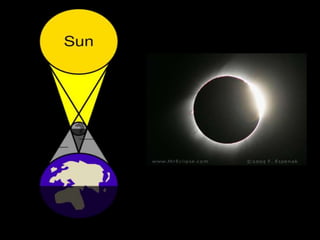
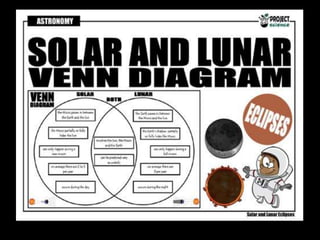
The document explains the concepts of solar and lunar eclipses, detailing their occurrences based on the alignment of the sun, earth, and moon. It describes types of solar eclipses (total, partial, and annular) and lunar eclipses (total, partial, and penumbral), as well as the frequency of these events. Additionally, it includes specific dates and locations for upcoming eclipses.