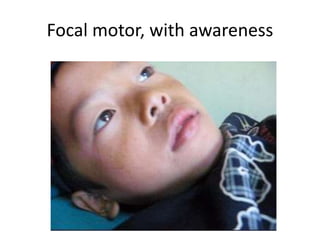
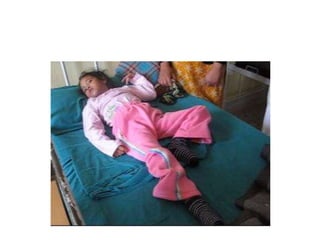
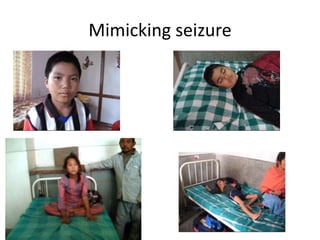
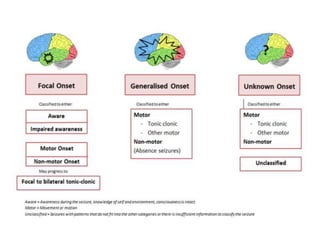
This document discusses seizure classification according to the International League Against Epilepsy in 2017. It defines a seizure as the clinical expression of abnormal neuronal activity in the brain, typically lasting seconds to minutes. Seizures are classified as focal onset, generalized onset, or unknown onset, with further subcategories of motor or non-motor seizures. Focal onset seizures may be subtle or unusual, while generalized onset include absence seizures, tonic-clonic, and myoclonic jerks. The document provides descriptions to help classify example seizure histories.