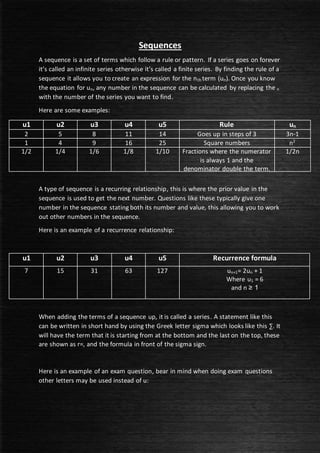
A sequence is a set of terms that follow a pattern or rule. If the sequence continues indefinitely, it is called an infinite sequence, otherwise it is finite. The rule allows you to write an expression for the nth term (un). Common examples include arithmetic sequences where the difference is constant, and geometric sequences where each term is obtained by multiplying the previous term by a fixed value. A recurrence relation defines each term in terms of the preceding ones. To solve problems involving sequences, you determine the expression for successive terms and find sums by adding terms up using the Greek letter sigma. Exam questions may involve finding individual terms, sums, or showing sums are divisible.