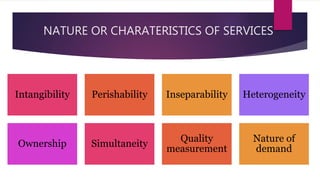
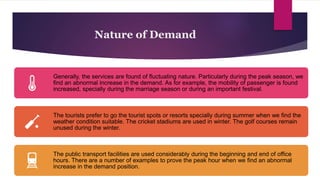
The document discusses trends in India's growing services sector. It notes that the services sector contributes over half of India's GDP and has attracted significant foreign investment. Within services, healthcare and tourism are growing rapidly. For healthcare, trends include rapid infrastructure growth, the role of traditional medicine, and rising medical tourism. Tourism is also expanding quickly in India, driven by trends like eco-tourism, heritage tourism, and adventure tourism. The services sector is a major source of employment and exporter of services in the Indian economy.