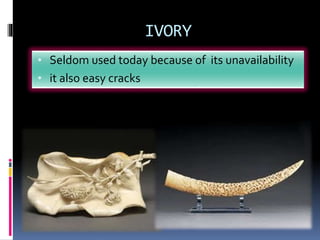
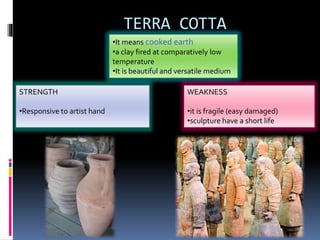
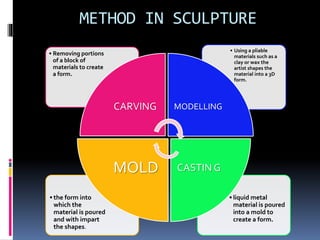
This document defines and describes various aspects of sculpture. It begins by listing students enrolled in a sculpture class and their student IDs. It then defines sculpture as the art of carving, casting or modeling materials into 3D forms. The document outlines the main types of sculpture as relief, free-standing, kinetic and assemblage. It provides examples of different relief sculptures and discusses commonly used materials like stone, bronze, wood and their strengths and weaknesses for sculpting. The document concludes by covering various sculpting methods such as carving, modeling, and casting in molds.