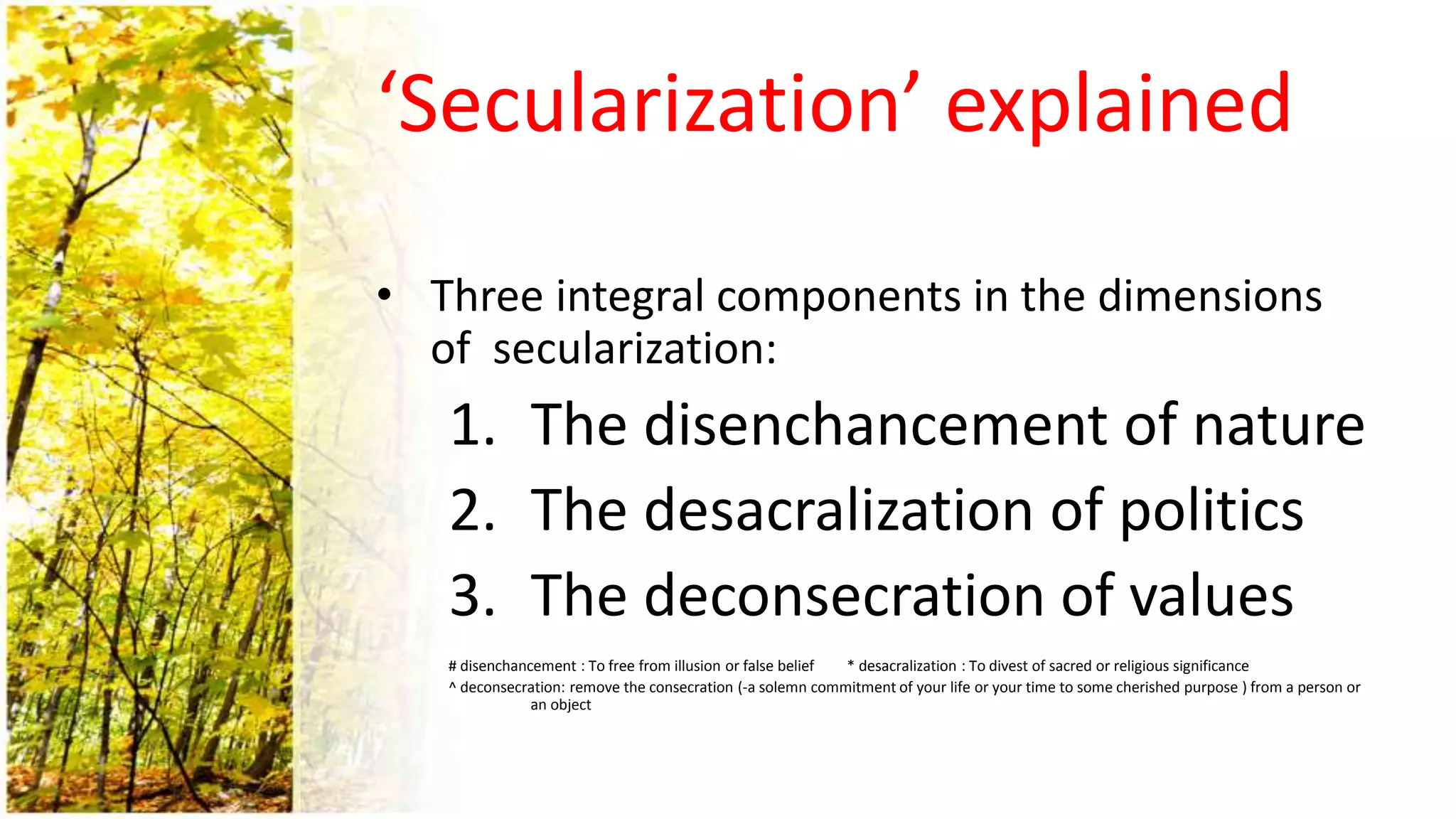
The document discusses the concept of secularism and secularization, defining key terms and exploring their implications on religion and society. It traces the historical roots of secularization in Western thought and emphasizes the conflict between secularization and religious beliefs, particularly Christianity's attempts to resist it. The text also contrasts Western and Islamic understandings of religion, highlighting Islam's perceived completeness and relevance in a secularizing world.