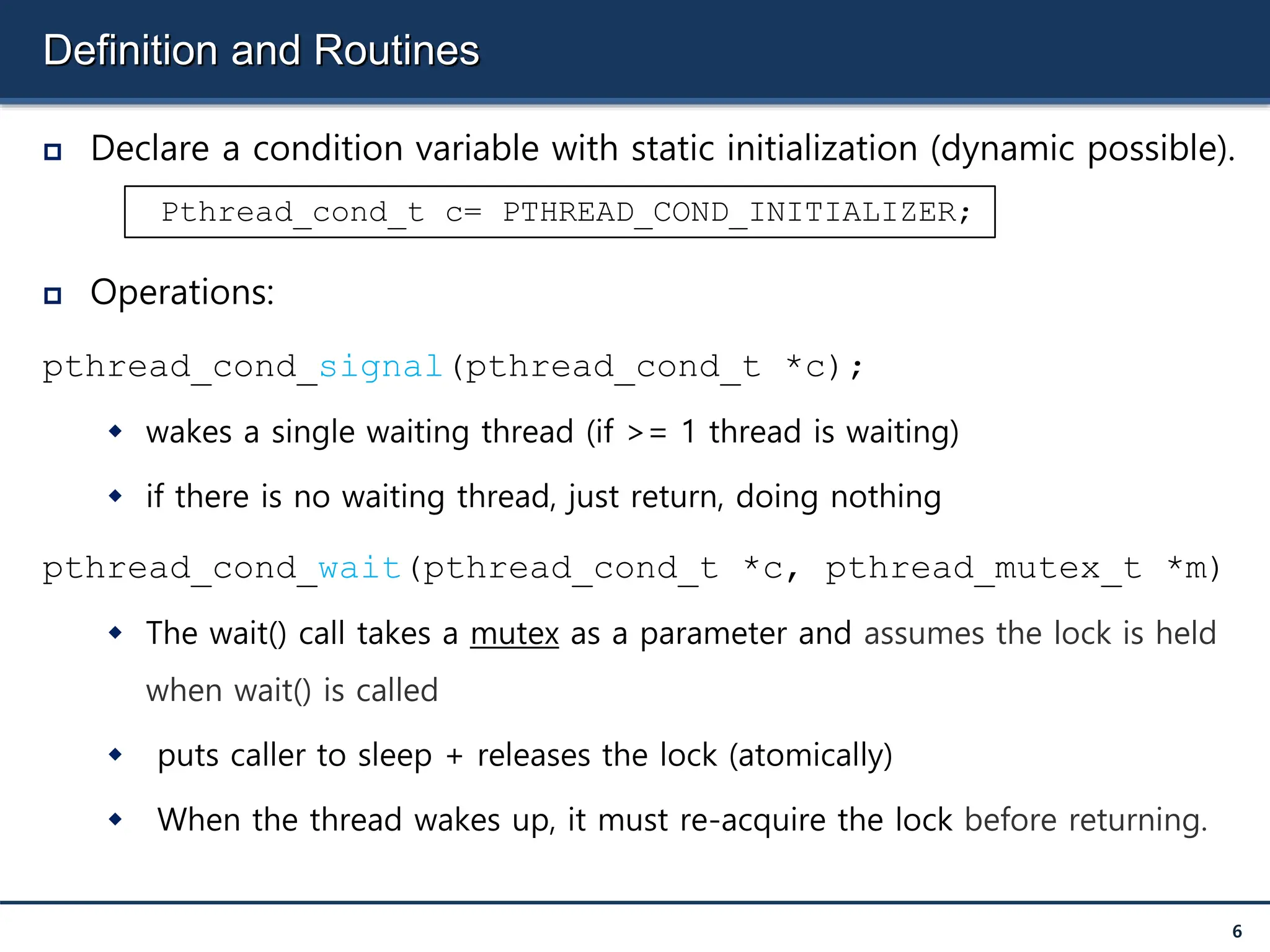
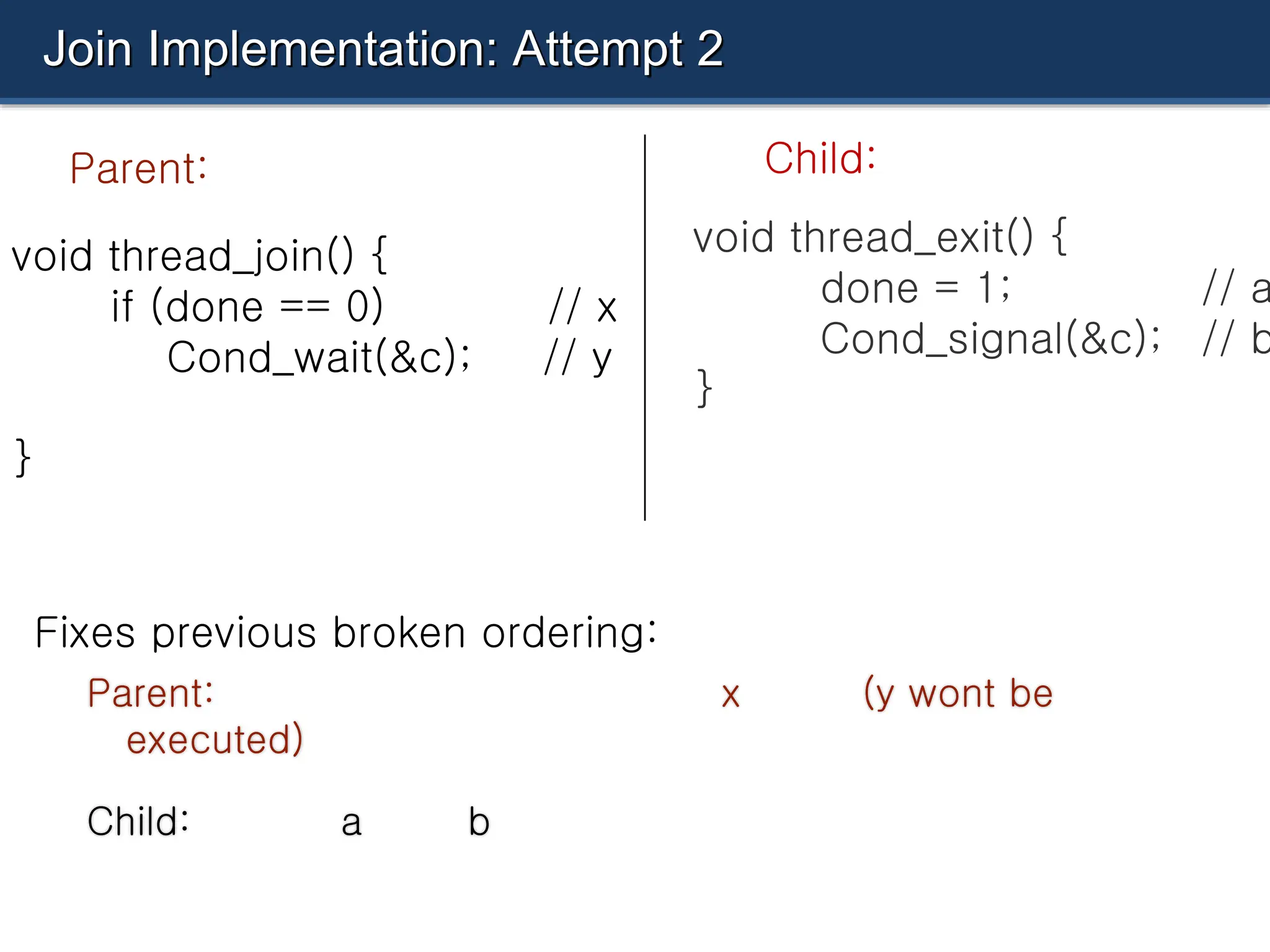
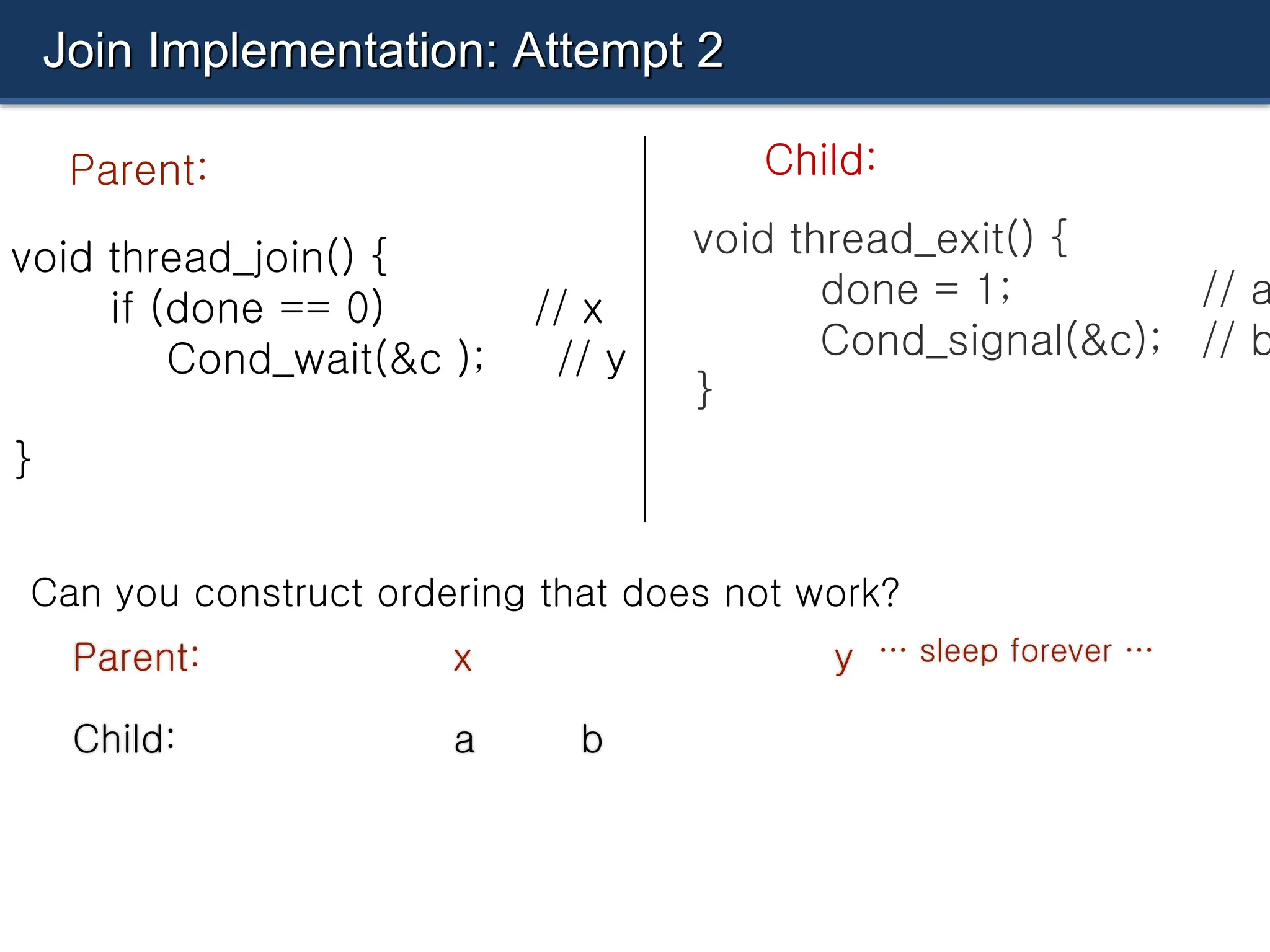
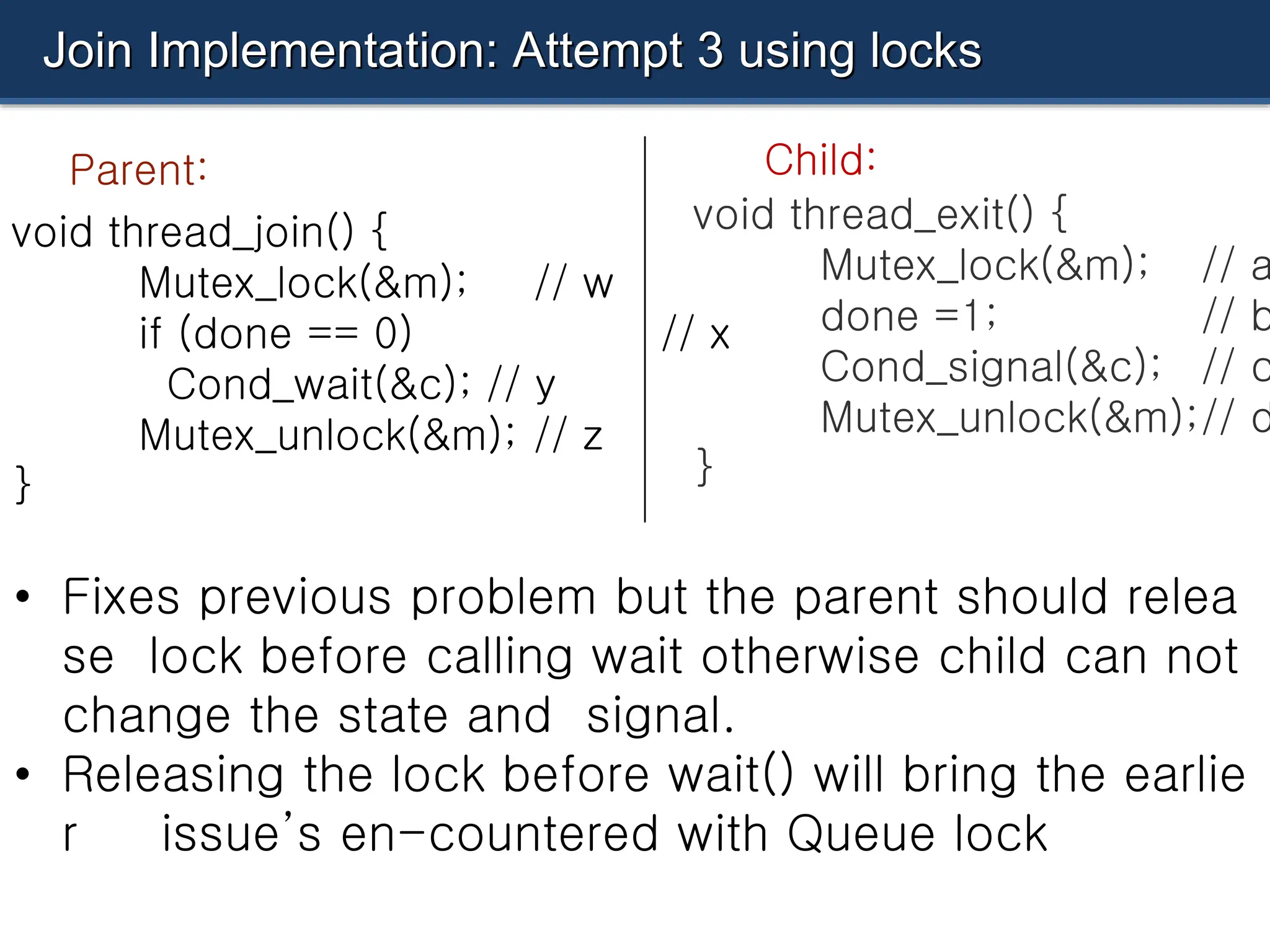
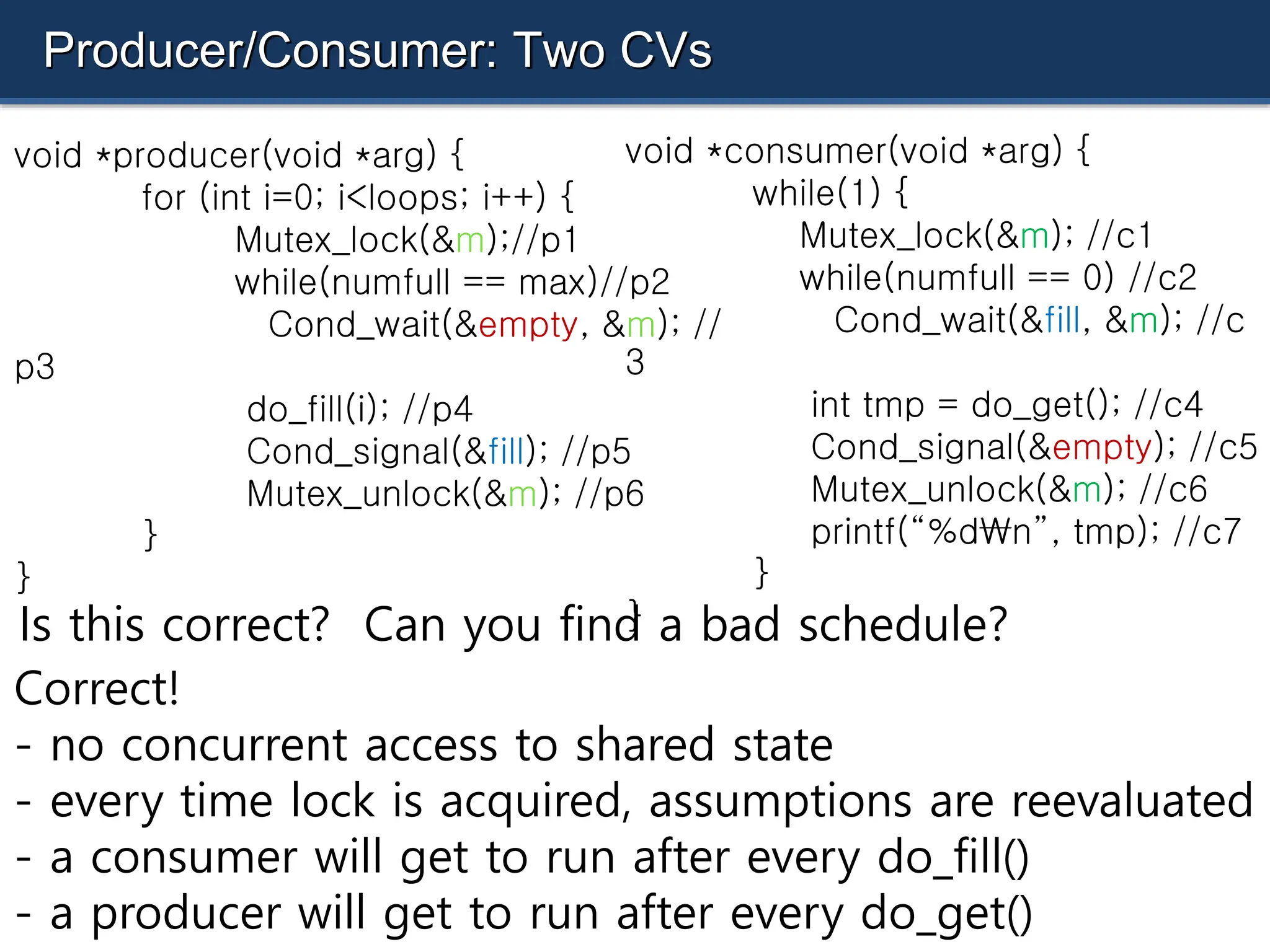
The document discusses condition variables as a synchronization mechanism in multithreading, enabling threads to wait for specific conditions to be met before continuing execution. It outlines the implementation of join operations using condition variables to avoid inefficient spin-waiting and provides examples of producer-consumer problems to illustrate the use of condition variables in managing resource access between concurrent threads. Ultimately, the document emphasizes the importance of state management alongside condition variables to ensure efficient synchronization.


![Ordering Example: Join
3
1 void *child(void *arg) {
2 printf("childn");
3 // XXX how to indicate we are done?
4 return NULL;
5 }
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
8 printf("parent: beginn");
9 pthread_t c;
10 Pthread_create(&c, NULL, child, NULL);
11 // XXX how to wait for child?
12 printf("parent: endn");
13 return 0;
14 }
parent: begin
child
parent: end
A Parent Waiting For Its Child
What we would like to see here is:
how to implement join()?
how to implement exit()?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-3-2048.jpg)
![Parent waiting for child: Spin-based Approach
This is hugely inefficient as the parent spins and wastes CPU time.
4
1 volatile int done = 0;
2
3 void *child(void *arg) {
4 printf("childn");
5 done = 1;
6 return NULL;
7 }
8
9 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
10 printf("parent: beginn");
11 pthread_t c;
12 Pthread_create(&c, NULL, child, NULL);
13 while (done == 0)
14 ; // spin
15 printf("parent: endn");
16 return 0;
17 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-4-2048.jpg)



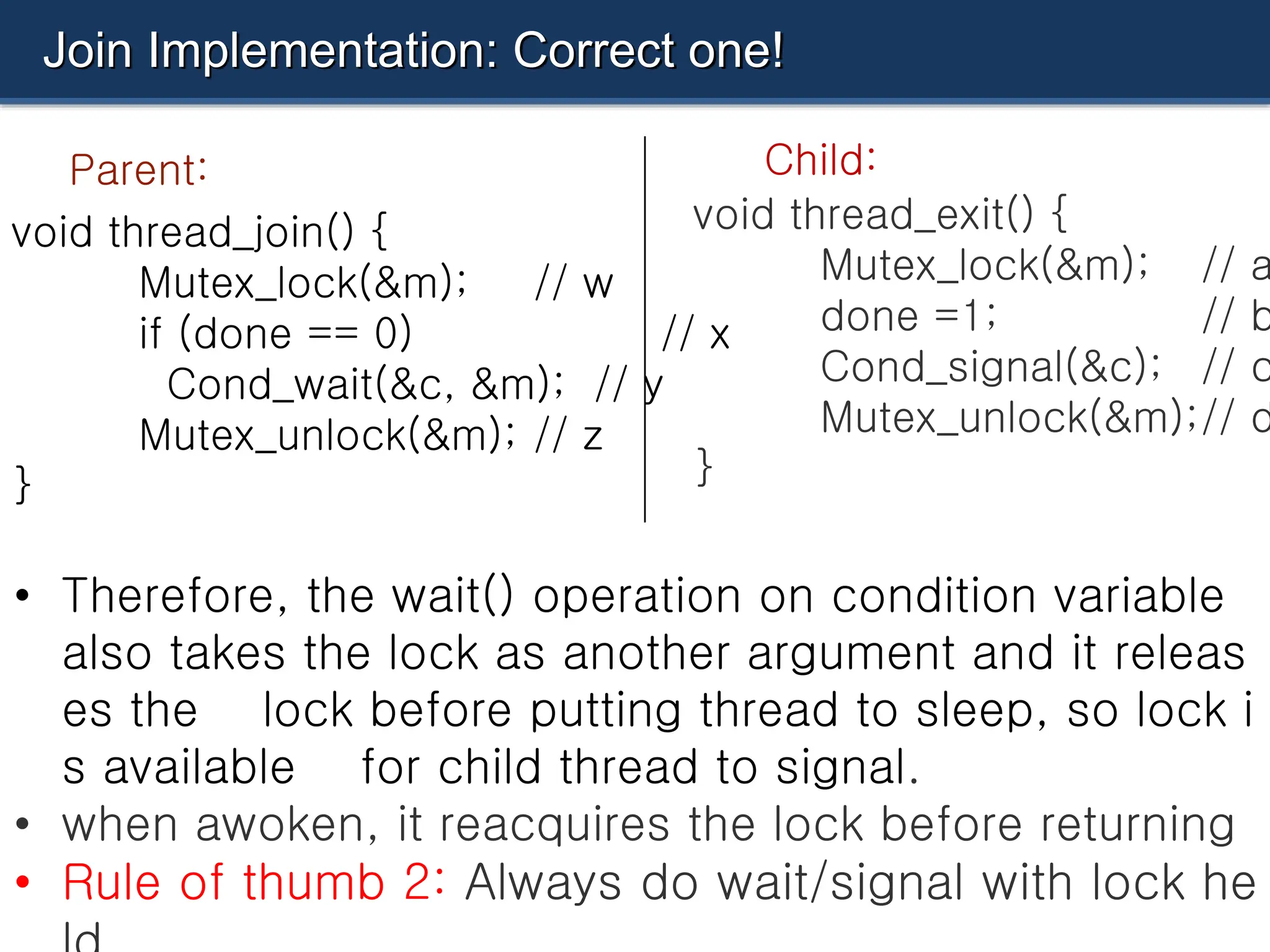
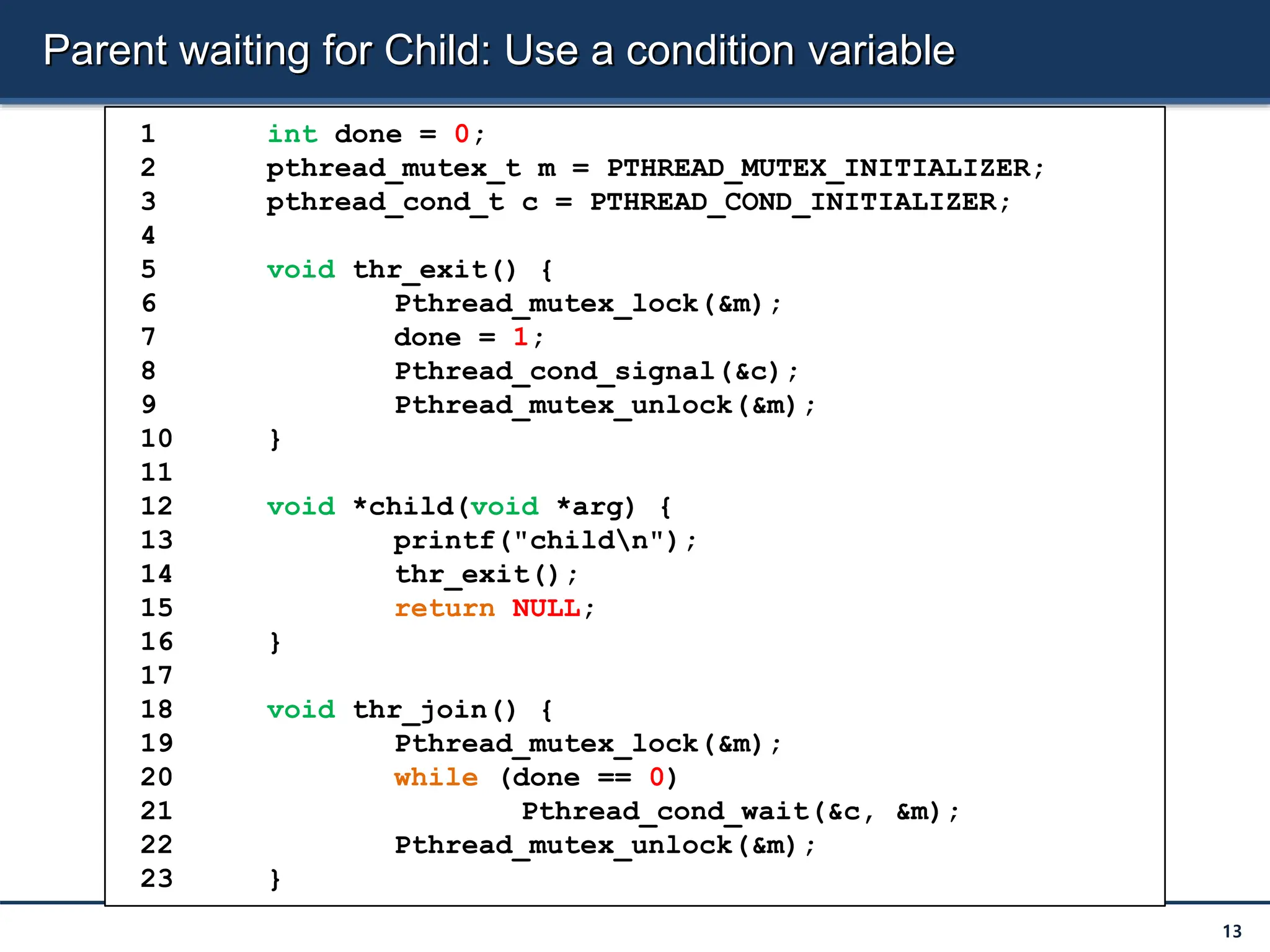
![Parent waiting for Child: Use a condition variable
14
(cont.)
25 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
26 printf("parent: beginn");
27 pthread_t p;
28 Pthread_create(&p, NULL, child, NULL);
29 thr_join();
30 printf("parent: endn");
31 return 0;
32 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-14-2048.jpg)

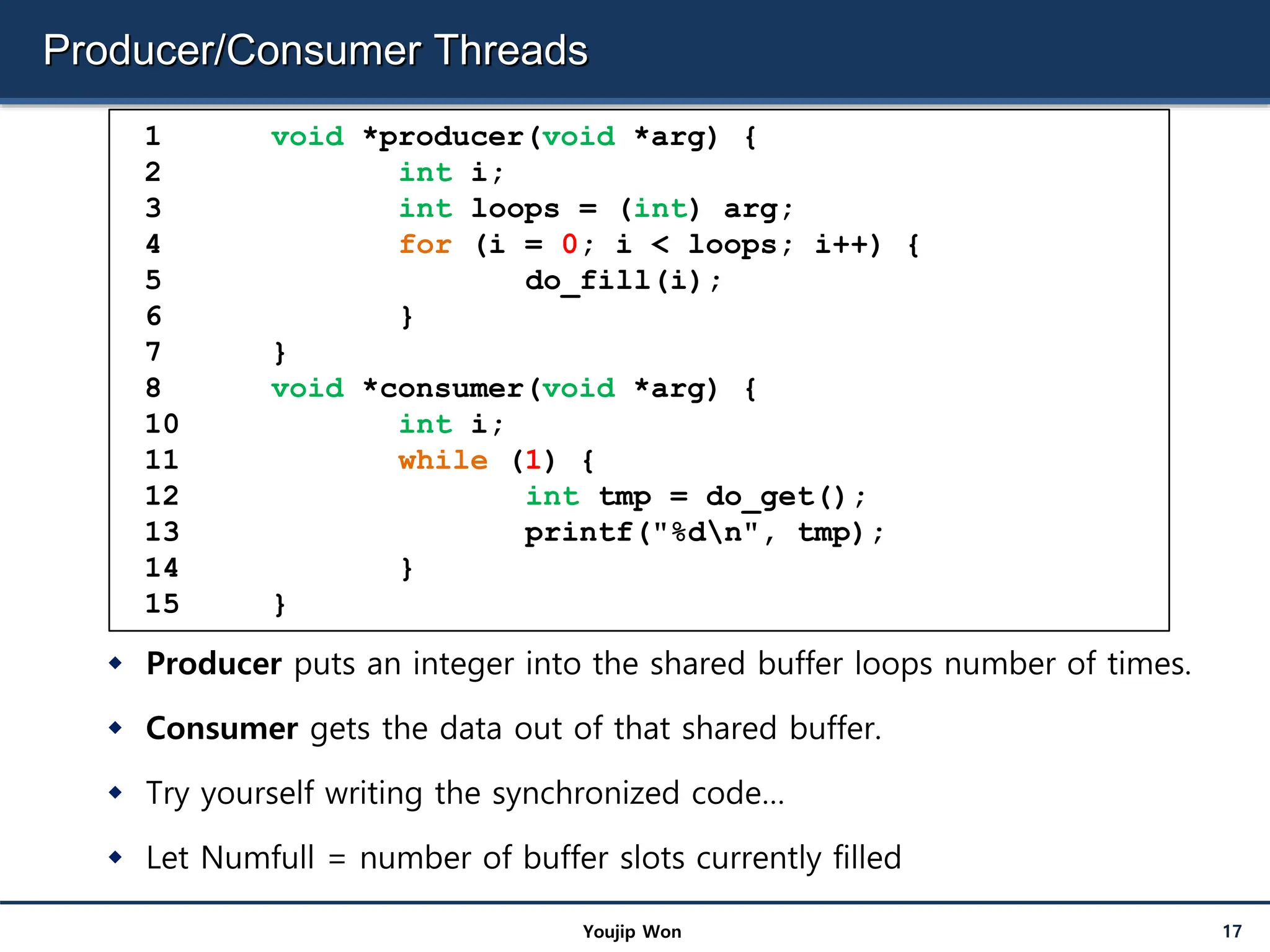
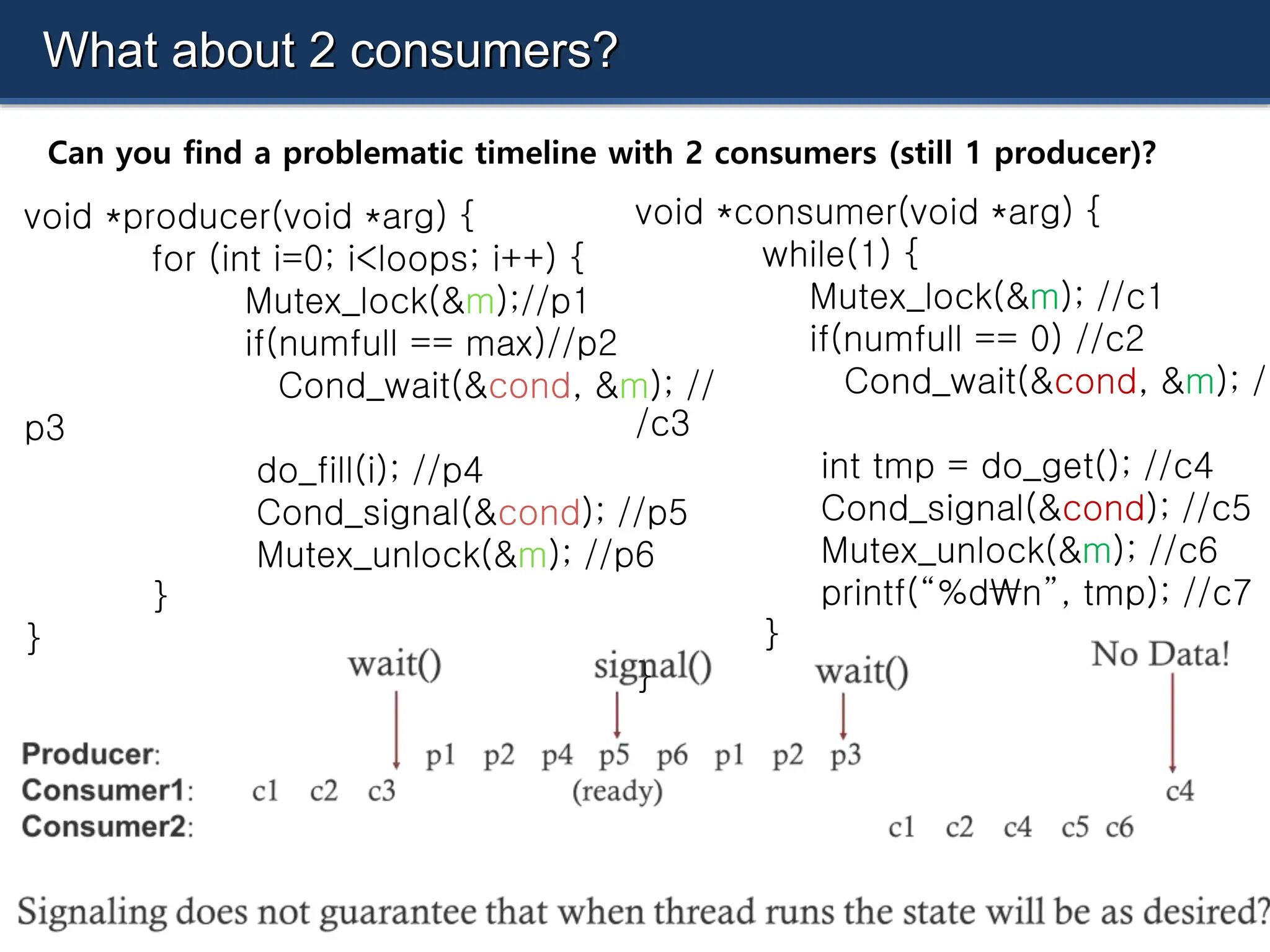
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNABLE] [RUNNING]
numfull=0
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-18-2048.jpg)
![[RUNNABLE] [RUNNING]
numfull=0
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-19-2048.jpg)
![[RUNNABLE] [RUNNING]
numfull=0
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-20-2048.jpg)
![[RUNNABLE] [RUNNING]
numfull=0
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-21-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNABLE] [SLEEPING]
numfull=0
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-22-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [SLEEPING]
numfull=0
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-23-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [SLEEPING]
numfull=0
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-24-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [SLEEPING]
numfull=0
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-25-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [SLEEPING]
numfull=0
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-26-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [SLEEPING]
numfull=1
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-27-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [RUNNABLE]
numfull=1
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-28-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [RUNNABLE]
numfull=1
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-29-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [RUNNABLE]
numfull=1
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-30-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [RUNNABLE]
numfull=1
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-31-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[RUNNING] [RUNNABLE]
numfull=1
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-32-2048.jpg)
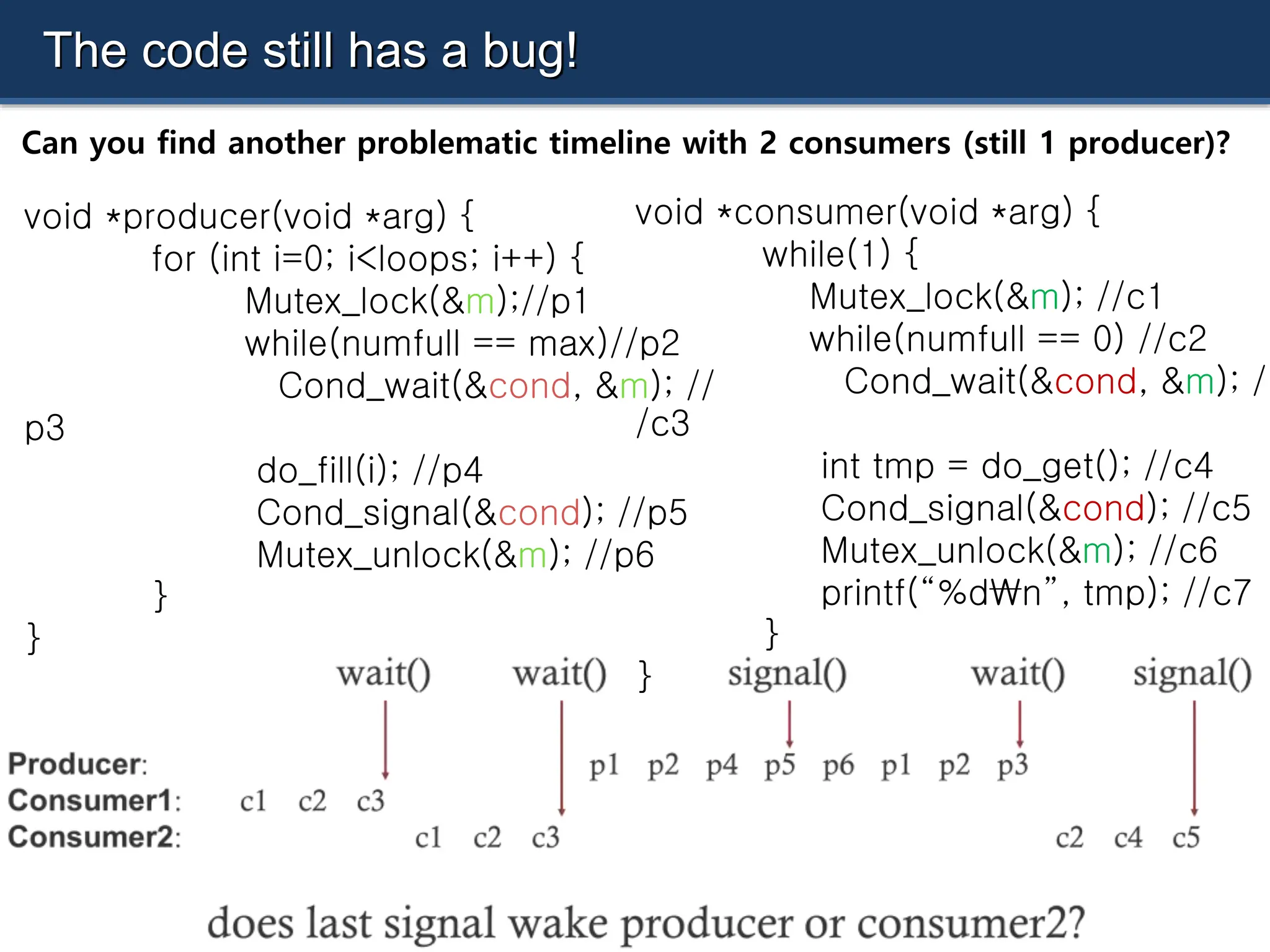
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
[SLEEPING] [RUNNABLE]
numfull=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-33-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
[SLEEPING] [RUNNING]
numfull=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-34-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
[SLEEPING]
numfull=1
[RUNNING]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-35-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
[SLEEPING]
numfull=0
[RUNNING]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-36-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
[RUNNABLE]
numfull=0
[RUNNING]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-37-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
numfull=0
[RUNNING]
[RUNNABLE]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-38-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
numfull=0
[RUNNING]
[RUNNABLE]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-39-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
numfull=0
[RUNNING]
[RUNNABLE]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-40-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
numfull=0
[RUNNING]
[RUNNABLE]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-41-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
numfull=0
[RUNNING]
[RUNNABLE]
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-42-2048.jpg)
![void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
numfull=0
[SLEEPING]
[RUNNABLE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-43-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
numfull=0
[SLEEPING]
[RUNNING]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-44-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
numfull=0
[SLEEPING]
[RUNNING]
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-45-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
numfull=1
[SLEEPING]
[RUNNING]
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-46-2048.jpg)
![void *consumer(void *arg) {
while(1) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == 0)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
int tmp = do_get();
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
printf(“%dn”, tmp);
}
}
numfull=1
[RUNNABLE]
[RUNNING]
void *producer(void *arg) {
for (int i=0; i<loops; i++) {
Mutex_lock(&m);
if(numfull == max)
Cond_wait(&cond, &m
);
do_fill(i);
Cond_signal(&cond);
Mutex_unlock(&m);
}
}
With just a single producer and consumer the code
works fine!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-47-2048.jpg)



![Circular buffer with N elements
Add more buffer slots More concurrency and efficiency.
enables multiple values to be produced or consumed.
Reduce context switches.
54
1 int buffer[MAX];
2 int in = 0;
3 int out = 0;
4 int count = 0;
5
6 void do_fill(int value) {
7 buffer[in] = value;
8 in = (in + 1) % MAX;
9 count++;
10 }
11
12 int do_get() {
13 int tmp = buffer[out];
14 out = (out + 1) % MAX;
15 count--;
16 return tmp;
17 }
The do_fill( ) and do_get( ) Routines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30-240712071319-bc694970/75/semaphre-and-condition-variable-in-Operating-system-54-2048.jpg)
