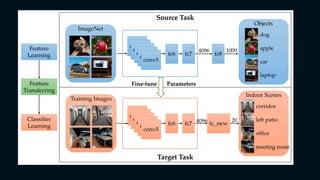
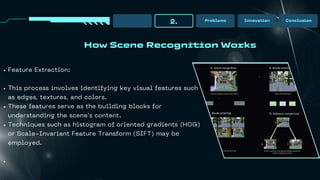
Scene recognition is a subfield of digital image processing focused on identifying and categorizing entire scenes within images, distinct from object recognition. It has applications in various fields such as autonomous vehicles and surveillance, but faces challenges including data dependency and variability in scenes. The importance of this field is underscored by advancements in machine learning techniques, particularly convolutional neural networks, which enhance the analysis and understanding of visual data.