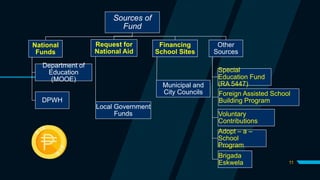
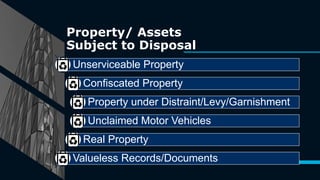
This document outlines guidelines for the proper utilization and disposal of school facilities in the Philippines. It discusses allowed public uses of school grounds and facilities with approval from the Schools Division Superintendent. Illegal uses are prohibited. School properties must be used for educational purposes and not personal conveniences. When facilities are no longer usable, a disposal committee oversees inspection, appraisal, and approved modes of disposal such as condemnation, transfer, donation, or sale. Proper documentation and legal procedures must be followed to ensure accountability and fair compensation.