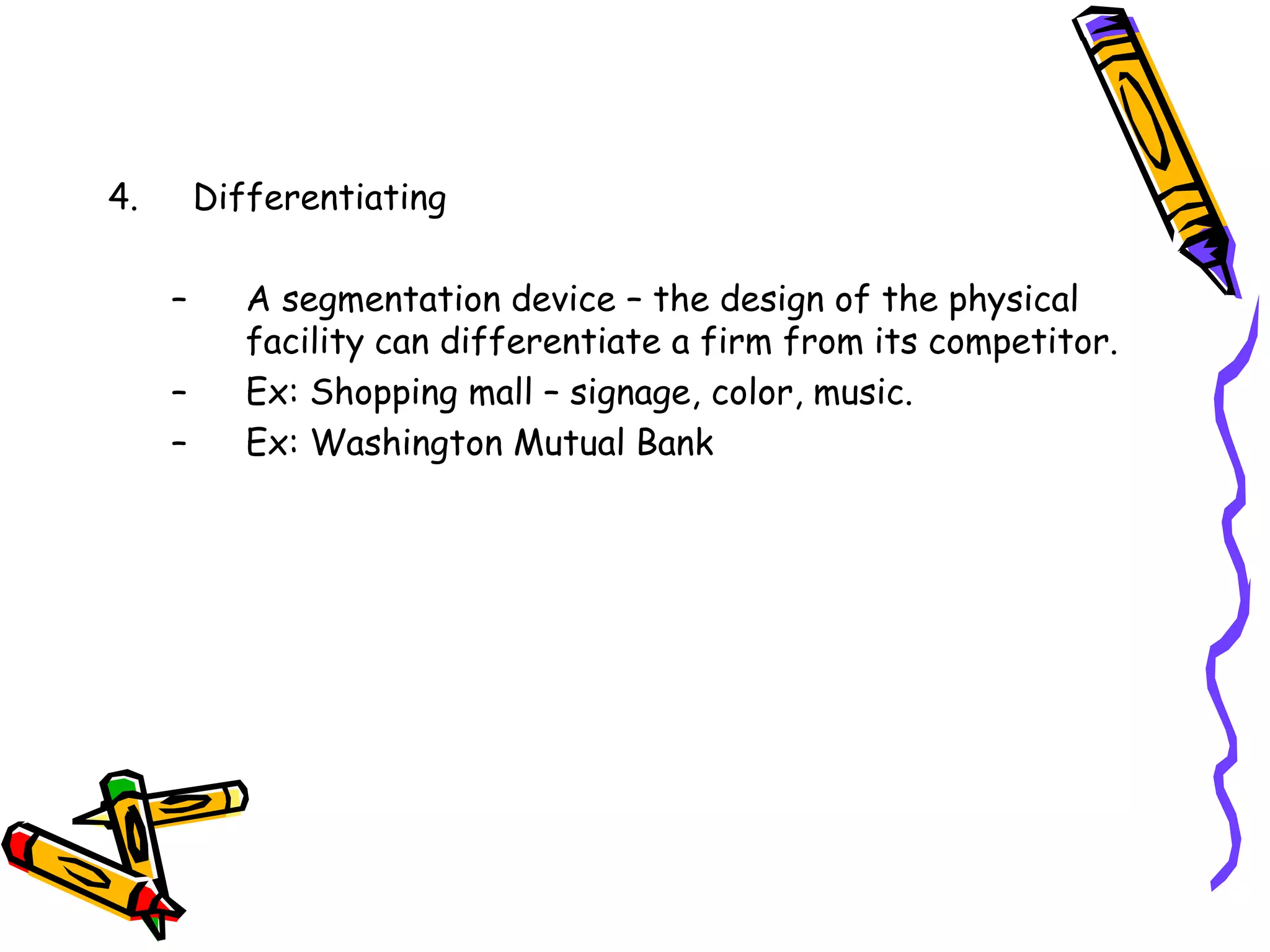
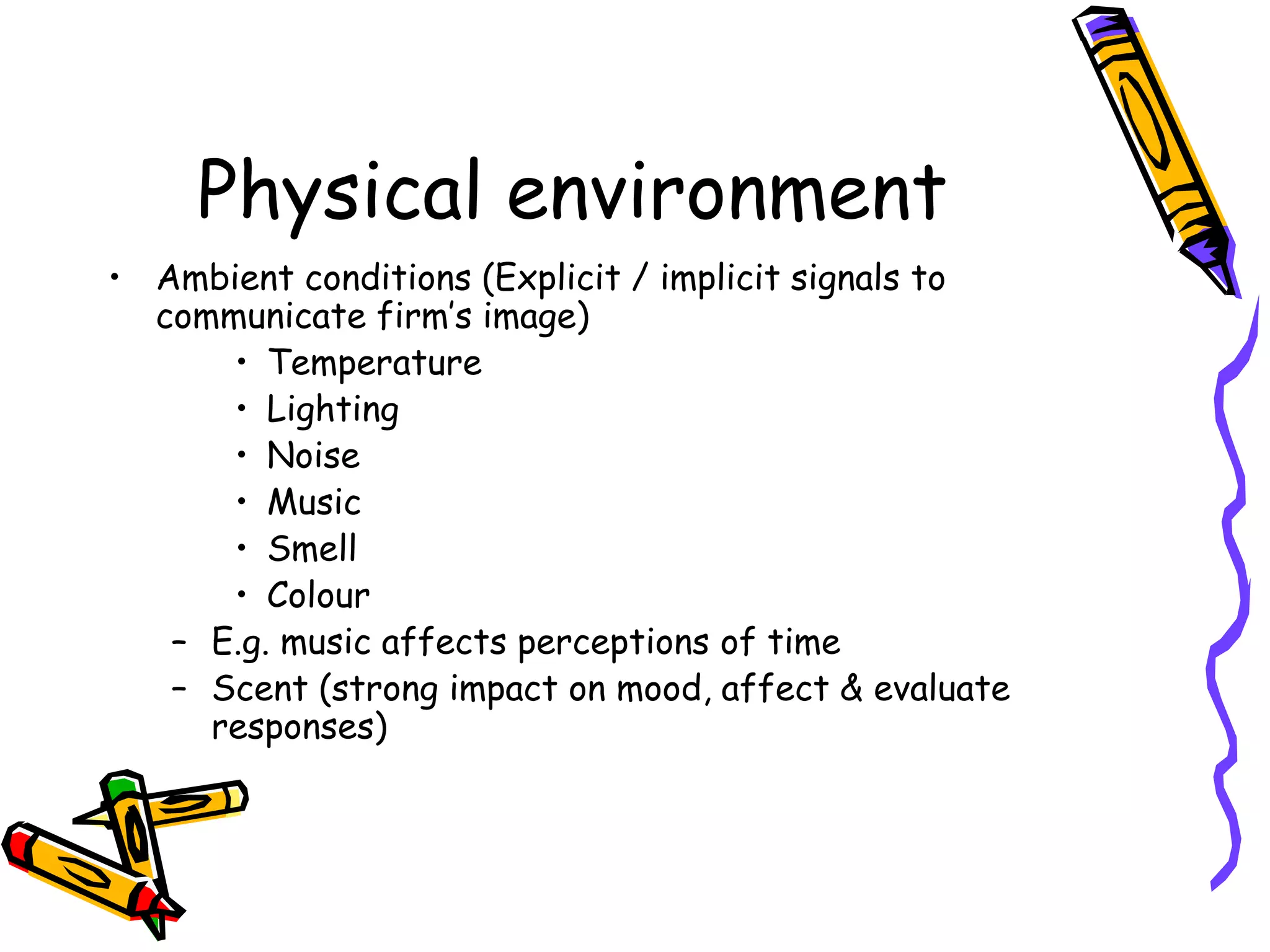
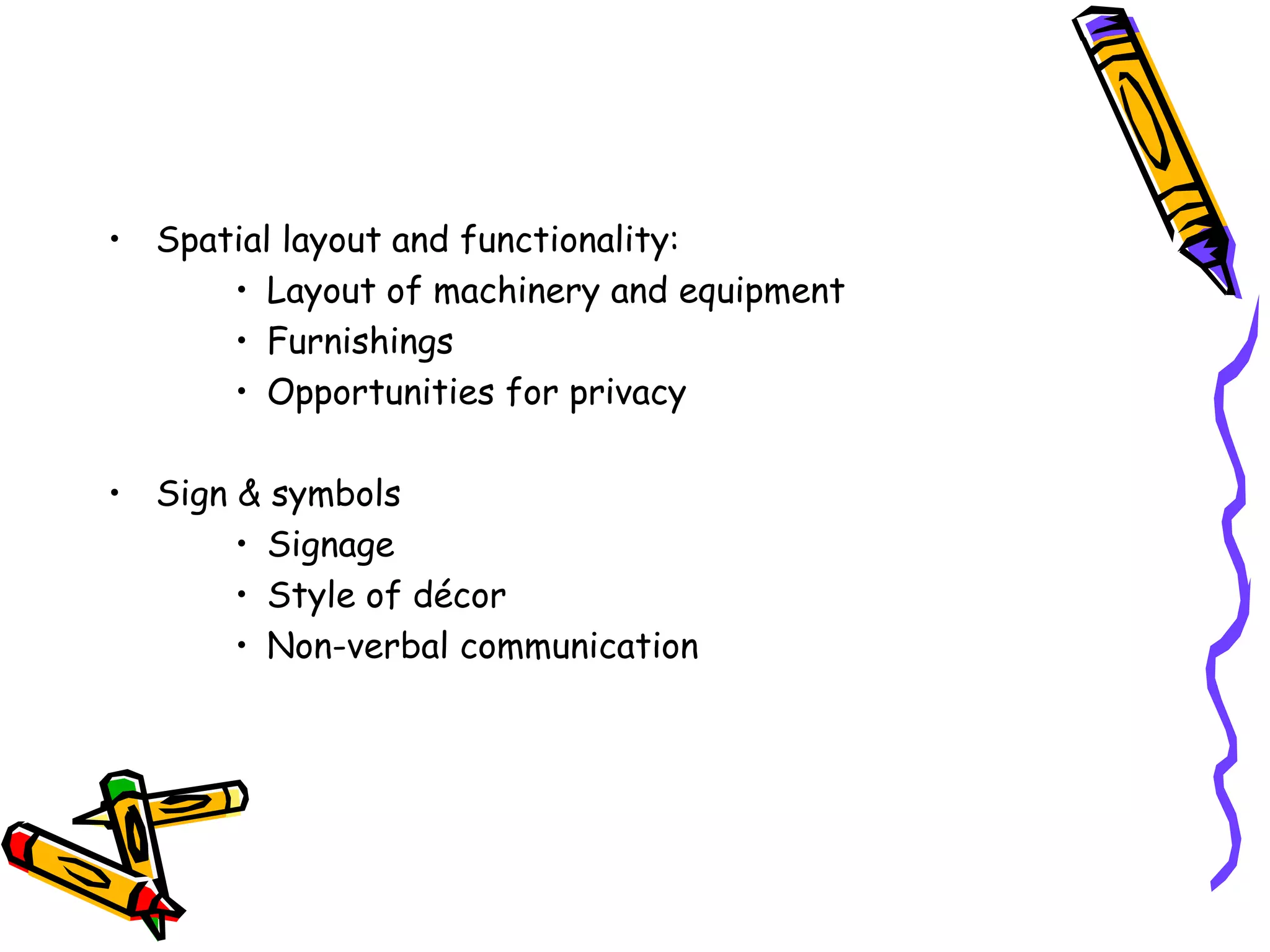
This document discusses the impact of physical evidence and servicescapes on customer perceptions. It defines servicescapes as the actual physical environment where a service is delivered and consumed. Servicescapes can include elements like facility exteriors and interiors, signage, equipment, and other tangible aspects of service delivery. The document explores how servicescapes affect customer and employee behaviors, and influence factors in designing servicescapes based on the complexity of the service. It outlines different types of servicescapes and their roles in packaging, facilitating, socializing, and differentiating a service. The document also discusses how physical environments can impact cognitive, affective, physiological, and social responses that influence customer behaviors.