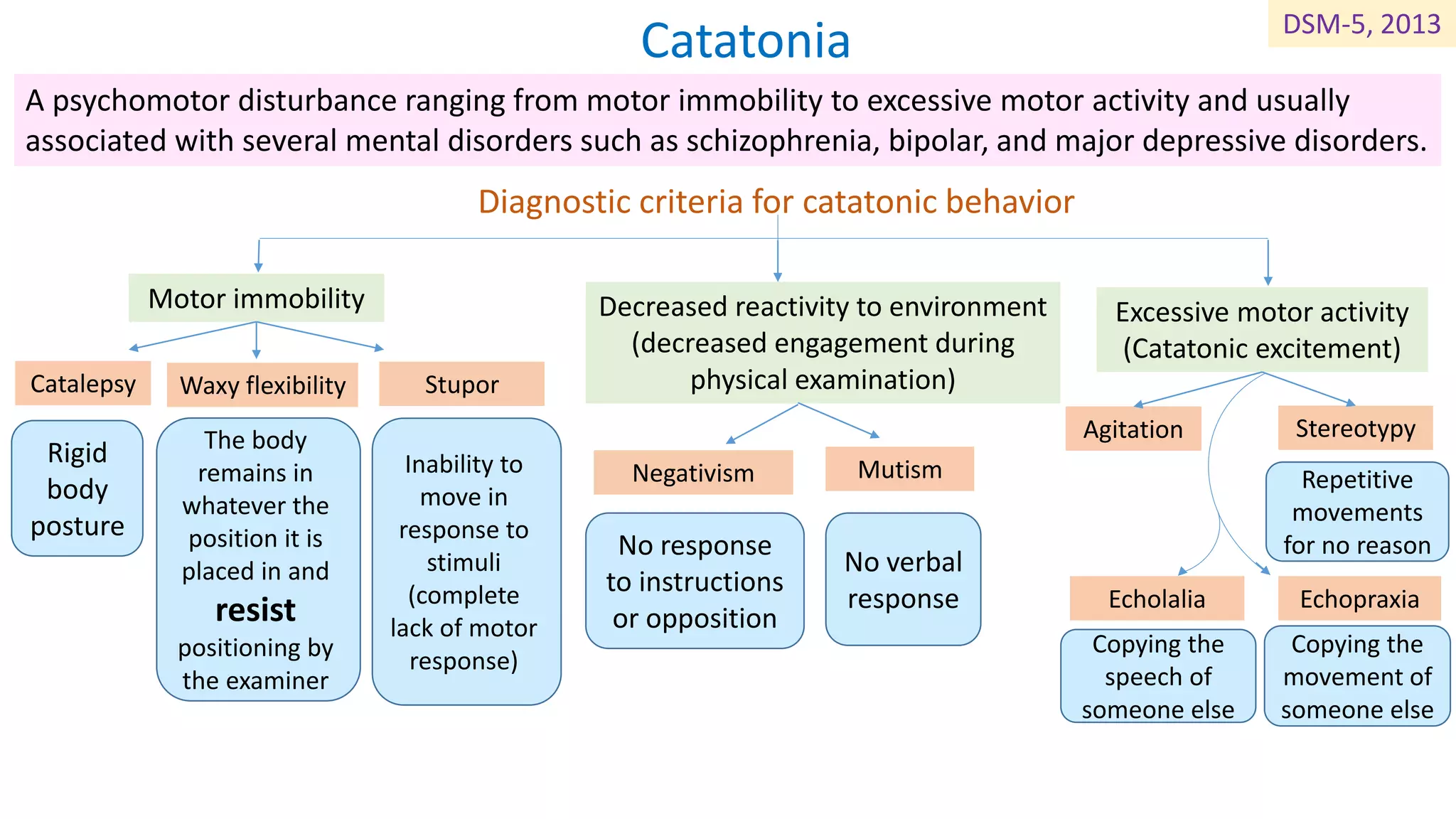
Schizophrenia is a psychotic disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech and behavior, and negative symptoms. The diagnostic criteria include false beliefs not based in reality, hearing or seeing things that are not there, disorganized "word salad" speech that jumps topics, and diminished emotional expression, pleasure, and motivation. Catatonia is a psychomotor disturbance seen in schizophrenia and other disorders marked by either motor immobility like catalepsy or excessive motor behavior like agitation, repetitive movements, and copying others' speech or movements without understanding.