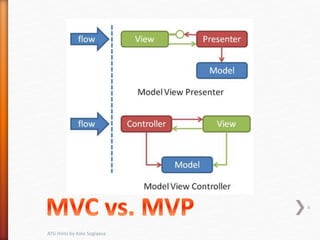
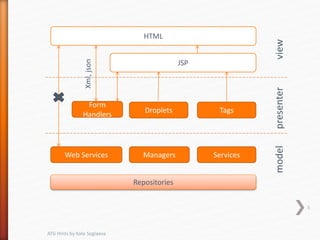
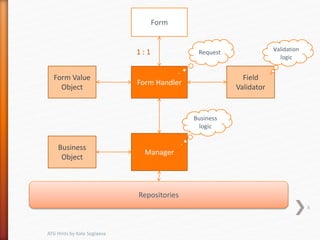
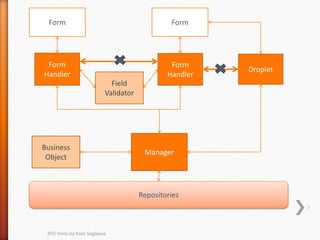
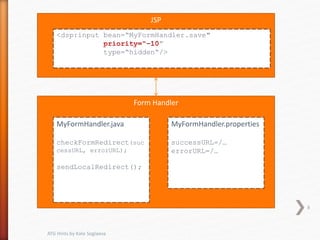
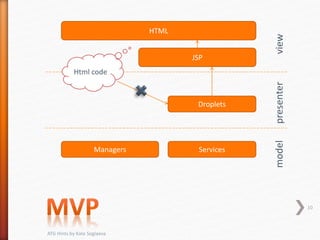
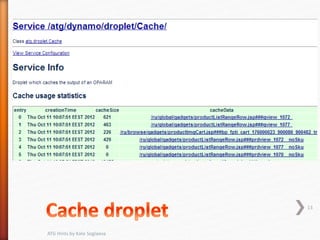
This document provides tips and hints for working with various ATG components, including Form Handlers, Droplets, Repositories, Services, and more. It discusses best practices for using these components, common issues that may arise, and examples of how to implement the components correctly. The document is meant to help developers optimize and troubleshoot their use of ATG.