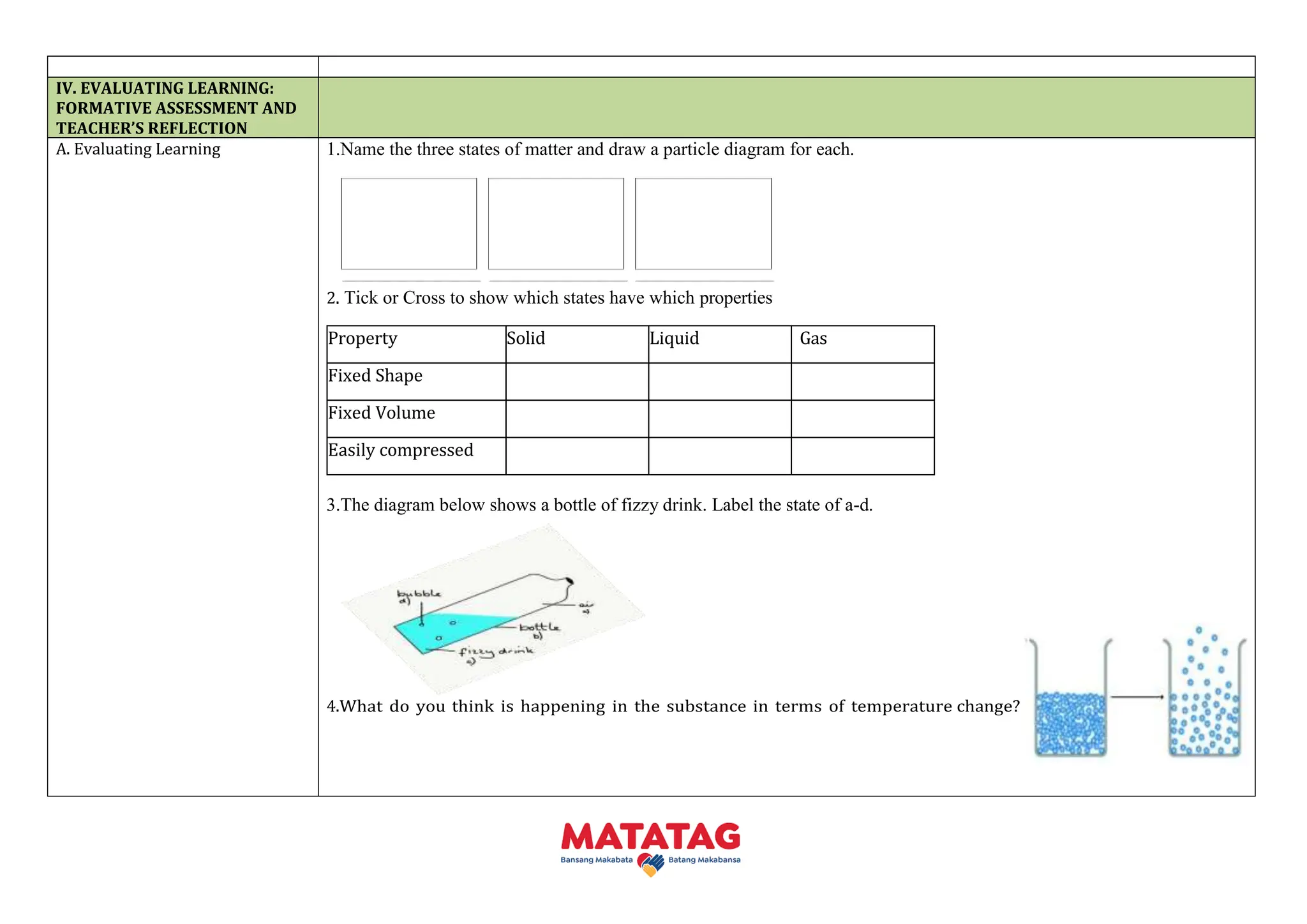
This document outlines a daily lesson plan for Grade 7 Science students in the Philippines, focusing on the particle model of matter and its properties across different states. It includes curriculum content, performance standards, learning objectives, and engaging teaching activities to reinforce understanding of kinetic molecular theory (KMT). Assessment methods are also described to evaluate students' grasp of the material and encourage critical thinking.