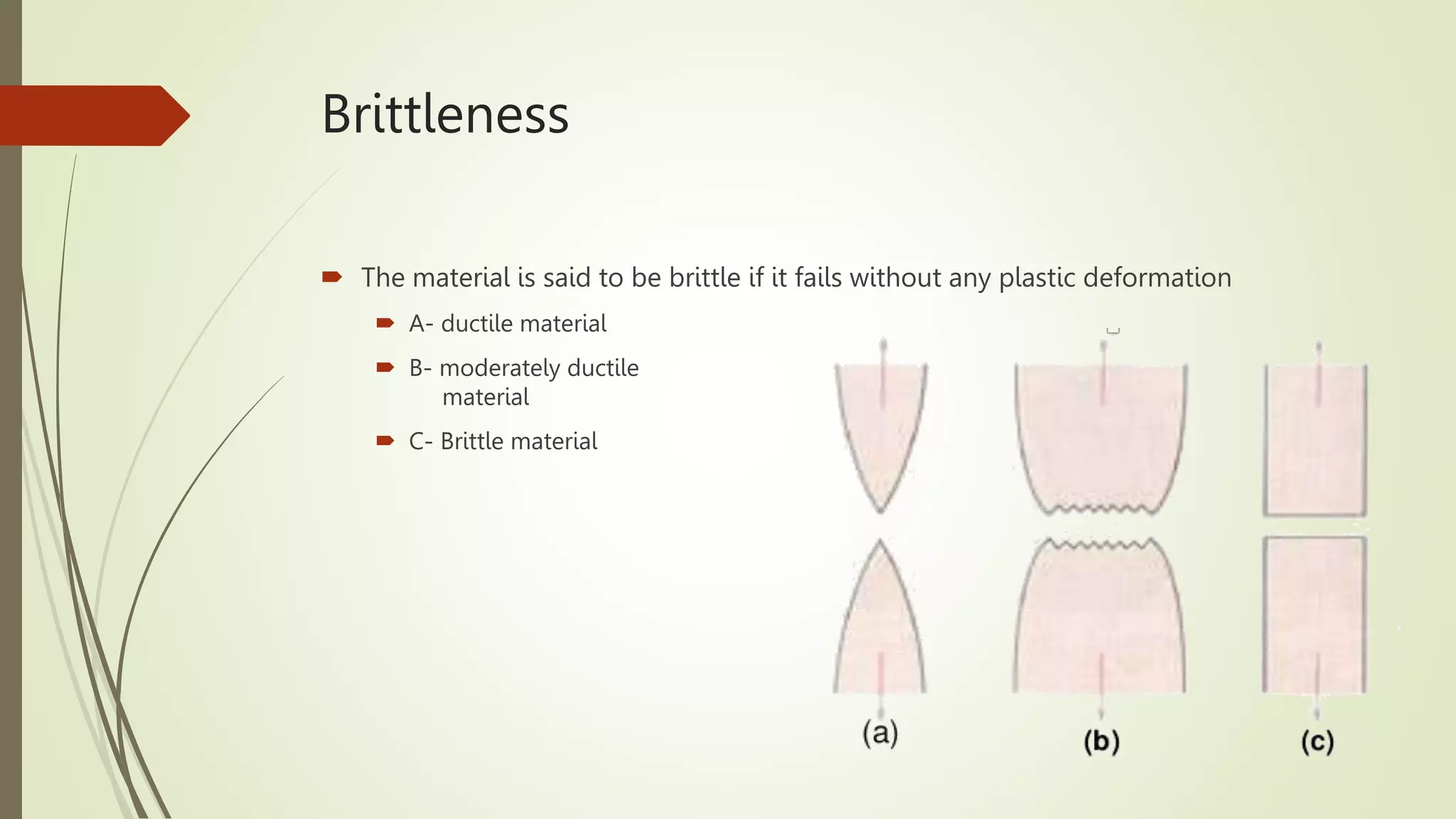
This document provides notes on material science concepts. It discusses key points about assignments, quizzes, reports and presentations. It also covers classifications of materials, basic concepts like deformation, stress, strain and mechanical properties including elasticity, ductility, brittleness, hardness and toughness. Graphs of stress-strain curves are presented and terms like elastic limit, yield point and ultimate tensile strength are defined. Students are instructed to submit assignments on time and follow the instructor's directions.