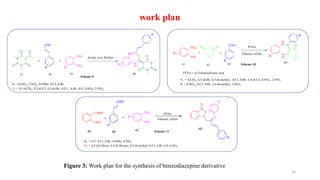
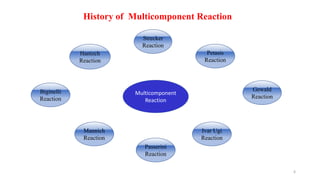
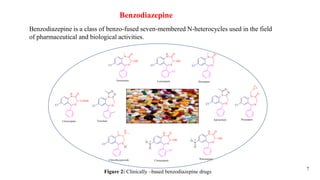
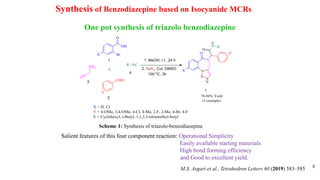
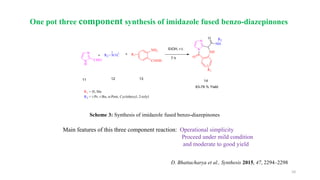
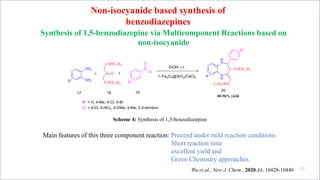
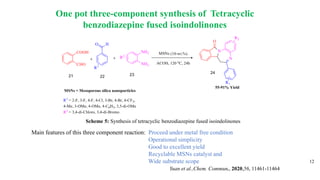
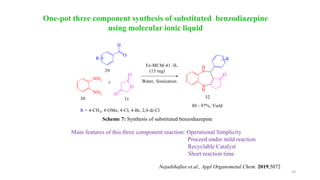
This document summarizes a research seminar presentation on the synthesis of benzodiazepine derivatives using multicomponent reactions. The presentation outlines the advantages of multicomponent reactions over traditional multistep reactions, provides a history of notable multicomponent reactions, and summarizes recent research using isocyanide- and non-isocyanide-based multicomponent reactions to synthesize various benzodiazepine derivatives in one pot with good yields. It concludes by outlining future work plans to synthesize additional benzodiazepine derivatives and acknowledges the presenter's supervisor and department for their support.




![15
One pot three-component synthesis of Benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-
3-ones via Dual C−O Bond Cleavage
Main features of this three component reaction: Proceed under mild reaction condition
Broad substrate scope and
has potential applications in chemistry and medicines
Geng et al., Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 18, 7504–7508
Scheme 8: Synthesis of benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-3-ones](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarpresentationonheterocyclicscaffold-220103085118/85/Seminar-presentation-on-heterocyclic-scaffold-15-320.jpg)