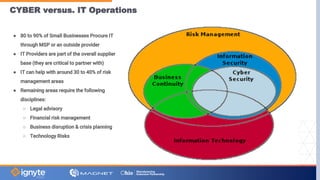
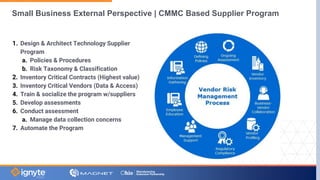
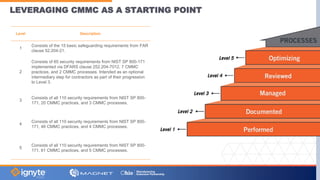
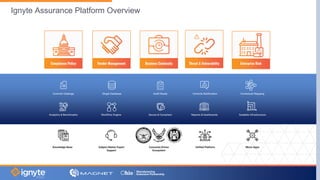
The document outlines a webinar hosted by Magnet focused on cybersecurity for small to medium manufacturing businesses, highlighting significant concerns such as the current state of the industry, Biden's executive order, and the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). Key speakers include Max Aulakh and Joe Vinciquerra, who discuss strategies for improving cybersecurity and compliance. It emphasizes the importance of partnerships and training in managing cybersecurity risks and enhancing business resilience.