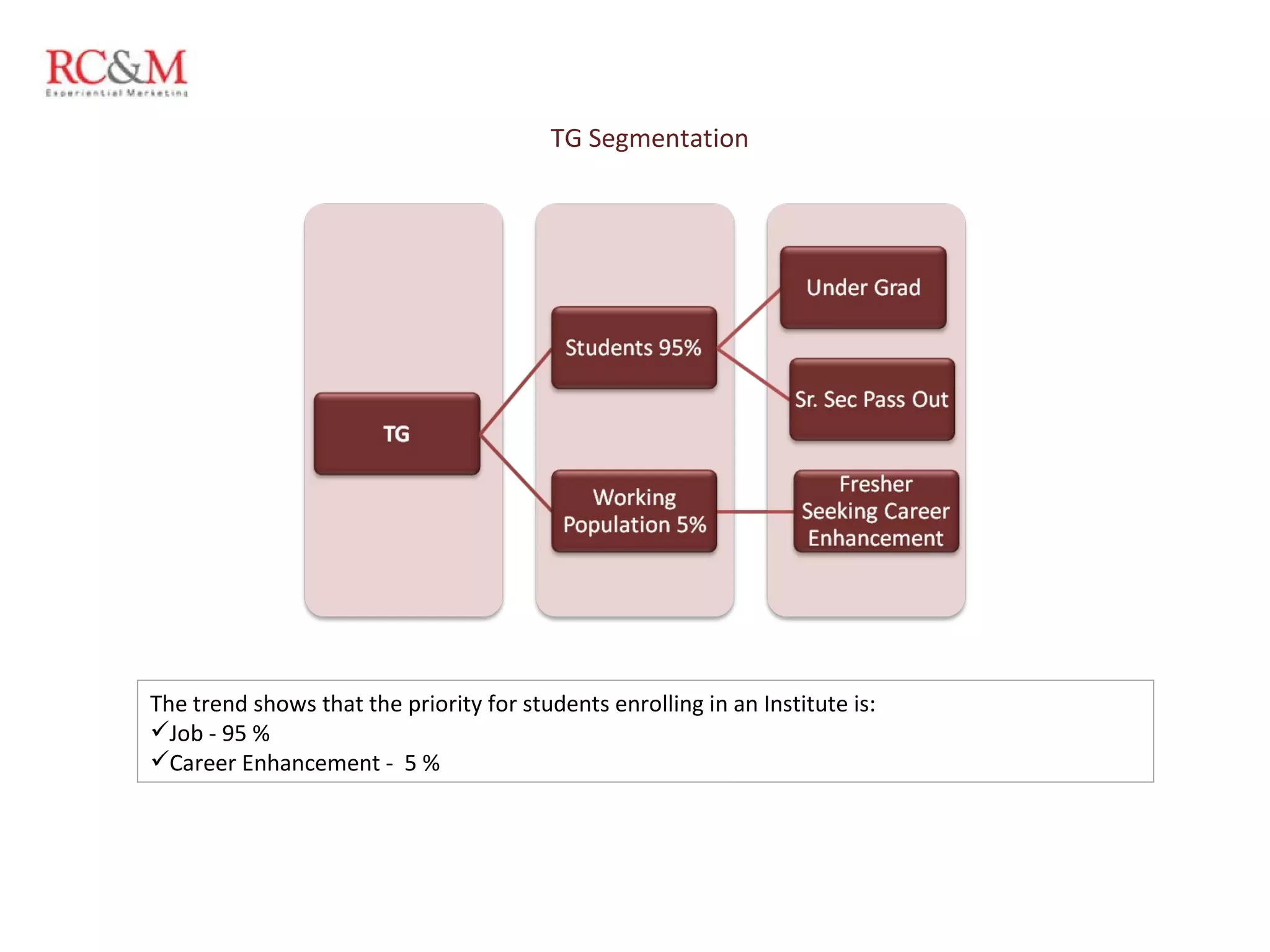
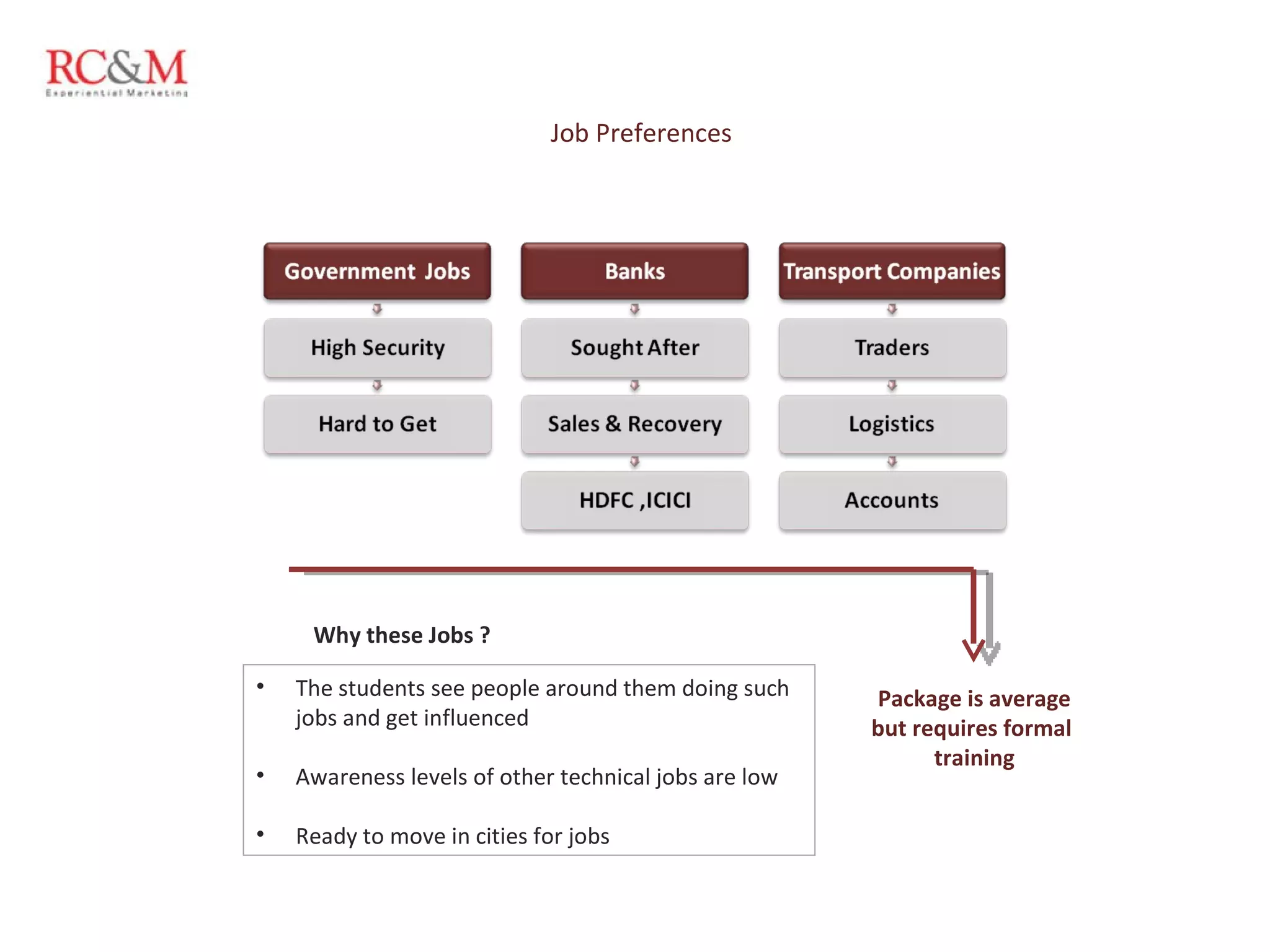
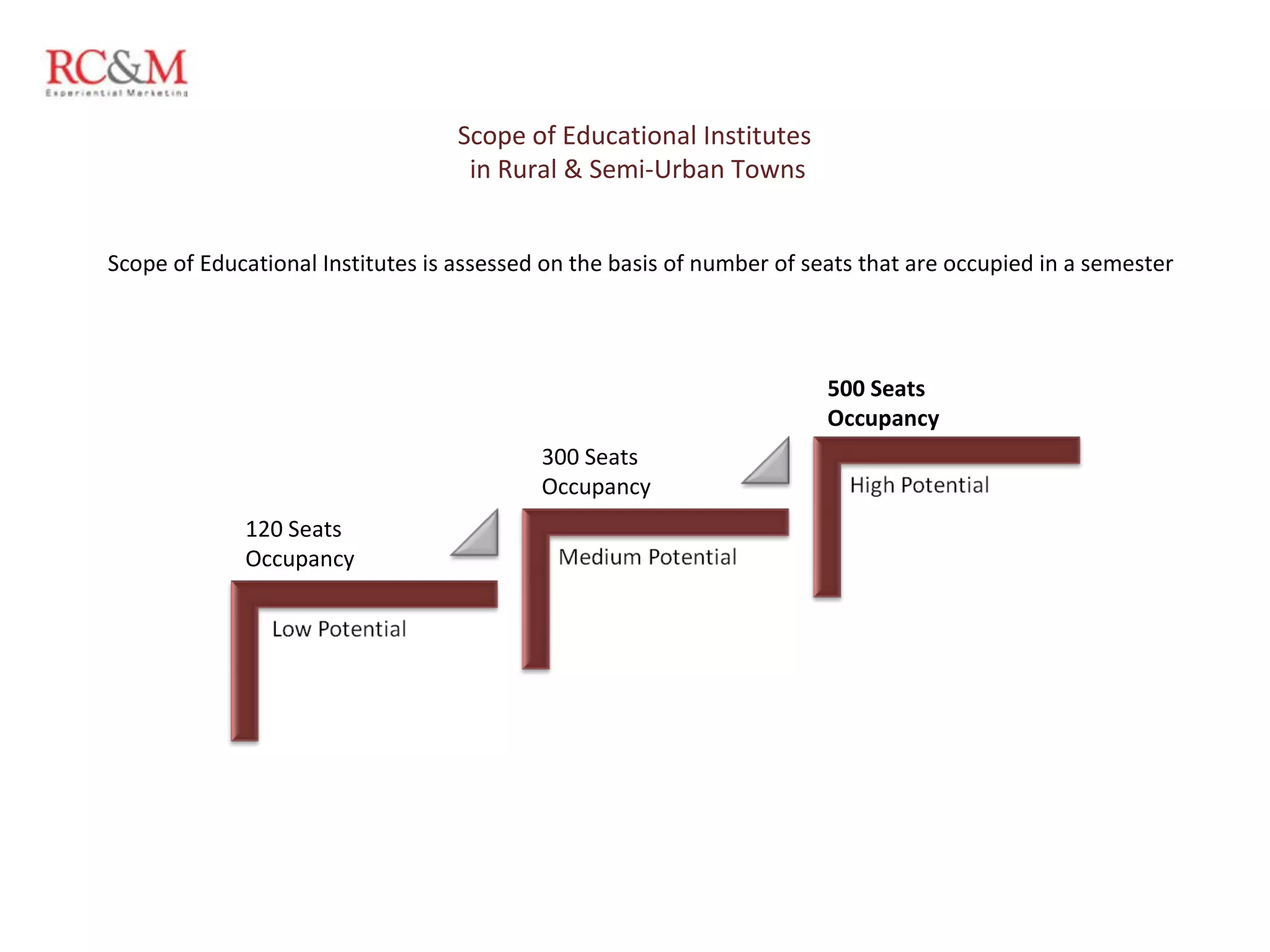
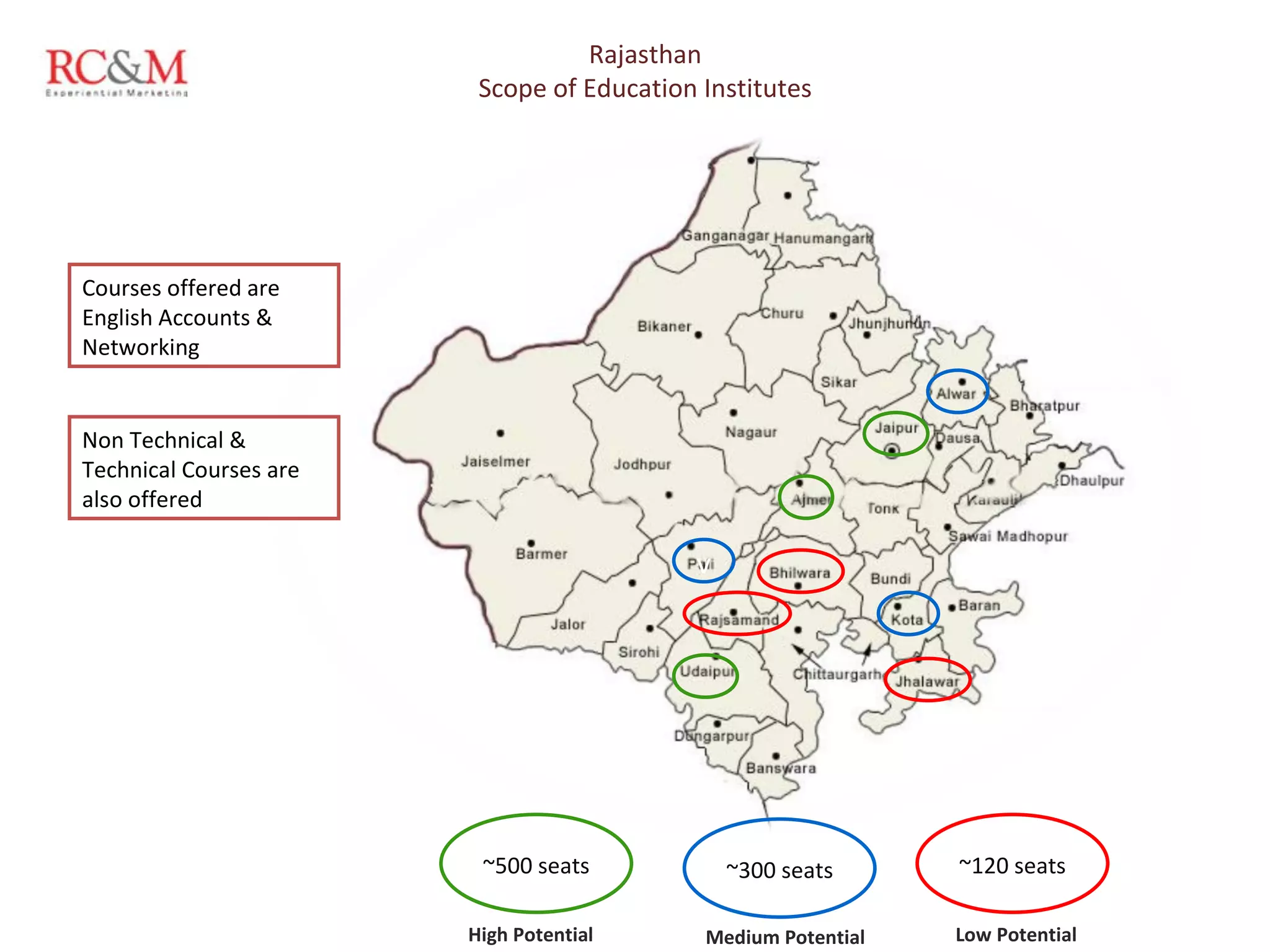
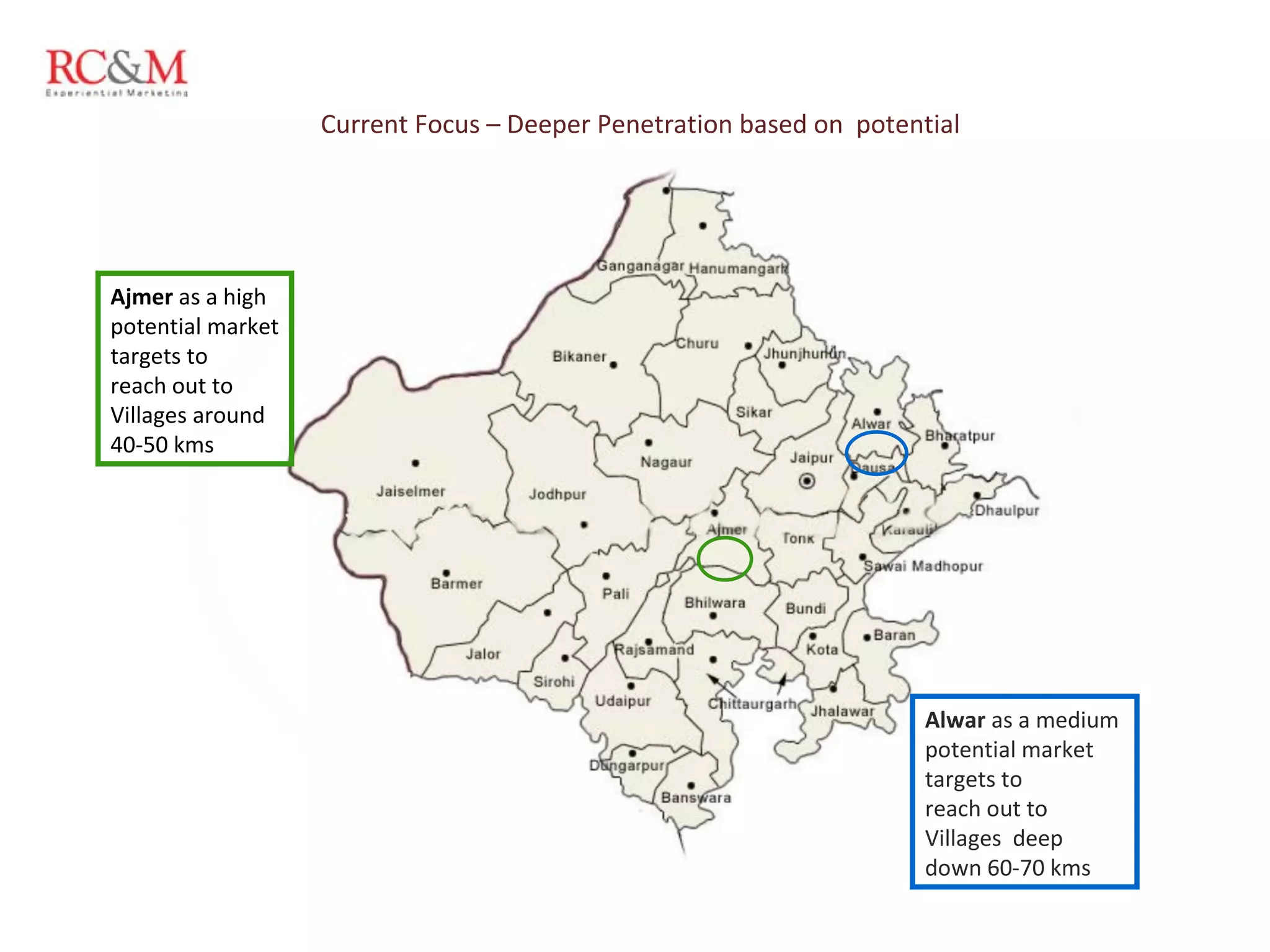
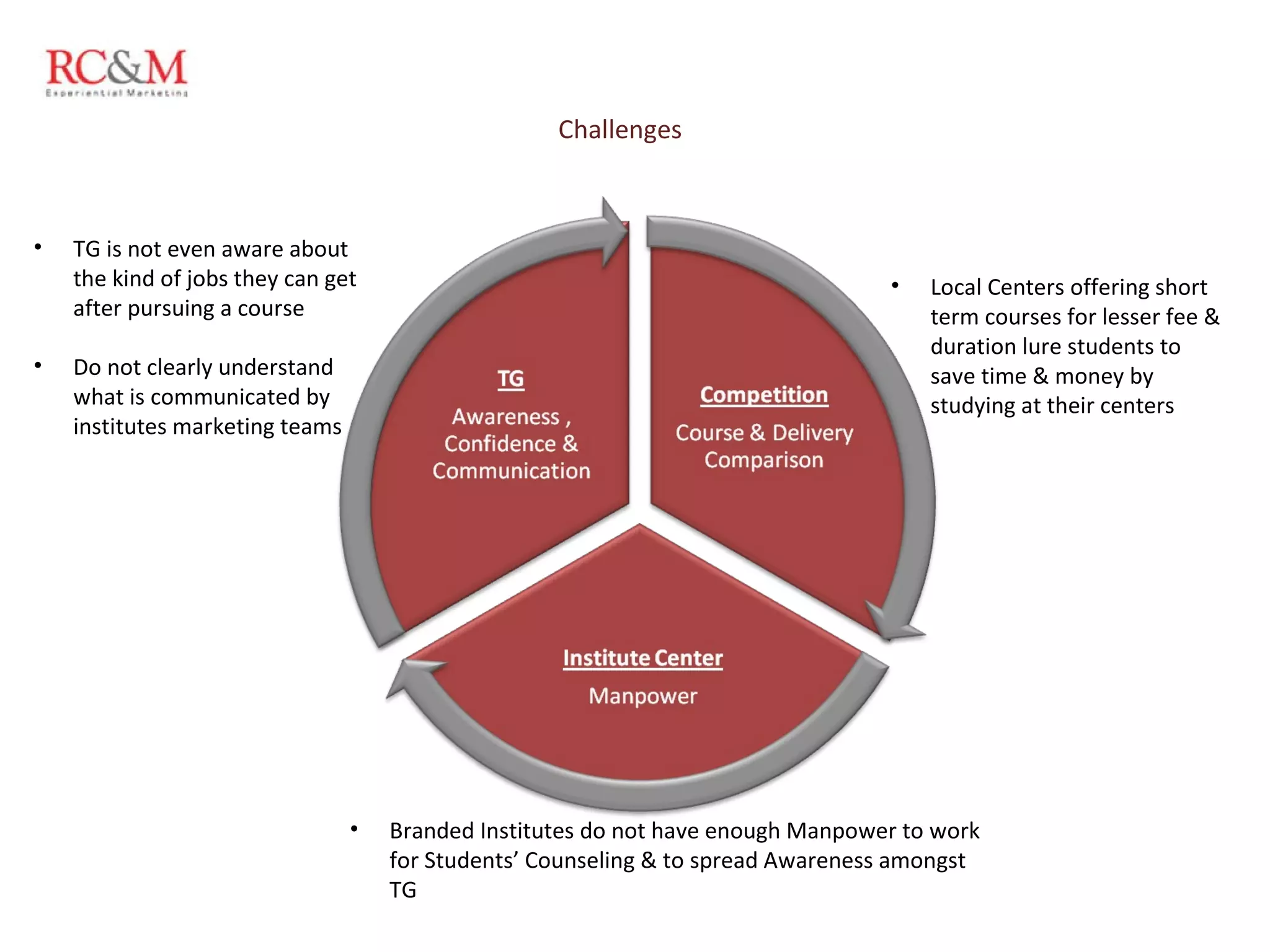
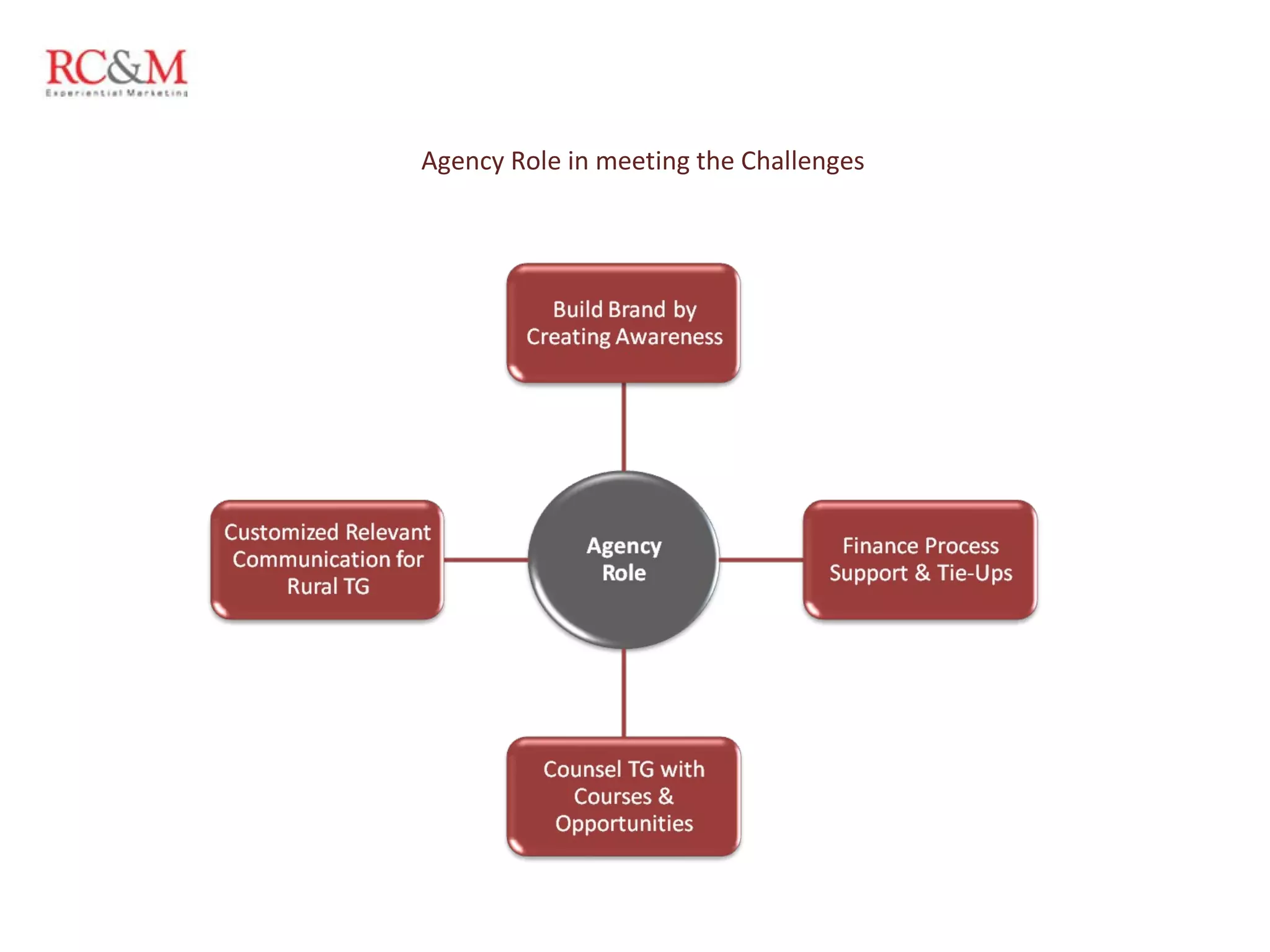
The document discusses the evolution of education in rural India over the past five years, highlighting an increase in vocational training and a shift in parental aspirations for their children's education. It examines the role of educational institutes in these regions, including the challenges they face in providing resources and awareness, as well as the impact of digital teaching methods. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of guidance and trust in educational choices made by families in rural areas.