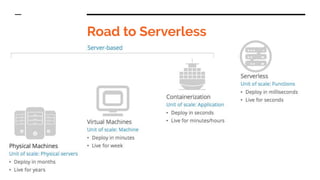
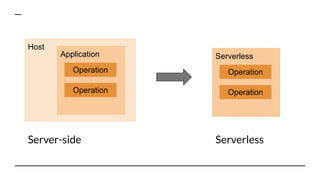
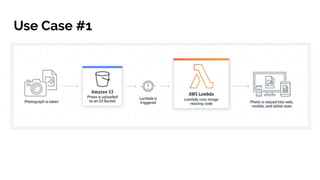
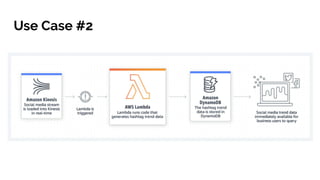
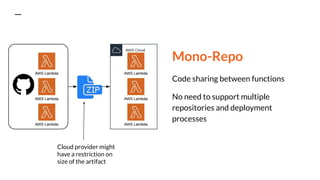
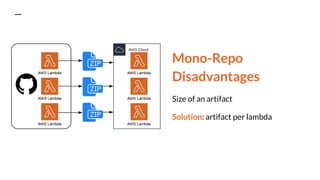
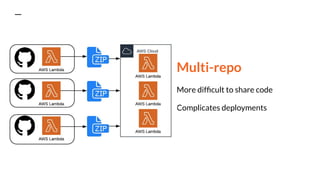
This document discusses serverless pitfalls, including code management challenges when using a mono-repo versus multi-repo approach, local testing difficulties, cold start performance issues, limited monitoring and logging with cloud providers, and vendor lock-in concerns. It also provides some solutions to these pitfalls like using unit tests, PR environments for integration testing, and sending logs and metrics to third party services. Overall, the document outlines several potential downsides to serverless architectures around code organization, testing, performance, observability, and flexibility.