SenSocial is a middleware proposed to simplify the implementation of applications that integrate online social network (OSN) and mobile sensor data streams. It uses a publish-subscribe interaction model to allow applications to subscribe to different data streams. This reduces programming effort and lines of code compared to not using SenSocial. Two prototype applications demonstrated reduced lines of code by 9 and 24 times when using SenSocial. The paper argues that integrating OSNs and sensor data can provide richer contextual information and SenSocial is presented as a solution to simplify building such ubiquitous computing applications.













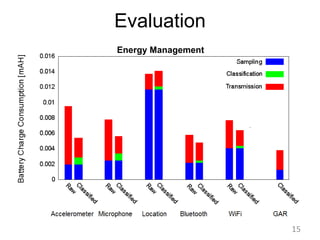
![Evaluation
CPU consumption with varying number streams
Average battery consumption with varying number of OSN actions
OSN actions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Charge consumed [μAH] 51.7 97.1 142.5 187.8 233.2 278.5 324.3
Note: the above OSN actions occurred within 20 minute time period and
each triggered remote sampling of all five supported sensor modalities.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sensocial-141214101709-conversion-gate01/85/SenSocial-16-320.jpg)






