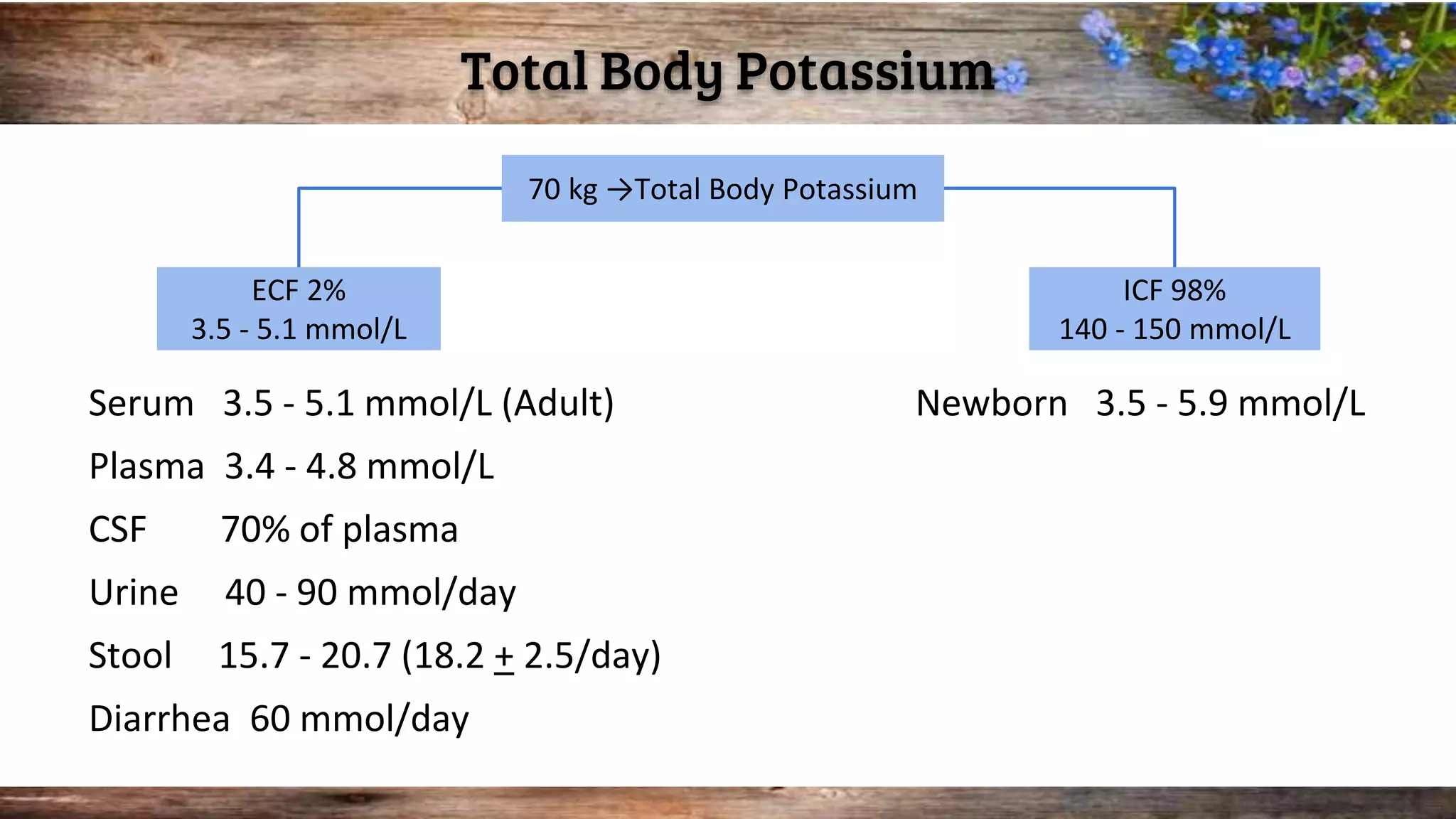
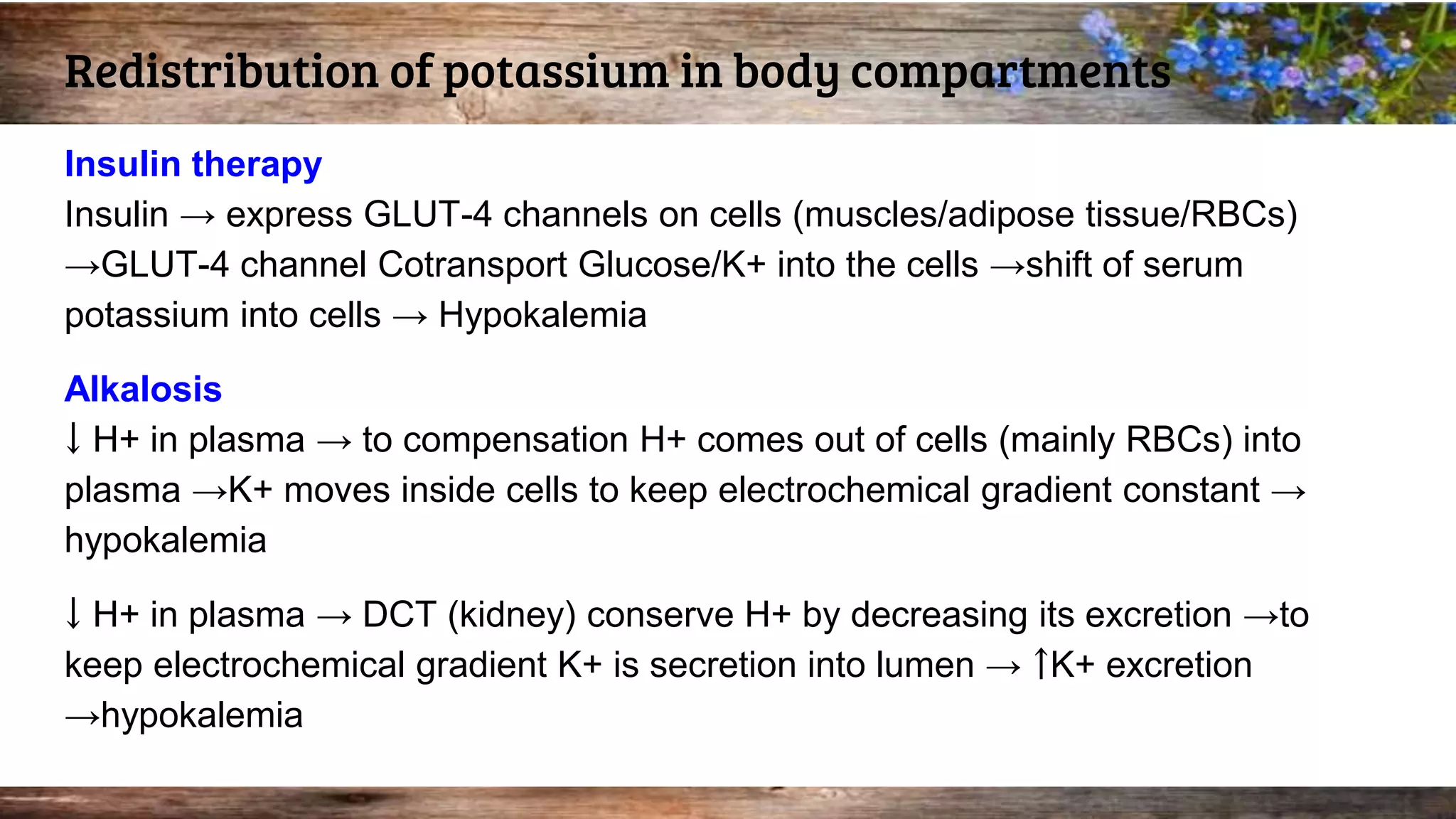
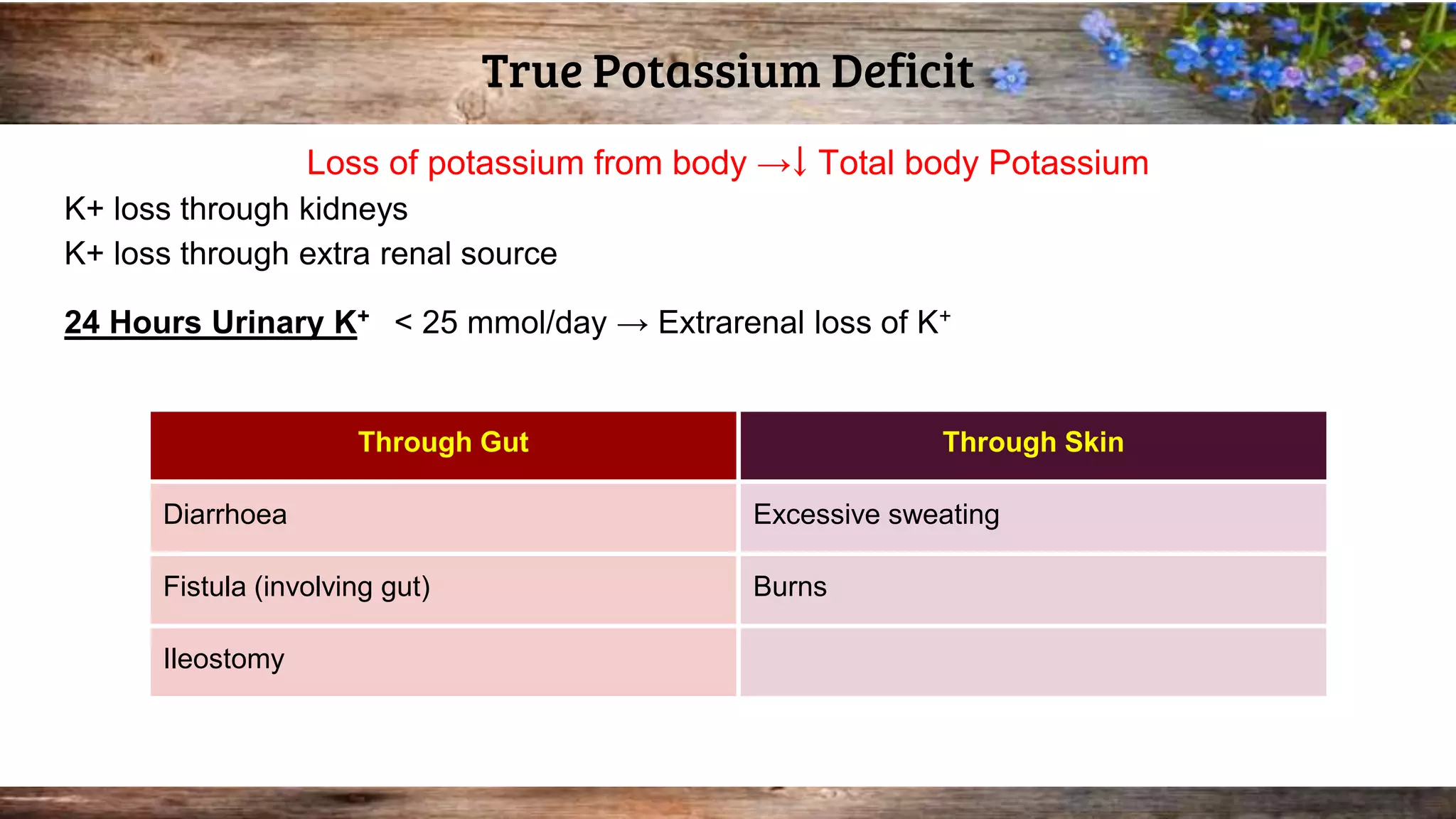
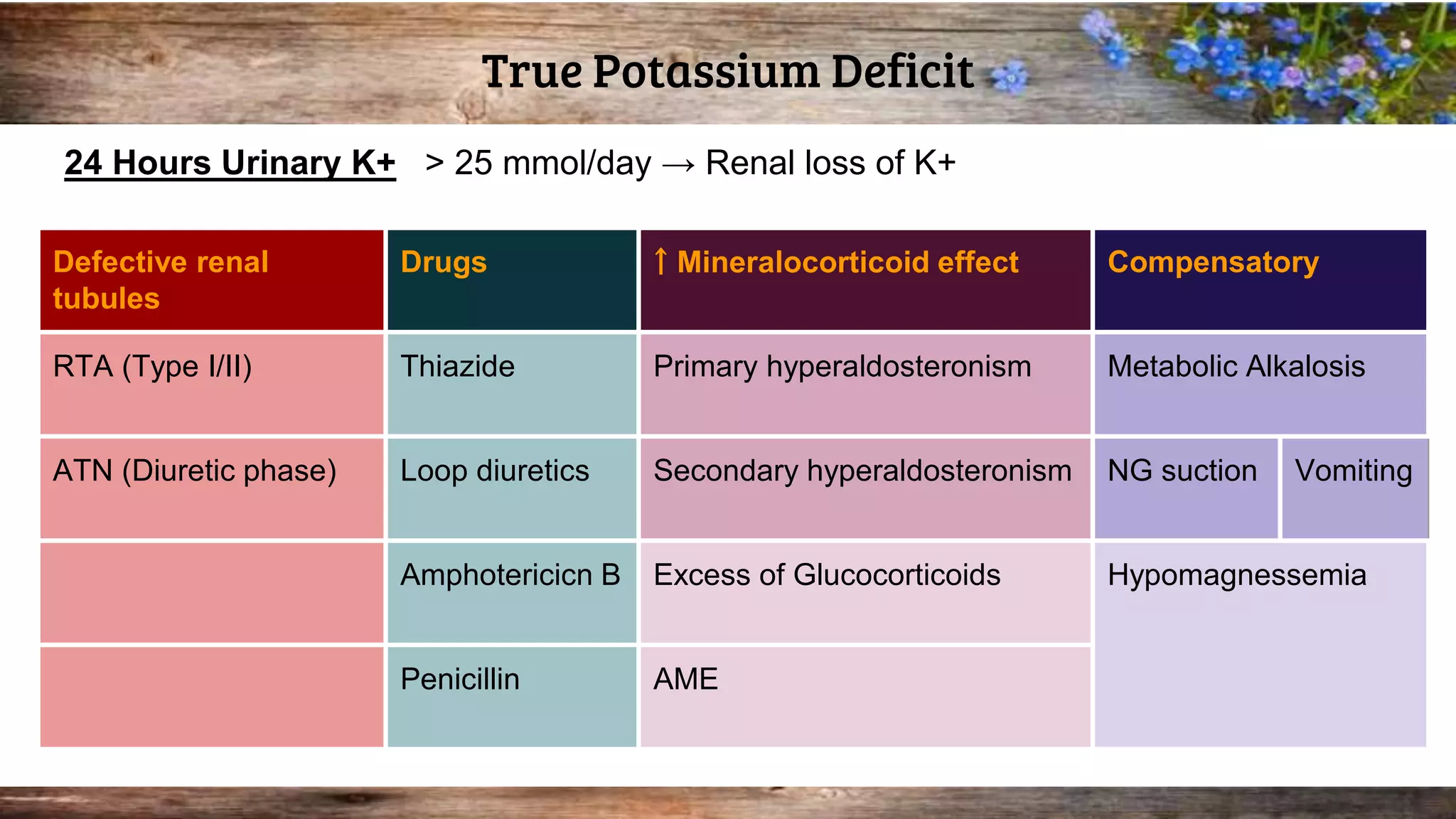
This document discusses serum potassium levels and their significance in both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia, outlining normal ranges, causes, and clinical effects associated with potassium imbalances. It highlights the importance of potassium in various physiological functions, and the impacts of pre-analytical errors and conditions such as refeeding syndrome. It also explains the differences between pseudohyperkalemia and reverse pseudohyperkalemia, along with causes and management strategies for potassium disorders.