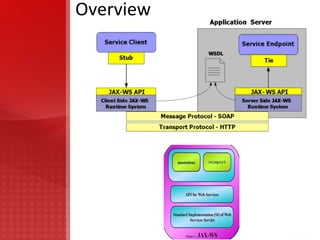
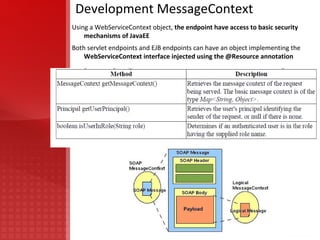
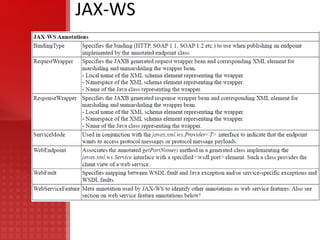
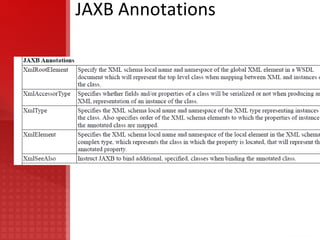
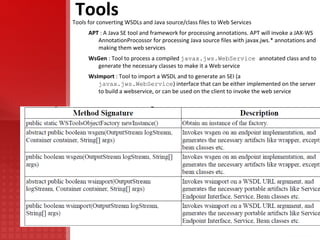
JAX-WS simplifies application development through support of a standard, annotation-based model to develop Web Service applications and clients. It replaces remote procedure calls defined by JAX-RPC and allows developers to write message-oriented and RPC-oriented web services. JAX-WS uses platform-independent technologies like HTTP, SOAP and WSDL and provides tools for generating artifacts and importing WSDL definitions.