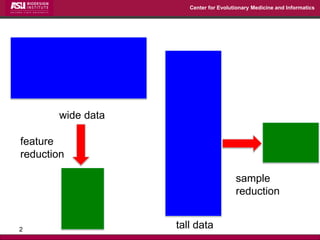
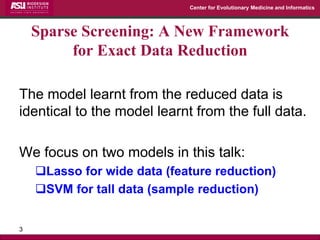
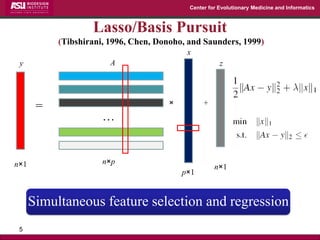
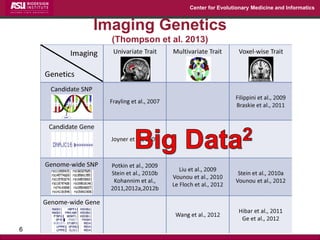
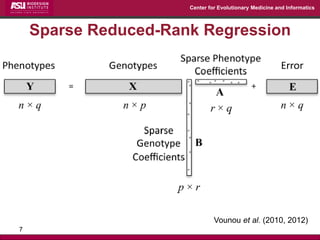
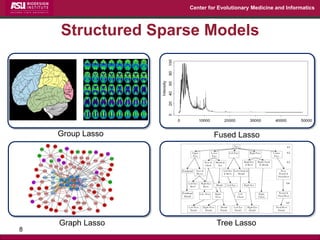
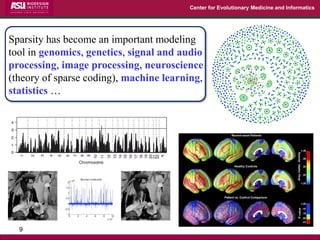
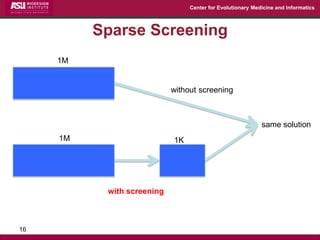
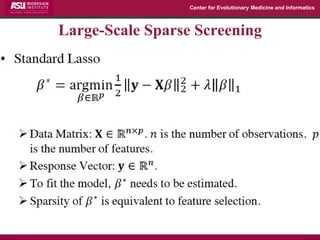
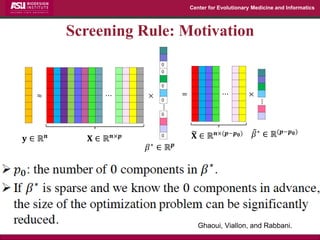
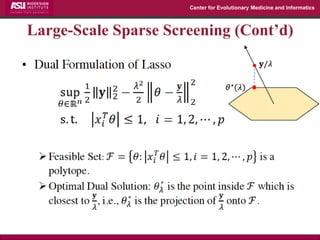
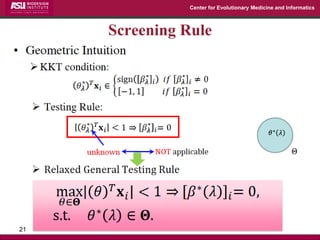
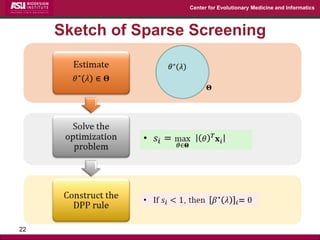
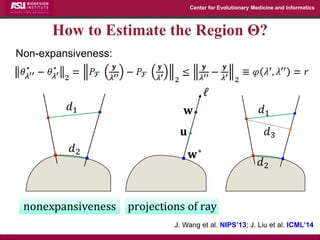
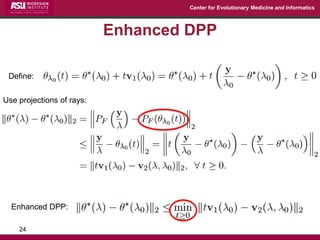
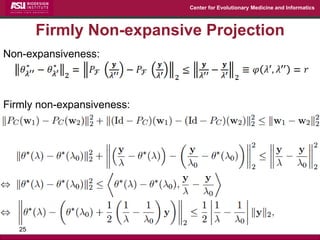
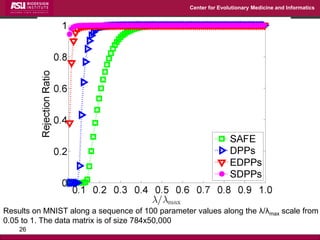
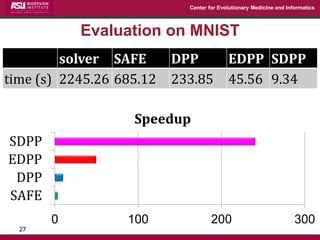
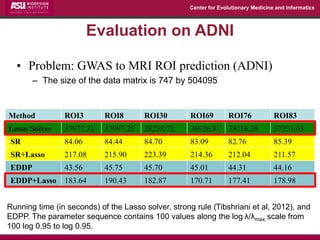
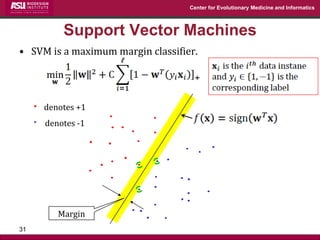
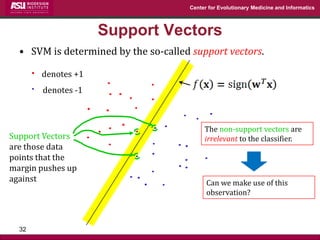
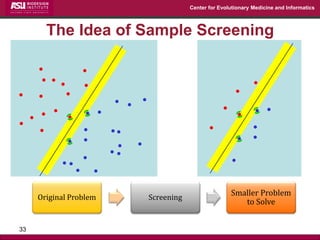
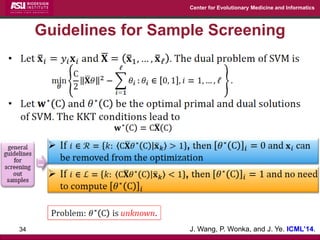
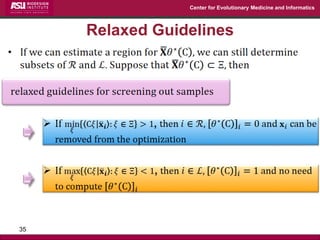
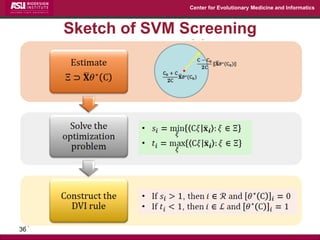
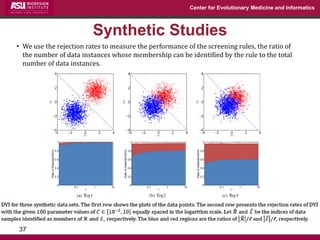
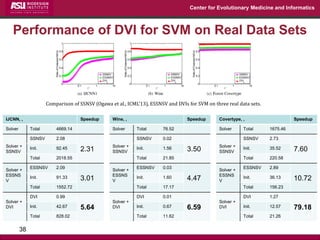
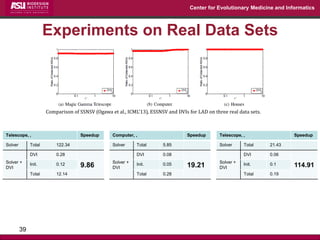
The document discusses the development of exact data reduction techniques using sparse screening methods for both feature and sample reduction, specifically through lasso and support vector machines (SVM). It highlights the efficiency of these approaches in maintaining model integrity while significantly speeding up processing times. Additionally, the document presents various optimization algorithms and extensions of sparse screening to broader applications in machine learning and data science.