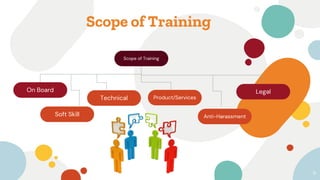
The document discusses the scope of training at an organization, including shadowing training to onboard new employees, management development programs to improve skills for future jobs, and various topics covered by training such as soft skills, technical skills, products/services, anti-harassment, and legal issues. It provides details on different types of onboarding, soft skills, technical skills, training on products and services, the need for anti-harassment training, and methods of management development including on-the-job and off-the-job training.